1912 Chinese National Assembly election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 870 seats in the National Assembly (274 seats in the Senate and 596 seats in the House of Representatives) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1912 Chinese National Assembly elections, held in December 1912 to January 1913, were the first elections for the newly founded National Assembly of the Republic of China, which was a bicameral parliament with a Senate and a House of Representatives.
Overview[]
The election was indirect, as voters chose some 30,000 electors who chose about 2,000 members of the provincial assemblies and 596 members of the House of Representatives. This system caused instances of bribery.
The 274-member Senate were elected by the provincial assemblies who themselves had been elected in 1909 during the Qing dynasty.
Adult males over the age of 21 who were educated or owned property and paid taxes, and who could prove a two-year residency in a particular county, could vote.[1] An estimated 40 million or 4-6% of China's population were registered for the election.[2] This was an increase from the size of the electorate in the 1909 Chinese provincial elections, when less than 1% of the population was enfranchised.
The president had to pick the 64 members representing Tibet, Outer Mongolia, and Overseas Chinese due to the fact that the government in Beijing did not exercise enough control over these populations to organize elections. Despite the compromises, this election had the participation of over 300 civic groups and was the first and most competitive nationwide election in Chinese history.
The Kuomintang (Chinese Nationalist Party) led by Song Jiaoren won a plurality in both houses of the assembly, and Song was expected to become the Premier of China.[2] After losing the election, the Republican, Unity, and Democratic (formerly Constitutionalist) parties merged into the Progressive Party with Liang Qichao as leader. The Progressive Party became the main rival to the Nationalists.
Song was assassinated on 20 March 1913 in Shanghai. When the assembly convened for the first time on April 8 amid heated debate over the assassination, the Nationalists were divided over solutions on how to deal with Yuan Shikai, the provisional president, who was suspected of ordering the assassination. On 12 July, Sun Yat-sen led the Nationalists and a faction of provinces into armed rebellion against Yuan, coined the Second Revolution. However, the Second Revolution was completely defeated within two months by Yuan's forces.
The National Assembly members were compromised by threats and bribes from Yuan. He confined the National Assembly and forced them to elect him as the formal president in the October presidential election. Yuan quickly outlawed the Nationalists and expelled them from the assembly. Without a quorum, the National Assembly could not convene, so Yuan disbanded it on 10 January 1914.
Voter and seat distributions[]

| Electoral district | Chinese | Pinyin | Population | Voters | % | House Seats | Senate Seats |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chihli | 直隸省 | Zhílì | 25,932,133 | 9,195,757 | 35.46 | 46 | 10 |
| Fengtien | 奉天省 | Fèngtiān | 12,133,303 | 896,408 | 7.39 | 16 | 10 |
| Kirin | 吉林省 | Jílín | 5,580,030 | 108,835 | 1.95 | 10 | 10 |
| Heilungkiang | 黑龍江省 | Hēilóngjiāng | 2,028,776 | 288,234 | 14.21 | 10 | 10 |
| Shantung | 山東省 | Shāndōng | 30,987,853 | 1,368,184 | 4.42 | 33 | 10 |
