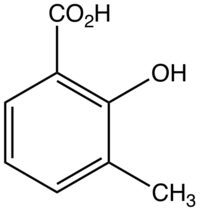
3-Methylsalicylic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Hydroxy-3-methylbenzoic acid | |
| Other names
2,3-Cresotic acid
o-Cresotinic acid 2-Hydroxy-m-toluic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.340 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 152.149 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 165.5 °C (329.9 °F; 438.6 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
Signal word
|
Danger |
| H302, H315, H318, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
3-Methylsalicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3(CO2H)(OH). It is a white solid that is soluble in basic water and in polar organic solvents. At neutral pH, the acid exists as 3-methylsalicylate Its functional groups include a carboxylic acid and a phenol group. It is one of four isomers of methylsalicylic acid.
It can be produced by carboxylation of o-cresol.[1]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Takayuki Iijima; Tatsuaki Yamaguchi (2001). "K2CO3-Catalyzed Direct Synthesis of Salicylic Acid from Phenol and Supercritical CO2". Applied Catalysis A. 345: 12–17. doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2008.03.037.
Categories:
- Salicylic acids
- Aromatic compound stubs