6 Geminorum
 | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Gemini |
| Right ascension | 06h 12m 19.09889s[1] |
| Declination | +22° 54′ 30.6580″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.74 - 8.10[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M1-2 Ia-Iab[3] |
| U−B color index | +1.93[4] |
| B−V color index | +1.63[4] |
| Variable type | LC[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +27.16±0.42[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +0.090[1] mas/yr Dec.: −2.426[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 0.7071 ± 0.2376[1] mas |
| Distance | approx. 5,000 ly (approx. 1,400 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | -6.32[6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | ~20[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 821+60 −27[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 86,000[9] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.0[6] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,789[10] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
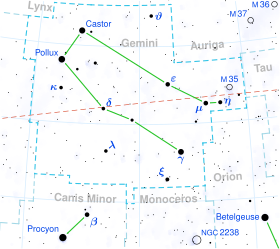
6 Geminorum is a variable star in the zodiac constellation of Gemini, located roughly 5,000 light years away from the Sun.[1] It has the variable star designation BU Geminorum; 6 Geminorum is the Flamsteed designation. At its brightest this reddish hued star is barely visible to the naked eye but is readily visible with binoculars, found southwest of M 35, below WY Geminorum. It is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +27 km/s.[5] The star is a member of the Gemini OB1 association.[12]
This is an evolved red supergiant with a stellar classification of M1-2 Ia-Iab.[3] It is a semiregular variable star, ranging from visual magnitude +5.7 down to +7.5 over a period of 325 days. It has been given the sub-classification of Lc, which means "Irregular variable supergiants of late spectral types having amplitudes of about 1 mag. in V.O".[13] The star has expanded to 821[8] times the Sun's radius and is radiating 86,000[9] times the luminosity of the Sun from its swollen photosphere at an effective temperature of 3,789 K.[10]
References[]
- ^ a b c d e f Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ a b Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S. 1. Bibcode:2009yCat....102025S.
- ^ a b Keenan, Philip C.; McNeil, Raymond C. (1989), "The Perkins catalog of revised MK types for the cooler stars", Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 71: 245, Bibcode:1989ApJS...71..245K, doi:10.1086/191373.
- ^ a b Mermilliod, J.-C. (1986). "Compilation of Eggen's UBV data, transformed to UBV (unpublished)". Catalogue of Eggen's UBV Data. Bibcode:1986EgUBV........0M.
- ^ a b Famaey, B.; et al. (January 2005), "Local kinematics of K and M giants from CORAVEL/Hipparcos/Tycho-2 data. Revisiting the concept of superclusters", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 430 (1): 165–186, arXiv:astro-ph/0409579, Bibcode:2005A&A...430..165F, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041272, S2CID 17804304.
- ^ a b Levesque, Emily M. (2005). "The Effective Temperature Scale of Galactic Red Supergiants: Cool, but Not As Cool As We Thought". The Astrophysical Journal. 628 (2): 973–985. arXiv:astro-ph/0504337. Bibcode:2005ApJ...628..973L. doi:10.1086/430901. S2CID 15109583.
- ^ "6 GEM". 2012. Retrieved 15 December 2016.
- ^ a b Norris, Ryan P. (2019). Seeing Stars Like Never Before: A Long-term Interferometric Imaging Survey of Red Supergiants (PDF) (PhD). Georgia State University.
- ^ a b Mauron, N; Josselin, E (2011). "The mass-loss rates of red supergiants and the de Jager prescription". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 526: A156. arXiv:1010.5369. Bibcode:2011A&A...526A.156M. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201013993. S2CID 119276502.
- ^ a b Mármol-Queraltó, E; Cardiel, N; Cenarro, A. J; Vazdekis, A; Gorgas, J; Pedraz, S; Peletier, R. F; Sánchez-Blázquez, P (2008). "A new stellar library in the region of the CO index at 2.3 μm. New index definition and empirical fitting functions" (PDF). Astronomy and Astrophysics. 489 (2): 885–909. arXiv:0806.0581. Bibcode:2008A&A...489..885M. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200810044. S2CID 15411613.
- ^ "6 Gem". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2019-04-24.
- ^ Laur, Jaan; et al. (February 2017), "Variability survey of brightest stars in selected OB associations", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 598: 27, arXiv:1611.02452, Bibcode:2017A&A...598A.108L, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201629395, S2CID 119076598, A108.
- ^ Variable Star Type Designations in VSX- Retrieved 2016-11-06
- M-type supergiants
- Slow irregular variables
- Gemini (constellation)
- 2MASS objects
- Durchmusterung objects
- Flamsteed objects
- Henry Draper Catalogue objects
- Hipparcos objects
- HR objects
- IRAS catalogue objects
- Objects with variable star designations