Achaean League
League of the Achaeans Κοινὸν τῶν Ἀχαιῶν Koinon ton Achaion | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 280 BC–146 BC | |||||||||||
 Reverse of the Achaean coins probably depicting the symbol of the league (right).
| |||||||||||
 Achaean League in 150 BC | |||||||||||
| Capital | Aigion (meeting place) | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Achaean Doric Koine, Koine Greek | ||||||||||
| Religion | Ancient Greek religion | ||||||||||
| Government | Republican Confederacy | ||||||||||
| Strategos | |||||||||||
| Legislature | Achaean assembly | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Classical Antiquity | ||||||||||
• Re-founded | 280 BC | ||||||||||
• Conquered by the Roman Republic in the Achaean War | 146 BC | ||||||||||
| Currency | Drachma | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Greece | ||||||||||

The Achaean League (Greek: Κοινὸν τῶν Ἀχαιῶν, Koinon ton Akhaion "League of Achaeans") was a Hellenistic-era confederation of Greek city states on the northern and central Peloponnese. The league was named after the region of Achaea in the northwestern Peloponnese, which formed its original core. The first league was formed in the fifth century BC. The second Achaean League was established in 280 BC. As a rival of Antigonid Macedon and an ally of Rome, the league played a major role in the expansion of the Roman Republic into Greece. This process eventually led to the League's conquest and dissolution by the Romans in 146 BC.
The League represents the most successful attempt by the Greek city states to develop a form of federalism, which balanced the need for collective action with the desire for local autonomy. Through the writings of the Achaean statesman Polybius, this structure has had an influence on the constitution of the United States and other modern federal states.[1]
History[]
Classical league[]
The first Achaean League became active in the fifth century in the northwestern Peloponnese.[2] After the catastrophic destruction of the ancient capital Helike by an earthquake and tsunami in 373 BC, it appears to have lapsed sometime in the fourth century.[2]
Hellenistic league[]
The regional Achaean League was reformed in 281/0 BC by the communities of Dyme, Patrae, Pharae and Tritaea, joined in 275 by Aegium, which controlled the important sanctuary of Zeus Homarios.[3][2] The league grew quickly to include the entire Achaean heartland, and after a decade it had ten or eleven members.[2] The key moment for the League's transformation into a major power came in 251, when Aratus, the exiled son of a former magistrate of Sicyon, overthrew the tyranny in his native city and brought it into the Achaean League. Since the Sicyonians were of Dorian and Ionian origin, their inclusion opened the League for other national elements. Aratus, then only twenty years old, rapidly became the leading politician of the League. In the thirty two years between 245 and his death in 213, Aratus would hold the office of general a total of sixteen times.[3][2]
At this time, Central Greece and the Peloponnese were dominated by the Macedonian Kingdom of Antigonus II Gonatas who maintained garrisons at key strategic points such as Chalcis, Piraeus and Acrocorinth, the so-called "fetters of Greece". In other cities of the Peloponnese, namely Argos, Orchomenus, and Megalopolis, Antigonus had installed friendly rulers who were perceived as tyrants by the Achaeans. Aratus, who had lost his father by the hands of such a man, called for the liberation of these cities and secured financial support for the League from Ptolemy II of Egypt, an enemy of the Antigonids. He then used the money to challenge the Macedonian hold on the Peloponnese.[4]
Aratus' greatest success came when he captured Corinth and the fortress of Acrocorinth in 243 BC in a daring night attack. This effectively blocked Macedonian access to the Peloponnese by land, isolating their allies at Megalopolis and Argos.[5] In light of this success, a number of Greek communities, including Epidaurus and Megara joined the League and Ptolemy III increased Egypt's support for the Achaeans, being elected as the League's hegemon (leader) in return.[5] Antigonus Gonatas finally made peace with the Achaean League in a treaty of 240 BC, ceding the territories that he had lost in Greece.[6]
The increased size of the league meant a bigger citizen army and more wealth, which was used to hire mercenaries, but it also led to hostility from the remaining independent Greek states, especially Elis, the Aetolian League and Sparta, which perceived the Achaeans as a threat. Corinth was followed by Megalopolis in 235 BC and Argos in 229 BC.[7] However the league soon ran into difficulties with the revived Sparta of Cleomenes III. Aratus was forced to call in the aid of the Macedonian King, Antigonus III Doson, who defeated Cleomenes in Sellasia. Antigonus Doson re-established Macedonian control over much of the region.
