1600s in England
| Other decades |
| 1580s | 1590s | 1600s | 1610s | 1620s |
Events from the 1600s in England. This decade marks the end of the Elizabethan era with the beginning of the Jacobean era and the Stuart period.
Incumbents[]
- Monarch – Elizabeth I (until 24 March 1603), then James I
- Parliament – 10th of Queen Elizabeth I (starting 27 October, until 19 December 1601), Blessed (starting 19 March 1604)
Events[]
- 1600
- January – in Ireland, Hugh O'Neill, 2nd Earl of Tyrone, renews the Nine Years' War against England with an invasion of Munster.[1]
- 11 February–March – clown William Kempe ("Will Kemp") morris dances from London to Norwich.[2]
- c. April – publication of Ben Jonson's play Every Man out of His Humour;[1] it goes through three editions this year.
- 26 July – the original Banbury Cross is demolished on the orders of a Puritan local corporation.[3]
- 31 December – East India Company granted a Royal Charter.[4]
- William Shakespeare's plays Henry IV, Part 2, Henry V, The Merchant of Venice, A Midsummer Night's Dream and Much Ado About Nothing are published in London.[1]
- William Gilbert publishes De Magnete, discussing Earth's magnetic field, one of the first important scientific works to be published in England.
- Caister Castle falls into ruin.
- 1601
- 7–8 January – Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, stages a short-lived rebellion against Elizabeth I.[1]
- 25 February – Essex executed for treason,[1] becoming the last person beheaded on Tower Green in the Tower of London, the sword being wielded by Thomas Derrick.
- 22 April – the first expedition of the East India Company, having set out from Woolwich on 13 February, sets sail from Torbay for the Spice Islands with John Davis as pilot-major.[5]
- Spring – possible first performance of Shakespeare's tragedy Hamlet.[4][6]
- 2 October–3 January 1602 – the Siege of Kinsale ends the Nine Years' War.[1]
- November – Elizabeth I addresses her final parliament with the Golden Speech.[1]
- An Act for the Relief of the Poor codifies the English Poor Laws.
- 1602
- 2 February (Candlemas night) – first recorded performance of Shakespeare's comedy Twelfth Night, in Middle Temple Hall, London.[7]
- 3–4 October – Battle of the Narrow Seas: an English fleet pursues six Spanish galleys through the Strait of Dover.
- 8 November – the Bodleian Library at the University of Oxford is opened.[4]
- Publication of Shakespeare's comedy The Merry Wives of Windsor.[8]
- Richard Carew publishes The Survey of Cornwall.[4]

King James I of England/VI of Scotland, the first monarch to rule the Kingdoms of England and Scotland at the same time
- 1603
- 24 March – Queen Elizabeth I dies at Richmond Palace aged 69, after 45 years on the throne, and is succeeded by her distant cousin King James VI of Scotland (where he has ruled since 1567), thus uniting the crowns of Scotland and England. Elizabeth was never married and had no children, neither did her only legitimate siblings, the late Mary and Edward VI.[9]
- 31 March – the Nine Years' War is ended by the submission of Hugh O'Neill, Earl of Tyrone, to the English Crown and the signing of the Treaty of Mellifont.[1]
- April – Thomas Cartwright delivers his Millenary Petition, demanding an end to ritualistic practices, and signed by 1,000 Puritan ministers, to the King.[4]
- c. April – Outbreak of bubonic plague epidemic in London in which between 29,000 and 40,000 die.[10][11][12][13]
- 28 April – funeral of Elizabeth I in Westminster Abbey.
- 17 July – Sir Walter Ralegh arrested for treason.[9]
- 21 July – Thomas Howard created the 1st Earl of Suffolk.[14]
- 25 July – coronation of James I as King of England in Westminster Abbey.[9]
- 17 November – Ralegh goes on trial for treason in the converted Great Hall of Winchester Castle.[9] He is found guilty but his life is spared by the King at this time and he is returned to imprisonment in the Tower of London.
- 1604
- 14–16 January – Hampton Court Conference with James I, the Anglican bishops and representatives of Puritans. Work begins on the Authorized King James Version of the Bible[4] and revision of the Book of Common Prayer.
