5th century BC
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2015) |
| Millennium: | 1st millennium BC |
|---|---|
| Centuries: |
|
| Timelines: |
|
| State leaders: |
|
| Decades: | |
| Categories: | Births – Deaths Establishments – Disestablishments |
The 5th century BC started the first day of 500 BC and ended the last day of 401 BC.

This century saw the establishment of Pataliputra as a capital of the Magadha Empire. This city would later become the ruling capital of different Indian kingdoms for about a thousand years. This period saw the rise of two great philosophical schools of the east, Jainism and Buddhism. This period saw Mahavira and Buddha spreading their respective teachings in the northern plains of India. This essentially changed the socio-cultural and political dynamics of the region of South Asia. Buddhism would later go on to become one of the major world religions.
This period also saw the work of Yaska, who created Nirukta, that would lay the foundation stone for Sanskrit grammar and is one of the oldest works on grammar known to mankind.
This century is also traditionally recognized as the classical period of the Greeks, which would continue all the way through the 4th century until the time of Alexander the Great. The life of Socrates represented a major milestone in Greek philosophy though his teachings only survive through the work of his students, most notably Plato and Xenophon. The tragedians Aeschylus, Sophocles, and Euripides, as well as the comedian Aristophanes all date from this era and many of their works are still considered classics of the western theatrical canon.
The Persian Wars, fought between a coalition of Greek cities and the vast Achaemenid Persian Empire was a pivotal moment in Greek politics. After having successfully prevented the annexation of Greece by the Persians, Sparta, the dominant power in the coalition, had no intention of further offensive action and considered the war over. Meanwhile, Athens counter-attacked, liberating Greek subjects of the Persian Empire up and down the Ionian coast and mobilizing a new coalition, the Delian League. Tensions between Athens, and its growing imperialistic ambitions as leader of the Delian League, and the traditionally dominant Sparta led to a protracted stalemate in the Peloponnesian war.
The world in the 5th century BC[]
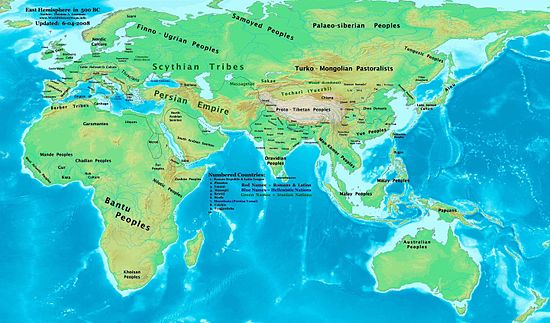
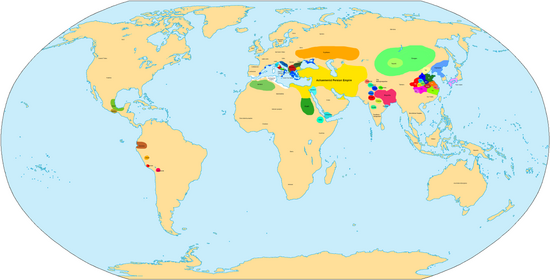
Events[]
- Demotic becomes the dominant script of ancient Egypt.
490s BC[]
- 499 BC: Aristagoras, acting on behalf of the Persian Empire, leads a failed attack on the rebellious island of Naxos.
- 499 BC: Aristagoras instigates the Ionian Revolt, beginning the Persian Wars between Greece and Persia.
- 499 BC: Sardis sacked by Athenian and Ionian troops.
- 498 BC: Leontini subjugated by Hippocrates of Gela.
- 498 BC: Alexander I succeeds his father Amyntas I as king of Macedon.
- 496 BC: Battle of Lake Regillus: A legendary early Roman victory, won over either the Etruscans or the Latins.
- 496 BC: Sophocles is born.
- 495 BC: Temple to Mercury on the Circus Maximus in Rome is built.
- 494 BC: The Battle of Lade, where Persians take back Ionia.
- 494 BC: Two tribunes of the plebs and two plebeian aediles are elected for the first time in Rome: the office of the tribunate is established.
- 494 BC: The year Rome changed from an Aristocratic Republic to a Liberalized Republic.
- 493 BC: Piraeus, the port town of Athens, is founded.
- 493 BC: Coriolanus captures the Volscian town of Corioli for Rome.
- 492 BC: First expedition of King Darius I of Persia against Greece, under the leadership of his son-in-law Mardonius. This marks the start of the campaign that culminated in the Battle of Marathon in 490 BC.
- 491 BC: Leotychidas succeeds his cousin Demaratus as king of Sparta.
- 491 BC: Gelo becomes Tyrant of Gela.