In 220 BC, the Achaean League entered into a war against the Aetolian League, which was called the "Social War". The young king Philip V of Macedon sided with the Achaeans and called for a Panhellenic conference in Corinth, where the Aetolian aggression was condemned.
After Aratus's death, however, the League joined Rome in the Second Macedonian War (200–196 BC), which broke Macedonian power in mainland Greece. The Achaean League was one of the main beneficiaries. Under the leadership of Philopoemen, the League was able to finally defeat a heavily weakened Sparta and take control of the entire Peloponnese.

The League's dominance was not to last long, however. During the Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC), the League flirted with the idea of an alliance with Perseus of Macedon, and the Romans punished it by taking several hostages to ensure good behavior, including Polybius, the Hellenistic historian who subsequently wrote about the rise of the Roman Republic. In 146 BC, the league's relations with Rome completely collapsed, leading to the Achaean War. The Romans under Lucius Mummius defeated the Achaeans at the Battle of Corinth, razed Corinth and dissolved the League, finally putting an end to the independence of Ancient Greece from external rule and ushering in the Roman era. G.T. Griffith has written that Achaean War was "a hopeless enterprise for the Achaeans, badly led and backed by no adequate reserves of money or men."[7] Lucius Mummius received the agnomen Achaicus ("conqueror of Achaea") for his role.
Roman era[]
The original name Koinon of Achaeans (Achaean League) continues to exist in epigraphy, denoting either the previous Peloponnesian members (see koinon of Free Laconians) or the whole of Roman Achaea. In c. 120 BC Achaeans of cities in the Peloponnese dedicated an honorary inscription to Olympian Zeus, after a military expedition with Gnaeus Domitius against the Galatians in Gallia Transalpina.[8] In Athens, in AD 221–222, the koinon of Achaeans, when the strategos was Egnatius Brachyllus, decided to send an embassy to the emperor Caracalla[9]
Government[]
The government of the league consisted of an assembly of citizens, a smaller council, and a strategos (general).[10]
The strategos (general) controlled the league's military forces. Originally, two strategoi held office simultaneously, but from 251, there was only one, who was elected annually by the assembly. Until 217 the strategos entered office in May; afterwards he assumed power at the beginning of winter. Individuals could hold the office more than once (and frequently did so), but not in consecutive years.[2] The general was assisted in his duties by a board of ten demiourgoi, a secretary, a hipparch (cavalry commander), a navarch (admiral), and hypostrategoi (sub-generals commanding in military districts).[11] The office of Hegemon (leader) was given to various Antigonid and Ptolemaic kings at various points in Achaean history. Ostensibly, the hegemon had ultimate command on land and sea, but in fact the office seems to have been an honorary position which obliged the holder to contribute money to the League and support the League's military ventures.[5]
Ultimate decision-making power rested with the assembly (synodos), which was held at Aegium four times a year. All male citizens of communities belonging to the League were entitled to attend. Alongside the assembly there was a council (boule), which was open to citizen men over thirty years old. Special meetings (synkletoi) had to be called in order for the league to declare war, form an alliance, or receive official communications from the Macedonian king or (later) the Roman Republic.[11]
The league was ostensibly a democracy, but control seems to have consistently rested with a small elite group who monopolised the generalship and other official positions. Given the difficulty of travelling to Aegium, assemblies were probably dominated by the wealthy.[4]
Army[]
The Achaean army was an army of the traditional hoplite type. From the 270s onwards however, much like the rest of Greece, the emergence of the shield known as the thyreos was incorporated into Greek warfare and a new type of troop was developed. Reforming their troops into thyreophoroi, the Achaean army was now composed of light troops. The thyreophoroi were a mixture of evolved peltasts and light hoplites, carrying the thureos shield, a thrusting spear and javelins. Plutarch says that they could be effective at a distance, but in close combat the narrow thureos shield disadvantaged them. He also says that their formation was ineffective, because it lacked inter-locked shields or a ‘leveled line of spears’.[12] Aratus, one of the major Achaean strategoi (generals) and statesmen was known for his use of light forces for irregular operations, a type of warfare suited to the thyreophoroi but not suited to operations in the open field.[13]
The League in 217 decided to maintain a standing force of 8,000 mercenary foot and 500 mercenary cavalry, added to a picked citizen force of 3,000 infantry and 300 cavalry, of which 500 foot and 50 horse would come from Argos and the same amount from Megalopolis.[14] Aratus also obtained 500 foot and 50 horse each from Taurion and the Messenians for defence of parts of the League open to attack via Laconia.[14] The citizen infantry would have been armed as thyreophoroi, apart from the citizen light troops who would have been archers and slingers etc. This picked citizen force may well have existed before these so-called reforms, at least on an official basis, as we know of a similar elite force of the same size at the Battle of Sellasia in 222.