- 19 March – Parliament assembles and debates Robert Cecil's proposal for union with Scotland.[14]
- 2 April – Speaker of the House of Commons Sir Edward Phelips rules that members of the House may not bring forward an identical (or near-identical) motion to one that has already been decided in that same session.[15]
- 20 May – Gunpowder Plot conspirators first meet, in London.
- 20 June – The Form of Apology and Satisfaction is read out in the House of Commons to justify the conduct of Parliament following a dispute between King and Parliament over a contested election in Buckinghamshire.[14]
- 18 August – the Treaty of London brings an end to the Anglo–Spanish War, an intermittent conflict which has been going on since 1585.[16]
- 7 July – Parliament prorogued.[14]
- 20 October – King James assumes the style king of Great Britain.[17]
- 1 November (Hallowmas day) – first recorded performance of Shakespeare's tragedy Othello, at Whitehall Palace in London.
- 10 December – Richard Bancroft (a leading participant in the King James Version Bible translation) is installed as Archbishop of Canterbury.
- Christopher Marlowe's play The Tragicall History of D. Faustus (probably written and first performed between 1588/89 and 1592/94) is published.
- King James publishes A Counterblaste to Tobacco.
- Table Alphabeticall, the first known English dictionary to be organised by alphabetical ordering, is published.
- Blundell's School is founded in Tiverton, Devon, under the will of merchant Peter Blundell.
- 1605
- 10 April – Spanish Catholic missionary Luisa Carvajal y Mendoza arrives in England.
- October – publication of Francis Bacon's treatise The Advancement of Learning.
- 5 November – Gunpowder Plot: a plot to blow up the Houses of Parliament is foiled when, following an anonymous tip-off (passed to Lord Monteagle in October), Sir Thomas Knyvet, a justice of the peace, finds Catholic plotter Guy Fawkes in a cellar below the Parliament building and orders a search of the area, finding 36 barrels of gunpowder. Fawkes is arrested for trying to kill King James I and the members who were scheduled to sit together in Parliament the next day. Fawkes speaks the legendary words: "Remember, remember, the Fifth of November".[1][18]
- 8 November – Gunpowder Plot conspirator Robert Catesby is among those shot while plotters are being arrested at Holbeche House in the west midlands.[4]
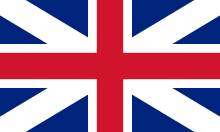
First version of the Union Flag, see 12 April 1606
- 1606
- 31 January – Fawkes and his co-plotters are executed by hanging, drawing and quartering,[1] four having been executed the previous day.
- 24 February – commercial treaty between England and France signed in Paris.[19]
- 10 April – Charter of 1606: The First Charter of Virginia is adopted, by which King James I of England grants rights to the Virginia Company (comprising the London Company and Plymouth Company) to settle parts of the east coast of North America.[4]
- 12 April – first version of the Union Flag created,[9] designed by Charles Howard, 1st Earl of Nottingham, to be worn at the maintopmast of English and Scots ships.
- Spring – Ben Jonson's satiric play Volpone first performed.
- May – severe penalties are imposed for Catholic recusancy, and for refusal to take an Oath of Allegiance to James to serve in public office, by An Act for the better discovering and repressing of popish recusants (proclaimed law 22 June).[4]
- 27 May – second session of Parliament under King James prorogued.[14]
- 7 August – possible first performance of Shakespeare's tragedy Macbeth.[4][20]
- 18 November – third session of Parliament begins.[14]
- 19 December – the Susan Constant sets out from the River Thames leading the Virginia Company's fleet for the foundation of Jamestown, Virginia.
- 26 December (St. Stephen's night) – one of the first performance of Shakespeare's tragedy King Lear, before the King at Whitehall.[20]
- Paston School founded in Norfolk.
- 1607
- 30 January – Bristol Channel floods (a possible tsunami)[21] result in the drowning of an estimated 2,000 people, with 200 square miles (518 km2) of farmland inundated.[22]
- late April – start of Midland Revolt against land enclosures.[1] The rebels are referred to as "Levellers".