- 490 BC: The Battle of Marathon, where Darius I of Persia is defeated by the Athenians and Plataeans under Miltiades
- 490 BC: Phidippides runs 40 kilometers from Marathon to Athens to announce the news of the Greek victory; origin of the marathon long-distance race.
480s BC[]
- 489 BC: Cities of Rhodes unite and start construction of the new city of Rhodes.
- 488 BC: Leonidas I succeeds his brother Cleomenes I as king of Sparta after Cleomenes is judged insane.
- 487 BC: Egypt revolts against the Persians.
- 487 BC: Aegina and Athens go to war.
- 487 BC: Athenian Archonship becomes elective by lot, an important milestone in the move towards radical Athenian democracy.
- 487 BC: Siaspiqa becomes ruler of the Kushite kingdom of Meroe.
- 486 BC: First part of the Grand Canal of China is built.
- 486 BC: Xerxes I succeeds Darius I as Great King of Persia.
- 486 BC: Egypt revolts against Persian rule.
- 486 BC: First Buddhist Council at Rejgaha, under the patronage of King Ajatasattu. Oral tradition established for the first time.
- 484 BC: Athenian playwright Aeschylus wins a poetry prize.
- 484 BC: Xerxes I abolishes the Kingdom of Babel and removes the golden statue of Bel (Marduk, Merodach).
- 484 BC: Persians regain control of Egypt.
- 483 BC: Gautama Buddha dies.
- 483 BC: Xerxes I of Persia starts planning his expedition against Greece
- 481 BC: The Isthmus of Corinth ends a war between Athens and Aegina.
- 480 BC: King Xerxes I of Persia sets out to conquer Greece.
- 480 BC: Cimon and his friends burn horse-bridles as an offering to Athena and join the marines
- 480 BC: Pleistarchus succeeds his father Leonidas I as king of Sparta.
- August, 480 BC: Battle of Artemisium—The Persian fleet fights an inconclusive battle with the Greek allied fleet.
- August 11, 480 BC: The Battle of Thermopylae, a costly victory by Persians over the Greeks.
- September 23, 480 BC: Battle of Salamis between Greece and Persia, leading to a Greek victory.
- 480 BC: Battle of Himera—The Carthaginians under Hamilcar are defeated by the Greeks of Sicily, led by Gelon of Syracuse.
- 480 BC: Roman troops march against the Veientines.
470s BC[]
- 479 BC: The Battle of Plataea, the Greeks defeat the Persians, ending the Persian Wars.
- 479 BC: Battle of Mycale.
- 479 BC: Potidaea is struck by a tsunami.
- 479 BC: Chinese philosopher Confucius dies.
- 478 BC: Establishment of the Temple of Confucius at (modern-day) Qufu.
- 477 BC: The Delian League is inaugurated.
- 476 BC: Archidamus II succeeds his grandfather Leotychides, who is banished to Tegea, as king of Sparta.
- 475 BC: King Xuan of Zhou becomes King of the Zhou Dynasty.
- 474 BC: Battle of Cumae—The Syracusans under Hiero I defeat the Etruscans and end Etruscan expansion in southern Italy.
- 474 BC: Greek poet Pindar moves to Thebes.
- 473 BC: The Chinese State of Wu is annexed by the State of Yue.
- 472 BC: Carystus in Euboea is forced to join the Delian League (approximate date).
- 472 BC: The tragedy The Persians is produced by Aeschylus.
- 471 BC: Athenian politician Themistocles is ostracized.
460s BC[]
- 469 BC: Philosopher Socrates is born in Attica, Athens, Greece.
- 468 BC: Sophocles, Greek playwright, defeats Aeschylus for the .
- 468 BC: Antium captured by Roman forces.
- 468 BC: King Zhending of Zhou becomes King of the Zhou Dynasty of China.
- 466 BC: Delian League defeats Persia at the Battle of Eurymedon.
- 466 BC: The Greek colony of Taras, in Magna Graecia, is defeated by Iapyges, a native population of ancient Apulia; Tarentine monarchy falls, with the installation of a democracy and the expulsion of the Pythagoreans.
- 465 BC: King Xerxes I of the Persian Empire is murdered by Artabanus the Hyrcanian. He is succeeded by Artaxerxes I, possibly with Artabanus acting as Regent.
- 465 BC: Thasos revolts from the Delian League.
- 464 BC: An earthquake in ancient Sparta, Greece leads to a Helot uprising and strained relations with Athens, one of the factors that lead to the Peloponnesian War.
- 464 BC: Regent King Artabanus of Persia is killed by his charge Artaxerxes I.