However, it was the Achaean general Philopoemen in 208 who changed the Achaean fighting style and weaponry to the Macedonian fashion.[15] According to Plutarch, Philopoemen ‘persuaded them to adopt long pike and heavy shield instead of spear and buckler, to protect their bodies with helmets and breastplates and greaves, and to practice stationary and steadfast fighting instead of the nimble movements of light-armed troops’.[12] These ‘reforms’ were not necessarily new to some of the constituent cities of the League, as the city of Megalopolis had been given bronze shields and armed in the Macedonian fashion by Antigonus Doson for the Sellasia campaign many years before. Philopoemen then trained the new army how to fight with the new weapons and tactics and how to co-ordinate them with a new mercenary corps that was hired. He spent nearly 8 months of his term as strategos visiting, training and advising cities in this capacity.[16] At the Battle of Mantinea in 207 BC the Achaean phalanx was positioned with intervals between the companies with lighter troops. This was obviously a major attempt by Philopoemen to increase the flexibility of his phalanx.[17] He may have picked up this tactic too from his experience at the Battle of Sellasia, where the phalanx of Antigonus Doson was also divided up with light/medium troops in between them. As well as reforming and re-organizing the infantry, Philopoemen also reformed the citizen cavalry. The cavalry was recruited, much like in other Greek states, from the rich and noble classes. Philopoemen organized the cavalry in lochoi, which usually in ancient military treatises means ‘files’, most probably of 8 men, grouped into dilochiai, a formation of double-files of 16 and so forth.
However, by the time of the Achaean War in 146 BC, the League's army had decreased in strength and efficiency. The League was even reduced to freeing and arming 12,000 slaves. This was probably due to the 2nd century BC decline in population. This may well account for the increased hiring of mercenaries, especially Cretans and Thracians.[18]
Members[]
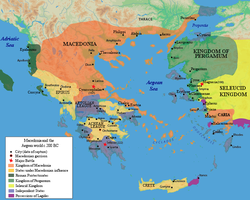
The below are the original Peloponnesian members, except the ancient regions of Sparta, Elis and Messenia. Later Hypana in Elis, Corone, Messene, Sparta and Pagae in Attica were joined by conquest. In 223 BC, Megara in Attica deserted the Achaean League and joined the Boeotian Confederacy.
Besides many city-states on the Mainland joining the Achaean Federation, certain Mediterranean island city-states also became part of the federation. For example, Kydonia on Crete joined at some time after 219 BC.[19]
The city of Helike had been an important member of the first Achaean League, but sank into the sea following a disastrous earthquake in 373 BC. The town of Olenus, also one of the twelve members of the first Achaean League, had been abandoned before 280 BC, but was sometimes counted as though still extant.
The dates in brackets indicate the year of first adhesion. Some cities had periods of separation or foreign occupation and later joined again.
From Achaea[]
- Dyme (281 BC)
- Patras (281 BC)
- Pharae (280 BC)
- Tritaia (280 BC)
- Aegium (275 BC)[2]
- Boura (~ 270 BC)
- Keryneia (~ 270 BC)
- Leontion (~ 265 BC)
- Aegira (~ 265 BC)
- Pellene (~ 265 BC)
- Olenus (after 272 BC)[20][11]
- Helike (before 373 BC)
From Corinthia[]
- Sicyon (251 BC)
- Corinth (243–224 BC, again 197 BC)
- Stymphalus
- Tenea
From Argolis[]
- Troezen (243 BC)
- Epidaurus (243 BC)
- Cleonae (235 BC)
- Argos (229 BC)
- Phlius (229 BC)
- Hermione (229 BC)
- Alea
- Asine
From Arcadia[]
From the ancient political geography of Arcadia, not totally compatible with modern Arcadia
- Megalopolis (235 BC)
- Mantineia (235/227 BC)
- Orchomenus (235 BC)
- Heraea (captured 236 BC)
- Caphyae (captured 228 BC)
- Tegea (223 BC)
- Psophis (218 BC)
- Lasion (218 BC)
- Alipheira
- Asea
- Cleitor
- Dipaea
- Elisphasi[21]
- Gortys
- Lusi
- Methydrium
- Pheneus
- Phigaleia
- Teuthis
- Theisoa
- Thelpusa
From other regions[]
- Megara (243–223 BC / after 197 BC again)
- Aegina (228–211 BC)
- Kydonia (after 219 BC)
- Sparta (192 BC)
- Elis (191 BC)
- Messene (191/182 BC)
- Pleuron (167 BC)
List of Strategoi (Generals)[]
- Margos of Keryneia 256–255 BC
- Aratus of Sicyon I 245–244 BC
- Aratus of Sicyon II 243–242 BC
- Aegialeas 242–241 BC (?)