- 14 May – Jamestown, Virginia, is established as the first permanent English settlement in North America.[4]
- 8 June – Midland Revolt suppressed at Newton, Northamptonshire, by local gentry.[23]
- 4 July – third session of Parliament ends, having refused a proposed union with the Parliament of Scotland. It does not assemble again until 1610.[14]
- September – the Scrooby Congregation of Protestant Separatists from Nottinghamshire attempt to flee to the Dutch Republic from The Haven, Boston, but are betrayed, arrested and imprisoned for a time.
- 14 September – Flight of the Earls from Ireland: Hugh O'Neill, 2nd Earl of Tyrone, and Rory O'Donnell, 1st Earl of Tyrconnell, flee to Spain to avoid capture by the English crown,[1] thus facilitating the Plantation of Ulster with English and Scots settlers.
- November – Case of Prohibitions: Sir Edward Coke determines that legal cases should not be tried by the monarch.
- 5 December–14 February 1608 – severe frost. Many rivers, including the Thames, freeze.[24]
- First performance of the first wholly parodic play in English, Francis Beaumont's The Knight of the Burning Pestle, unsuccessfully, probably by the Children of the Chapel at the Blackfriars Theatre in London.
- 1608
- Spring – the Scrooby Congregation successfully flees to the Dutch Republic from the Humber, origin of the Pilgrim Fathers who in 1620 move on to North America.
- April – performances of George Chapman's new play The Conspiracy and Tragedy of Charles, Duke of Byron by the Children of the Chapel at the Blackfriars Theatre in London are suppressed after the French Ambassador complains to King James.[1] After June the play is published with the offensive passages suppressed.
- July–December – plague in London (which recurs in the two following years).
- c. October – Thomas Middleton's city comedy A Mad World, My Masters published.[1]
- Muster rolls are compiled in the counties.
- Traditional date – golf first played in England, at Blackheath, London.[25]
- 1609
- 20 May – London publisher Thomas Thorpe issues Shake-speares Sonnets, with a dedication to "Mr. W.H.", and the poem A Lover's Complaint appended; it is uncertain whether this publication has Shakespeare's authority.
- 25 July – the London Company's ship Sea Venture, en route to relieve the Jamestown settlement, is driven ashore in Bermuda, thus effectively first settling the colony.
- 26 July – English scientist Thomas Harriot becomes the first to draw an astronomical object after viewing it through a telescope: he draws a map of the Moon, preceding Galileo by several months.[26][27]
- 28 August – English explorer Henry Hudson (in the service of the Dutch East India Company) finds Delaware Bay.[1][28]
- 11–12 September – explorer Henry Hudson's ship Halve Maen[28] sails into Upper New York Bay[29] and begins a journey up the Hudson River.[1]
- 12 October – A version of the rhyme "Three Blind Mice" is published in Deuteromelia or The Seconde part of Musicks melodie (London). The editor, and possible author of the verse, is the teenage Thomas Ravenscroft.[30] This collection follows his publication of the first rounds in English, Pammelia.
- Plantation of Ulster proceeds: Protestant English and Scots settlers take over forfeited estates of rebel leaders.[4]
- Trinity House establishes the first lighthouses at Lowestoft.
- Publication of Pericles, Prince of Tyre with attribution to Shakespeare.[1]
Births[]
- 1600
- February – Edmund Calamy the Elder, presbyterian (died 1666)
- November John Ogilby, writer and cartographer (died 1676)
- Sir Richard Grenville, 1st Baronet, Royalist leader (died 1658)
- William Prynne, puritan politician (died 1669)
- Brian Walton, divine and scholar (died 1661)
- probable date – Dud Dudley, ironmaster (died 1684)
- 1601
- 1602
- 29 March – John Lightfoot, churchman and rabbinical scholar (died 1675)
- April – William Lawes, composer and musician (died 1645)
- 1 May – William Lilly, astrologer (died 1681)
- 12 October – William Chillingworth, churchman (died 1644)