- 464 BC: Third Messenian war.
- 462 BC: The revolt of Thasos against the Delian League comes to an end with their surrender.
- 461 BC: Athenian politician Cimon is ostracized.
- 460 BC: Egypt revolts against Persia, starting a six-year war. An Athenian force sent to attack Cyprus is diverted to support this revolt.
- 460 BC: Cincinnatus becomes consul of the Roman Republic.
- 460 BC: Physician Hippocrates is born in Kos, Greece.
450s BC[]
- 459 BC: Pleistoanax succeeds his father Pleistarchus as king of Sparta.
- 459 BC: Destruction of the Sicilian town of Morgantina by Douketios, leader of the Sikels, according to Diodoros Siculus.
- 459 BC: Ezra leads the second body of Jews from Babylon to Jerusalem.
- 458 BC: Greek playwright Aeschylus completes the Oresteia, a trilogy that tells the story of a family blood feud. The plays will have a great influence on future writers.
- 458 BC: Cincinnatus is named dictator of the Roman Republic in order to defend it against Aequi. Sixteen days later, after defeating the invaders at the Battle of Mount Algidus, he resigns and returns to his farm.
- 457 BC: Athenian statesman Pericles' greatest reform, allowing common people to serve in any state office, inaugurates Golden Age of Ancient Athens.
- 457 BC: Battle of Tanagra—The Spartans defeat the Athenians, near Thebes.
- 457 BC: Battle of Oenophyta—The Athenians defeat the Thebans and take control of Boeotia.
- 457 BC: Decree of Artaxerxes I to re-establish the city government of Jerusalem. See Ezra 7, Daniel 9 and Nehemiah 1 in Old Testament.
- 455 BC: A thirty years' truce concluded between Athens and Lacedaemon.
- 455 BC: Euripides presents his first known tragedy, Peliades, in the Athenian festival of Dionysia.
- 454 BC: Athens loses a fleet and possibly as many as 50 000 men in a failed attempt to aid an Egyptian revolt against Persia.
- 454 BC: The treasury of the Delian League is moved from Delos to Athens.
- 454 BC: Hostilities between Segesta and Selinunte, two Greek cities on Sicily.
- 453 BC: Taiyuan, a city in China, gets flooded.
- 451 BC: Athens makes peace with Sparta and wages a war against Persia.
- 451 BC: The decemviri come to power in the Roman Republic. They enact the twelve tables, the foundation of Roman Law.
- 450 BC: Battle of Salamis: Athenians under Cimon defeat the Persian fleet.
- 450 BC: Perdiccas II succeeds Alexander I as king of Macedonia (approximate date).
- 450 BC to 325 BC: Olmecs leave La Venta, and it becomes depopulated by 325 BC.
440s BC[]
- 449 BC: The Peace of Callias between the Delian League and Persia ends the Persian Wars.
- 449 BC: Construction begins on the Temple of Hephaestus in Athens.
- 449 BC: The Twelve Tables are promulgated to the people of Rome—the first public laws of the Roman Republic.
- 449 BC: Romans revolt against the decemvirate. The decemvirs resign and the tribunate is re-established.
- 449 BC: Herodotus completes his History, which records the events concerning the Persian War.
- 448 BC: Phidias finishes a 9 meter high statue of Athena on the Acropolis.
- 447 BC: Athens begins construction of the Parthenon, at the initiative of Pericles.
- 447 BC: Battle of Coronea—The Athenians are driven out of Boeotia.
- 447 BC: Achaeus of Eretria, a Greek playwright, shows his first play.
- 445 BC: Pericles declares Thirty Years' Peace between Athens and Sparta.
- 445 BC: Artaxerxes I gives Nehemiah permission to rebuild Jerusalem.
- 445 BC: The Lacus Curtius is created by a lightning strike in Rome. It is consecrated by Gaius, or Marcus Curtius.
- 443 BC: The Roman Republic creates the office of censor, initially exclusive to patricians.
- 443 BC: Foundation of the Greek colony of Thurii in Italy. Its colonists include Herodotus and Lysias.
- 442 BC: Sophocles writes Antigone.
- 441 BC: King Ai of Zhou becomes King of the Zhou Dynasty of China but dies before the year's end.
- 440 BC: Famine in Rome.
- 440 BC: King Kao of Zhou becomes King of the Zhou Dynasty of China.
- 440 BC: Democritus proposes the existence of indivisible particles, which he calls atoms.
430s BC[]
- 439 BC: Cincinnatus again becomes dictator of the Roman Republic; during his term he defeats the Volsci.
- 439 BC: According to legend, Gaius Servilius Ahala saves Rome from Spurius Maelius.
