Édouard Joseph Dantan
Édouard Joseph Dantan | |
|---|---|
 Self-portrait (1875) | |
| Born | 26 August 1848 Paris |
| Died | 7 July 1897 (aged 48) Villerville |
| Nationality | French |
Édouard Joseph Dantan (Paris 26 August 1848 – 7 July 1897) was a French painter in the classical tradition. He was widely recognized in his day, although he was subsequently eclipsed by painters with more modern styles.
Biography[]
Édouard Joseph Dantan was born on 26 August 1848 in Paris. His grandfather, who had fought in the Napoleonic Wars, was a wood sculptor. His father, Antoine Laurent Dantan, and uncle, Jean-Pierre Dantan, were both well-known sculptors.[1] Dantan was a pupil of Isidore Pils and Henri Lehmann at the École nationale supérieure des Beaux-Arts in Paris.[2] At the age of nineteen he won a commission for a large mural painting of The Holy Trinity for the Hospice Brezin at Marne (Seine-et-Oise).[3] Dantan's first exhibit at the Paris Salon was An Episode in the Destruction of Pompeii in 1869. In 1870 the Franco-Prussian War interrupted his work, and he enlisted in the defence force.[4] He was given the rank of a sergeant, and was later promoted to lieutenant.[5] During the war the family home was burned down.[4]
In the years after the war Dantan exhibited a number of other paintings at the Salon including Hercules at the Feet of Omphale (1871), Death of Tusaphane (1875), The Nymph Salmacis (1876), Priam Demanding of Achillees the Body of Hector (1877), Calling of the Apostles Peter and Andrew (1878), Corner of a Studio (1880) and The Breakfast of the Model (1881).[3] He continued to exhibit at the Salon until 1895. In 1890, 1894 and 1895 he served on the jury of the Salon.
For twelve years Dantan's companion was the model Agostina Segatori, who had also posed for artists such as Jean-Baptiste Corot, Jean-Léon Gérôme, Eugène Delacroix and Édouard Manet. She bore a child to Dantan, Jean-Pierre, in 1873. On their separation, Agostina opened Café du Tambourin on the Boulevard de Clichy that became a meeting place for artists.[6][fn 1] Dantan spent his summers in Villerville, where he died on 9 July 1897 when the carriage in which he was riding crashed violently into the village church.[8]
Style and reception[]

At the 1870 exposition of the Ecole Nationale des Beaux-Arts Dantan received an honorable mention for his submission for the prix de Rome.[9] In 1874 he won a third class medal for his painting of a monk carving a Christ in wood.[10] In 1880 he won a second class medal for his painting Un coin d'atelier (a corner of the workshop).[11] He received a gold medal at the Paris Exposition of 1889,[12] and a number of his paintings were bought by the French state.
Dantan's works followed the academic tradition of painting, and were praised by his contemporaries. His technical mastery is illustrated by such paintings as Un coin d'atelier (1880), where he depicts his father working on a bas-relief in his studio, seen from behind. The studio is cluttered with paintings and sculptures. In the foreground, a nude woman is taking a break from modelling. A critic praised the painting for following all the rules of trompe-l'oeil and stereoscopic photography.[13] Describing a painting of a group of sailors following a clergyman going to bless the sea, another critic said in 1881 "he has written a page before which believers and skeptics must raise their hats".[14]
His Le déjeuner du modèle exhibited in the Salon in 1881 shows a model eating a plate of eggs in a break from the posing session. The scene is illuminated by a clear white light, with a delicate sense of reflected light. One reviewer said that Dantan had treated the subject with taste and grace, when it could easily have fallen into vulgarity.[11] He was by no means limited to one genre. Other paintings at this time included one of his mother outdoors in her invalid chair, her face sad, a pastoral portrait of a young blonde woman in a blue dress, full of life, and of a poor fisherman dining in his miserable cabin on a piece of bread and an onion.[15]
Later, Dantan's classical style fell out of fashion. Writing of the first exhibition of the Société Nationale des Beaux-Arts in the Champ de Mars in 1890, Walter Sickert was scathingly critical of most of the paintings, making exceptions for a series of far-eastern landscapes by Louis-Jules Dumoulin, a painting by Édouard Manet, some portraits by Jules-Élie Delaunay and some studies by Dantan. He praised Dumoulin as a master, described Manet's work as brilliant and powerful, Delaunay's as respectable and Dantan's as conscientious.[16]
Major works[]