- 13 October – Algernon Percy, 10th Earl of Northumberland, military leader (died 1668)
- 18 December – Simonds d'Ewes, antiquarian and politician (died 1650)
- John Berkeley, 1st Baron Berkeley of Stratton (died 1678)
- John Bradshaw, English judge and regicide (died 1659)
- John Greaves, mathematician and antiquary (died 1652)
- Edward Montagu, 2nd Earl of Manchester (died 1671)
- Henry Marten, regicide (died 1680)
- Dudley North, 4th Baron North (died 1677)
- Owen Feltham, religious writer (died 1668)
- 1602 or 1603
- Edward Somerset, 2nd Marquess of Worcester (died 1667)
- 1603
- 21 January – Shackerley Marmion, dramatist (died 1639)
- 27 January – Harbottle Grimston, politician (died 1685)
- 18 March – Simon Bradstreet, colonial magistrate (died 1697)
- 11 July – Kenelm Digby, privateer and alchemist (died 1665)
- 20 November (bapt.) – Daniel Blagrave, Member of Parliament (died 1668)
- 21 December – Roger Williams, theologian and colonist (died 1684)
- John Ashburnham, Royalist Member of Parliament (died 1671)
- 1604
- 29 May (bapt.) – Isaac Ambrose, Puritan divine (died 1664)
- 3 August – John Eliot, puritan missionary (died 1690)
- 13 September – William Brereton, soldier and politician (died 1661)
- 8 November (bapt.) – Edward Pococke, Orientalist and biblical scholar (died 1691)
- 23 November (bapt.) – Jasper Mayne, dramatist (died 1672)
- 1605
- June – Thomas Randolph, poet and dramatist (died 1635)
- August – Bulstrode Whitelocke, lawyer and parliamentarian (died 1675)
- 8 August – Cecilius Calvert, 2nd Baron Baltimore, colonial Governor of Maryland (died 1675)
- 18 August – Henry Hammond, churchman (died 1660)
- 12 September – William Dugdale, antiquary (died 1686)
- 19 October – Thomas Browne, physician and philosopher (died 1682)
- 4 November – William Habington, poet (died 1654)
- William Berkeley, governor of Virginia (died 1677)
- Approximate date
- 1606
- 4 January (bapt.) – Edmund Castell, orientalist (died 1685)
- 28 February – William Davenant, poet and playwright (died 1668)
- March – Henry Pierrepont, 1st Marquess of Dorchester (died 1680)
- 3 March – Edmund Waller, poet (died 1687)
- 27 September – Richard Busby, clergyman (died 1695)
- 4 November (bapt.) – Thomas Herbert, traveller and historian (died 1682)
- John Robartes, 1st Earl of Radnor, politician (died 1685)
- Approximate date
- 1607
- 31 January – James Stanley, 7th Earl of Derby, Royalist noble (executed 1651)
- 5 April (bapt.) – John Boys, Royalist soldier, Lord Warden of the Cinque Ports (died 1664)
- 10 March – Thomas Wriothesley, 4th Earl of Southampton, statesman (died 1667)
- 26 November – John Harvard, clergyman and colonist (died 1638)
- John Dixwell, judge and regicide (died 1689)
- 1608
- 15 April – John Huddleston, Catholic clergyman (died 1698)
- 20 April – Edward Rainbowe, clergyman and preacher (died 1684)
- June – Richard Fanshawe, diplomat (died 1666)
- 19 June – Thomas Fuller, churchman and historian (died 1661)
- 14 July – George Goring, Lord Goring, Royalist soldier (died 1657)
- 4 August – John Tradescant the Younger, botanist and gardener (died 1662)
- 13 November – John Desborough, soldier and politician (died 1680)
- 6 December – George Monck, 1st Duke of Albemarle, soldier (died 1670)
- 9 December – John Milton, poet (died 1674)
- Thomas Barlow, Bishop of Lincoln (died 1691)
- 1609
- 10 February – John Suckling, poet (died 1642)
- 18 February – Edward Hyde, 1st Earl of Clarendon, historian and statesman (died 1674)
- 29 March – Sarah Boyle, noblewoman (died 1633)
- 8 October – John Clarke, physician (died 1676)
- 19 October – Gerrard Winstanley, Protestant religious reformer (died 1676)
- 26 October – William Sprague, co-founder of Charlestown, Massachusetts (died 1675)
- 1 November – Matthew Hale, Lord Chief Justice (died 1676)
- 24 December – Philip Warwick, writer and politician (died 1683)
- Samuel Cooper, miniature painter (died 1672)
Deaths[]
- 1600
- April – Thomas Deloney, writer (born 1543)