- 438 BC: Ictinus and Callicrates finish construction of the Parthenon, located on Athens' Acropolis.
- 435 BC: The Statue of Zeus at Olympia by Phidias, one of the seven wonders of the world, is completed.
- 434 BC: Conflict occurs between the Greek island of Kerkyra and its mother-city Corinth.
- 434 BC: Anaxagoras tries to square the circle with straightedge and compass.
- 433 BC: Battle of Sybota between Kerkyra and Corinth.
- 433 BC (or later): Burial of Marquis Yi of Zeng in China.
- 432 BC: Athens adopts a 19-year cycle of synchronizing solar and lunar calendars.
- 432 BC: Athens defeats Corinth in the battle of Potidaea.
- 432 BC: The Greek colony of Heraclea is founded by Tarentum and Thurii.
- 431 BC: The Peloponnesian War begins between Sparta and Athens and their allies.
- 431 BC: Defeat of the Aequi by the Romans under the dictator Aulus Postumius Tubertus.
- 431 BC: The Greek physician and philosopher Empedocles articulates the notion that the human body has four humors: blood, bile, black bile, and phlegm, a belief that dominates medical thinking for centuries.
- 430 BC: Athens suffers a major pestilence, believed to be caused by epidemic typhus.
- 430 BC: The philosopher Xenophon is born.
- c. 430 BC: First performance of Sophocles's Oedipus Rex.
420s BC[]
- 429 BC: Battle of Chalcis—Chalcidians and their allies are defeated by Athens.
- 429 BC: Battle of Naupactus—Phormio defeats the Peloponnesian fleet.
- 429 BC: An outbreak of a plague kills over one-third of the population of Athens.
- 429 BC: King Sitalkes of Thrace invades Macedonia.
- 428 BC: Mytilene rebels against Athens but is crushed.
- 428 BC: Sparta attempts to crush a rebellion on Corcyra, but cancels the effort when the Athenians try to intercept them.
- 428 BC: The Greek colony of Cumae in Italy falls to the Samnites.
- 427 BC: The leaders of the Mytilenian revolt are executed.
- 427 BC: Platea surrenders to the Spartans, who execute over 200 prisoners and destroy the city.
- 427 BC: The Athenians intervene in Sicily to blockade Sparta from the island.
- 428 BC: The philosopher Plato is born.
- 426 BC: Demosthenes unsuccessfully besieges the Corinthian colony of Leukas.
- 426 BC: When Ambracia invades Acarnania, they seek help from the Spartans and Athenians respectively. The Athenians then defeat the Spartans in the Battle of Olpae.
- 425 BC: Demosthenes captures the port of Pylos in the Peloponnesus.
- 425 BC: The Athenians invade Sphacteria and defeat the Spartans in the Battle of Pylos.
- 424 BC: Sicily withdraws from the war and expels every foreign power. Thus, Athens is forced to withdraw from the island.
- 424 BC: The Athenians try to capture Megara, but are defeated by the Spartans.
- 424 BC: The Spartan general Brasidas captures Amphipolis, which is a setback for Athens. Thucydides is held responsible for the Athenian failure and is ostracised. This gives him time to start writing his history book.
- 423 BC: The Athenians propose a cease-fire, which the Spartan general Brasidas ignores.
- 422 BC: The Spartans defeat the Athenians in the Battle of Amphipolis, where the Athenian Cleon and the Spartan Brasidas are both killed.
- 421 BC: The Peace of Nicias puts a temporary end to the hostilities between Athens and Sparta.
- 420 BC: Alcibiades is elected strategos of Athens and begins dominating Athenian politics.
410s BC[]
- 419 BC: The Peace of Nicias is broken when Sparta defeats Argos.
- 418 BC: The Spartans win a major victory over the Athenians in the Battle of Mantinea, the biggest land battle of the Peloponnesian War.
- 416 BC: The Athenians capture the island of Melos and treat the inhabitants with great cruelty.
- 416 BC: The Athenians adhere to a plea of help from Sicily and start planning an invasion of the island.
- 415 BC: The sacred Hermae busts in Athens are mutilated just before the expedition to Sicily is sent away. One of the culprits, Andocides, is captured and is forced to turn informer. He names the other mutilators, among them Alcibiades, who are sentenced to death in their absence.
- 415 BC: Alcibiades defects from Athens to Sparta after having learned about his death sentence.
- 414 BC: The Athenians try to make a breakthrough in their siege of Syracuse but are defeated by the Spartans.
- 413 BC: Demosthenes suggests the Athenians leave Syracuse in order to return to Athens, where help is needed. However, Nicias refuses and they are again defeated in battle by the Spartans. Both Demosthenes and Nicias are killed.