| Honan | 河南省 | Hénán | 35,900,038 | 1,688,632 | 4.70 | 32 | 10 |
| Shansi | 山西省 | Shānxī | 12,269,386 | 2,588,068 | 21.10 | 28 | 10 |
| Kiangsu | 江蘇省 | Jiāngsū | 32,282,781 | 1,939,386 | 6.01 | 40 | 10 |
| Anhwei | 安徽省 | Ānhuī | 16,229,052 | 1,450,901 | 8.94 | 27 | 10 |
| Kiangsi | 江西省 | Jiāngxī | 23,987,317 | 4,986,883 | 20.79 | 35 | 10 |
| Fukien | 福建省 | Fújiàn | 15,849,296 | 1,283,348 | 8.10 | 24 | 10 |
| Chekiang | 浙江省 | Zhèjiāng | 21,440,151 | 1,184,629 | 5.53 | 38 | 10 |
| Hupeh | 湖北省 | Húběi | 25,590,308 | 5,670,370 | 22.16 | 26 | 10 |
| Hunan | 湖南省 | Húnán | 27,390,230 | 1,277,414 | 4.66 | 27 | 10 |
| Shensi | 陝西省 | Shǎnxī | 10,271,096 | 1,395,622 | 2.98 | 21 | 10 |
| Kansu | 甘肅省 | Gānsù | 4,989,907 | 148,526 | 2.98 | 14 | 10 |
| Sinkiang | 新疆省 | Xīnjiāng | 2,000,000 | 9,506 | 0.48 | 10 | 10 |
| Szechwan | 四川省 | Sìchuān | 48,129,596 | 1,729,368 | 3.59 | 35 | 10 |
| Kwangtung | 廣東省 | Guǎngdōng | 28,010,560 | 1,966,516 | 7.02 | 30 | 10 |
| Kwangsi | 廣西省 | Guǎngxī | 8,746,747 | 2,731,717 | 31.23 | 19 | 10 |
| Yunnan | 雲南省 | Yúnnán | 9,466,965 | 233,398 | 2.47 | 22 | 10 |
| Kweichow | 貴州省 | Guìzhōu | 9,665,227 | 792,290 | 8.20 | 13 | 10 |
| Mongolia | 蒙古選舉會 | Ménggǔ | — | — | — | 27 | 27 |
| Tibet | 西藏選舉會 | Xīzàng | — | — | — | 10 | 10 |
| Tsinghai | 青海選舉會 | Qīnghǎi | — | — | — | 3 | 3 |
| Oversea Chinese | 華僑選舉會 | Huáqiáo | — | — | — | 0 | 6 |
| Central Society | 中央學會 | — | — | — | — | 0 | 8 |
| Total | 406,880,486 | 42,933,992 | 10.50 | 596 | 274 | ||
Results[]
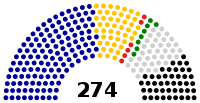  | ||||||
| Party | Seats | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senate | House | |||||
| Kuomintang | 132 | 269 | ||||
| Republican Party | 46 | 120 | ||||
| Unity Party | 6 | 18 | ||||
| Democratic Party | 8 | 16 | ||||
| Multi-party candidates | 38 | 147 | ||||
| Independents | 44 | 26 | ||||
| Total | 274 | 596 | ||||
Presidential elections in National Assembly[]
An important function of the National Assembly under the Provisional Constitution of the Republic of China was to elect the President and Vice President of China. The following elections were held by the 1st National Assembly of Beiyang government.
| Order | Presidential Election | President | Vice President | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 1913 Chinese presidential election | Yuan Shikai | Li Yuanhong | First formal presidential election in Chinese history |
| 1916 Chinese vice-presidential election | — | Feng Guozhang | To replace the vacancy of Li Yuanhong as he sworn in as the President after Yuan Shikai's death. | |
| 3rd | 1923 Chinese presidential election | Cao Kun | — | Resumed session after First Zhili–Fengtian War |
- The 2nd Presidential election was held by the 2nd National Assembly elected in 1918
See also[]
- 1909 Chinese provincial elections
- History of the Republic of China
- National Assembly (Beiyang government)
- History of the Kuomintang
- Progressive Party (China)
- History of Beijing
References[]
- ^ Cambridge History of China, Vol 12, Part 1: 222-223
- ^ a b Young, Ernest P. ""Politics in the Aftermath of Revolution: The Era of Yuan Shih-K'ai, 1912-16"". Cambridge History of China, Vol 12, Part 1. p. 222.
Bibliography[]
- Twitchett, Denis; Fairbank, John K, eds. (1983). The Cambridge History of China. Vol. Volume 12, Part 1. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-23541-9.
{{cite book}}:|volume=has extra text (help)
- 1912 in China
- 1912 elections in Asia
- Legislative elections in the Republic of China (1912–1949)