- 3 November – Richard Hooker, Anglican theologian (born 1554)
- 1601
- 19 January – Henry Herbert, 2nd Earl of Pembroke, statesman (born 1534)
- 25 February – Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, politician (born 1566)
- 27 February – Anne Line, Catholic martyr (executed) (born c. 1563)
- 7 September – John Shakespeare, glover and farmer, father of William Shakespeare (born 1529)
- 1602
- 13 February – Alexander Nowell, clergyman (born 1507)
- October – Thomas Morley, composer (born 1557)
- 29 November – Anthony Holborne, composer (born c. 1545)
- 1603
- 15 January – Catherine Carey, Lady in waiting to Elizabeth I of England (year of birth unknown)
- 24 March – Queen Elizabeth I (born 1533)[31]
- 8 September – George Carey, 2nd Baron Hunsdon, politician (born 1547)
- 28 October (burial) – Ralph Lane, explorer (born 1530)
- 9 December – William Watson, conspirator (born 1559)
- 10 December – William Gilbert, scientist (plague) (born 1544)
- 27 December – Thomas Cartwright, Puritan clergyman (born c. 1535)
- Edward Fenton, navigator (year of birth unknown)
- Probable date – Will Kempe, comic performer (year of birth unknown)
- 1604
- early – Thomas North, translator of Plutarch (born 1535)
- 29 February – John Whitgift, Archbishop of Canterbury (born 1530)
- 1 April – Thomas Churchyard, author (born 1520)
- 24 June – Edward de Vere, 17th Earl of Oxford, politician (born 1550)
- November – Thomas Storer, poet (born 1571)
- 3 December – George Hastings, 4th Earl of Huntingdon (born 1540)
- late – Richard Topcliffe, Member of Parliament and torturer (born 1532)
- 1605
- 5 April – Adam Loftus, Catholic archbishop (born c. 1533)
- 6 April – John Stow, historian and antiquarian (born 1525)
- 11 September – Sir Thomas Tresham, politician (born 1550)
- 8 November – Robert Catesby, conspirator (born 1573)
- December – Francis Tresham, conspirator (born 1567)
- 29 December – John Davis, explorer (born 1550)
- 1606
- 30 January
- Everard Digby, conspirator (executed) (born 1578)
- Robert Wintour, conspirator (executed) (born 1565)
- 31 January
- Guy Fawkes, conspirator (executed) (born 1570)
- Ambrose Rokewood, conspirator (executed) (born c. 1578)
- Thomas Wintour, conspirator (executed) (born 1571)
- 3 April – Charles Blount, 1st Earl of Devon, politician (born 1563)
- 3 May – Henry Garnet, Jesuit (executed) (born 1555)
- 20 November (burial) – John Lyly, writer (born 1553)
- 30 January
- 1607
- May – Edward Dyer, courtier and poet (born 1543)
- 21 May – John Rainolds, scholar and Bible translator (born 1549)
- 10 June – John Popham, Lord Chief Justice (born 1553)
- 7 July – Penelope Blount, Countess of Devonshire (born 1562
- 22 August – Bartholomew Gosnold, explorer and privateer (born 1572)
- 20 December – Sir John Bourke of Brittas, Irish recusant (executed) (born 1550)
- Henry Chettle, writer (born 1564)
- 1608
- 13 February – Bess of Hardwick, Countess of Shrewsbury (born 1527)
- 26 February – John Still, bishop (born c. 1543)
- 29 March – Laurence Tomson, Calvinist theologian (born 1539)
- 19 April – Thomas Sackville, 1st Earl of Dorset, statesman and poet (born 1536)
- c. 24 August – Edmund Whitelocke, soldier and courtier (born 1565)
- 19 October – Geoffrey Fenton, writer and politician (born c. 1539)
- December
- John Dee, mathematician, astronomer, and geographer (born 1527)
- William Davison, secretary to Queen Elizabeth I of England (born c. 1541)
- 1609
- 9 March – William Warner, poet (born c. 1558)
- December – Barnabe Barnes, poet (born c. 1571)
References[]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Williams, Hywel (2005). Cassell's Chronology of World History. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. pp. 238–243. ISBN 0-304-35730-8.
- ^ Kemp's Nine Daies Wonder.
- ^ "Banbury History". Banbury Cross. 2005. Retrieved 3 November 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Palmer, Alan; Veronica (1992). The Chronology of British History. London: Century Ltd. pp. 166–168. ISBN 0-7126-5616-2.