- 413 BC: Caria allies itself with Sparta.
- 412 BC: The Persian Empire starts preparing an invasion of Ionia and signs a treaty with Sparta about it.
- 411 BC: The democracy in Athens is overthrown and replaced by the oligarchic Council of Four Hundred. This council is itself soon defeated and order is almost restored, when the Five Thousand start ruling. Early next year, they are also overthrown and the old democracy is restored.
- 410 BC: Athens regains control over its vital grain route from the Black Sea by defeating Sparta in the Battle of Cyzicus.
400s BC[]
- 409 BC: Athens recaptures Byzantium, thereby putting an end to its revolt against Athens and taking control of the whole Bosporus.
- 409 BC: The city of Rhodes is founded.
- 409 BC: The Carthaginians invade Sicily.
- 408 BC: The Persian king, Darius II, decides to aid Sparta in the war and makes his son Cyrus a satrap. However, Cyrus starts collecting an army to benefit his own interests, rather than his father's.
- 408 BC: Alcibiades returns to Athens in triumph after an absence of seven years.
- 407 BC: The Athenian fleet is routed by the Spartan one in the Battle of Notium, which gives Alcibiades' opponents a reason to strip him of command. He never returns to Athens again.
- 406 BC: Athens defeats Sparta in the Battle of Arginusae and the blockade of Conon is lifted.
- 406 BC: Sparta sues for peace, but Athens rejects this.
- 406 BC: The Carthaginians once again invade Sicily and return to Carthage with spoils of war, but also with the plague.
- 405 BC: The Spartan king Pausanias lays siege to Athens, which makes the city start starving.
- 405 BC: Dionysius the Elder rises to power in Syracuse. He signs a peace with Carthage and starts consolidating and expanding his influence.
- April 25, 404 BC: Athens surrenders to Sparta, ending the Peloponnesian War. Sparta introduces an oligarchic system, the Thirty Tyrants, in Athens.
- 404 BC: Egypt rebels against Persian rule.
- 403 BC: The Chinese state of Jin is divided into three smaller nations.[1]
- 403 BC: The first hydraulic engineering in China for a large irrigation canal system is designed by Ximen Bao.
- 403 BC: Some exiled Athenians return to fight the Thirty Tyrants and restore democracy in Athens. They are, however, narrowly defeated by the Spartans in the Battle of Piraeus. After this, the Spartan king Pausanias allows democracy to be restored in Athens.
- 403 BC: Thrasybulus restores the Athenian democracy and grants an almost general amnesty.
- 403 BC: The Athenians adopt the Ionian alphabet.
- 401 BC: Cyrus the Younger rebels against the Persian king Artaxerxes II but is, however, eventually slain in battle.
- 400 BC: After Cyrus has been killed, his Greek mercenaries make their way back to Greece, where Sparta is so impressed with their feats in and march through Persia that they declare war on the Persians.
- 400 BC: The Carthaginians occupy Malta.
- 400 BC: The Egyptians successfully revolt against Persian rule.
- 400 BC: London has its origins as far back as this time.
- 400 BC: Jōmon period ends in Ancient Japan.
Inventions, discoveries, introductions[]
- Cast iron is first used in the Chinese Kingdom of Wu with the innovation of the blast furnace, and soon becomes widespread for agricultural tools and weapons during the Warring States.
- Trebuchet catapult is first used by followers of the Chinese philosopher Mozi.
- The Greeks invent the Anchor with flukes.
- The Greeks start to use shear-leg cranes for construction and loading of ships.
- The Greeks invent linear perspective.
- The Greeks develop an indirect lost wax process for casting bronze.
- The Chinese hydraulic engineer Ximen Bao (西門豹) oversees an enormous canal system for agricultural irrigation, while employed by Marquis Wen of Wei (文侯) (445 BC–396 BC).
- The Chinese philosopher Li Kui writes the Book of Law (Fajing, 法经) in 407 BC, the basis for the law codes of the following Qin Dynasty and partially that of the Han Dynasty.
- Scholars commonly accept that the Hindu text the Bhagavad Gita was written.
- Creation of the Berlin Foundry Cup (early 5th century).
- The oldest known Maya Calendar
Sovereign states[]
See: List of sovereign states in the 5th century BC.
References[]
- ^ Zhao, Dingxin (2004). "Comment: Spurious Causation in a Historical Process: War and Bureaucratization in Early China". American Sociological Review. 69 (4): 603–607. doi:10.1177/000312240406900407.
- 5th century BC
- 1st millennium BC
- Centuries