At first, Dantan's subjects were mainly drawn from classical mythology or religious subjects, as was common in his day. Later he made a number of paintings of scenes from sculpture workshops, familiar from his childhood. He also painted portraits and views of Villerville.
- 1869 Episode of the destruction of Pompeii
- 1872 The Trinity, chapel of the Hospital in Brezen-on-the-Marne
- 1872 Portrait His father, working on a marble bust
- 1874 Hercules at the feet of Omphale
- 1874 A monk as a wood sculptor, Musée des Beaux-Arts de Nantes
- 1875 The Quoit-Thrower, Musée des Beaux-Arts de Rouen, Rouen
- 1876 The Nymph Salmacis
- 1878 Phrosine et Mélidore after Pierre Paul Prud'hon, Musée des Beaux-Arts de Bordeaux
- 1879 Fête Foraine de Saint-Cloud
- 1880 Christ on the Cross, Church of Dombrowa, Poland
- 1880 Un Coin d'atelier, Paris, Palais du Luxembourg (filed in 1925, not found in 1977)
- 1880 Un Coin du Salon de 1880 (sale Sotheby's New York, 24 May 1995)
- 1881 Le déjeuner du modèle
- 1882 Corpus Christi Day
- 1884 Burial of a child, Villerville, Musée Malraux, Le Havre
- 1885 Shooting their nets
- 1886 Entracte Un à la Comedie-Francaise de première un soir, en 1885, Comédie-Française, Paris
- 1887 Un moulage sur Nature, Konstmuseum Gothenburg, Gothenburg
- 1887 L'Atelier du sculptor
Gallery[]
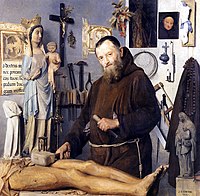
A monk as a wood sculptor (1874)

Phrosine et Mélidore (1878)

Portrait (ca 1880)

Portrait (ca 1880)

Burial of a child, Villerville (1884)

A Casting from Life (1887)

Sculptor

Studioscene (ca 1890)

A Restoration (1891)

Portrait (ca 1890)
Recent exhibitions[]
- "Édouard Dantan, de l'atelier à la lumière" Manoir de Villers, Saint-Pierre-de-Manneville, Normandy Impressionist Festival 2010
References[]
- Notes
- ^ Agostina was painted in 1887 in her café by Vincent van Gogh in the painting Agostina Segatori Sitting in the Café du Tambourin.[7]
- Citations
- ^ Montrosier & Fraipont 1881, p. 33.
- ^ Perkins 1886, p. 370.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Viardot 1883, p. 34.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Montrosier & Fraipont 1881, p. 34.
- ^ Enault 1881, p. 94.
- ^ Vazzana 2007, p. 44.
- ^ In the café.
- ^ Le Figaro (189). July 8, 1897 (in French)
- ^ Sargent 1874, p. 132.
- ^ Catalogue des objets..., p. 161.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Henriet 1884, p. 175.
- ^ Fine Arts in 1889, p. 319.
- ^ du Seigneur 1880, p. 35.
- ^ Montrosier & Fraipont 1881, p. 35.
- ^ Henriet 1884, p. 176.
- ^ Sickert & Robins 2002, pp. 67–68.
- Sources
- Catalogue des objets composant le musée municipal des Beaux-Arts (de la Ville de Nantes) (in French). impr. Mme Vue C. Mellinet. 1876.
- Enault, Louis (1881). "Edouard Dantan". Paris-Salon. E. Bernard & cie. p. 56.
- "Fine Arts in 1889 (Paris)". Appletons' annual cyclopaedia and register of important events. 14. D. Appleton and company. 1890.
- Henriet, Frédéric (1884). "L'Auberge de la Girafe". Annales, Société historique et archéologique de Château-Thierry (in French). G. Cagniard.
- "In the café: Agostina Segatori in Le tambourin, 1887". Van Gogh Museum. Retrieved 5 February 2012.
- de Juvigny, Sophie (2002). Édouard Dantan 1848–1897: Des ateliers parisiens aux marines normandes (in French). Paris: Somogy. p. 167. ISBN 2-85056-607-1.
- Montrosier, Eugène; Fraipont, Gustave (1881). "E. Dantan". Les artistes modernes: Peintres divers (in French). 4. H. Launette.
- Perkins, Charles Callahan (1886). "Dantan, Joseph Édouard". Cyclopedia of painters and paintings. 1. C. Scribner's Sons.
- Sargent, René (1874). Le Moniteur des architectes (in French). 8. A. Levy.
- du Seigneur, Maurice (1880). L'art et les artistes au Salon de 1880 (in French). P. Ollenforff. p. 35.
- Sickert, Walter; Robins, Anna Gruetzner (2002). Walter Sickert: The Complete Writings on Art. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-926169-5.
- Silvestre, Paul Armand; Bouguereau, William; Maignan, Albert; Merson, Luc-Olivier (1898). Discours prononcés sur la tombe de M. et de Mme Édouard Dantan (in French). Paris: Napoléon Chaix.
- Vazzana, Nicholas S. (2007). Van Gogh in Paris. iUniverse. ISBN 978-0-595-44160-0.
- Viardot, Louis (1883). "Dantan, Édouard Joseph". The masterpieces of French art illustrated: being a biographical history of art in France, from the earliest period to and including the Salon of 1882. 2. Gebbie.
External links[]
 Media related to Edouard Dantan at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Edouard Dantan at Wikimedia Commons
- 1848 births
- 1897 deaths
- Artists from Paris
- 19th-century French painters
- French male painters