- ^ "First Voyage of the English East India Company, in 1601, under the Command of Captain James Lancaster". Retrieved 8 February 2021.
- ^ Edwards, Phillip, ed. (1985). Hamlet, Prince of Denmark. New Cambridge Shakespeare. p. 8. ISBN 0-521-29366-9.
Any dating of Hamlet must be tentative.
Scholars date its writing as between 1599 and 1601. - ^ Shakespeare, William (2001). Smith, Bruce R. (ed.). Twelfth Night: Texts and Contexts. Boston, Mass: Bedford/St Martin's. p. 2. ISBN 0-312-20219-9.
- ^ Goff, Moira. "The Merry Wives of Windsor - Shakespeare in quarto". www.bl.uk. Retrieved 19 January 2022.
- ^ a b c d e Penguin Pocket On This Day. Penguin Reference Library. 2006. ISBN 0-14-102715-0.
- ^ Dekker, Thomas. The Wonderfull Yeare 1603, wherein is shewed the picture of London lying sicke of the plague.
- ^ Lee, Christopher (2014). 1613: The Death of Queen Elizabeth I, the Return of the Black Plague, the Rise of Shakespeare, Piracy, Witchcraft, and the Birth of the Stuart Era. St Martin's Press. ISBN 9781466864504.
- ^ "Worst Diseases in Shakespeare's London". Retrieved 15 May 2021.
- ^ Bell, Walter George (1951). Hollyer, Belinda (ed.). The Great Plague in London. Folio Society. pp. 3–5.
- ^ a b c d e f g "The government of James I". Archived from the original on 14 May 2008. Retrieved 17 March 2008.
- ^ "Speaker's Statement". Hansard. 18 March 2019. Retrieved 19 March 2019.
- ^ "Case 1: The Treaty of London". Retrieved 17 March 2008.
- ^ "A proclamation concerning the Kings Majesties Stile, of King of Great Britaine, &c". Archived from the original on 17 March 2008. Retrieved 17 March 2008.
- ^ "Guy Fawkes and Bonfire Night". 2008. Retrieved 25 February 2011.
- ^ de Milititz, Alexander (1839). Manuel des consuls: Établissement des consulats à l'étranger. Vol. 2. London: A. Asher. p. 65 – via Google Books.
- ^ a b Scholars date completion as between 1603 and 1606. Boyce, Charles (1990). Encyclopaedia of Shakespeare. New York: Roundtable Press.
- ^ Bryant, Edward; Haslett, Simon (2002). "Was the AD 1607 Coastal Flooding Event in the Severn Estuary and Bristol Channel (UK) Due to a Tsunami?" (PDF). Archaeology in the Severn Estuary (13): 163–7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 June 2011. Retrieved 6 September 2010.
- ^ "The great flood of 1607: could it happen again?". BBC Somerset. Archived from the original on 3 April 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
- ^ "Newton Rebels 1607". Archived from the original on 30 September 2011. Retrieved 22 October 2011.
- ^ Stratton, J. M. (1969). Agricultural Records. John Baker. ISBN 0-212-97022-4.
- ^ "Heritage". Eltham: Royal Blackheath Golf Club. Retrieved 12 June 2016.
- ^ McGourty, Christine (14 January 2009). "'English Galileo' maps on display". BBC News. Retrieved 4 July 2012.
- ^ "Thomas Harriot's Moon Drawings". The Galileo Project. 1995. Retrieved 4 July 2012.
- ^ a b Hunter, Douglas (2009). Half Moon: Henry Hudson and the voyage that redrew the map of the New World. London: Bloomsbury Press. ISBN 978-1-59691-680-7.
- ^ Nevius, Michelle; James (8 September 2008). "New York's many 9/11 anniversaries: the Staten Island Peace Conference". Inside the Apple: A Streetwise History of New York City. Retrieved 25 October 2011.
- ^ Opie, Iona; Peter (1997). The Oxford Dictionary of Nursery Rhymes (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 306. ISBN 0-19-860088-7.
- ^ "Elizabeth I | Biography, Facts, Mother, & Death | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 18 January 2022.
Categories:
- 1600s in England
- 17th century in England