- Aratus of Sicyon III 241–240 BC
- Aratus of Sicyon IV 239–238 BC
- Aratus of Sicyon V 237–236 BC
- Dioedas 236–235 BC (or 244–243 BC)
- Aratus of Sicyon VI 235–234 BC
- Lydiadas of Megalopolis I 234–233 BC
- Aratus of Sicyon VII 233–232 BC
- Lydiadas of Megalopolis II 232–231 BC
- Aratus of Sicyon VIII 231–230 BC
- Lydiadas of Megalopolis III 230–229 BC (Margos of Keryneia † was Navarch)
- Aratus of Sicyon IX 229–228 BC
- Aristomachos of Argos 228–227 BC
- Aratus of Sicyon X 227–226 BC (Lydiadas of Megalopolis † was Hipparch)
- Hyperbatas 226–225 BC
- Timoxenos 225–224 BC (Aratus of Sicyon held the exceptional office of strategos autokrator)
- Aratus of Sicyon XI 224–223 BC
- Timoxenos 223–222 BC (?)
- Aratus of Sicyon XII 222–221 BC
- Timoxenos 221–220 BC
- Aratus of Sicyon XIII 220–219 BC
- 219–218 BC (Mikkos of Dyme was Hypostrategos)
- Epiratos of Pharae 218–217 BC
- Aratus of Sicyon XIV 217–216 BC (Demodokos was Hipparch, Lykos of Pharae was Hypostrategos)
- Timoxenos 216–215 BC
- Aratus of Sicyon XV 215–214 BC
- Aratus of Sicyon XVI 213 BC (Aratus died before the end of the year)
- 211–210 BC
- Kykliadas of Pharae 210–209 BC (Philopoemen of Megalopolis was Hipparch)
- Philopoemen of Megalopolis I 209–208 BC
- 208–207 BC (Aristaenos of Dyme was Hipparch)
- Philopoemen of Megalopolis II 207–206 BC
- 202–201 BC (?)
- Philopoemen of Megalopolis III 201–200 BC
- Kykliadas of Pharae 200–199 BC
- Aristainos of Megalopolis 199–198 BC
- 198–197 BC
- 197–196 BC (?)
- Aristainos of Megalopolis 195–194 BC
- Philopoemen of Megalopolis IV 193–192 BC (Teison of Patras was Navarch)
- 192–191 BC
- Philopoemen of Megalopolis V 191–190 BC
- Philopoemen of Megalopolis VI 189–188 BC
- Philopoemen of Megalopolis VII 187–186 BC
- Aristainos of Megalopolis 186–185 BC
- Lycortas of Megalopolis 185–184 BC
- Archon of Aegeira 184–183 BC
- Philopoemen of Megalopolis VIII 183–182 BC † (Lycortas of Megalopolis was Hipparch)
- Lycortas of Megalopolis 182–181 BC
- 181–180 BC
- 180–179 BC
- ~ 178 BC
- ~ 176 BC
- Xenarchos 175–174 BC
- Archon of Aegeira 172–171 BC
- Archon of Aegeira 170–169 BC (Polybius was Hipparch)
- 151–150 BC
- Diaeos of Megalopolis 150–149 BC
- 149–148 BC
- Diaeos of Megalopolis 148–147 BC
- Kritolaos of Megalopolis 147–146 BC † (replaced by his predecessor)
- Diaeos of Megalopolis 146 BC (Sosikrates was Hipparch)
See also[]
- Koinon
- Achaea (disambiguation)
- Peloponnese
Notes[]
- ^ Walbank, Frank W. “Polybius and the Roman State.” Greek, Roman, and Byzantine Studies 5 (1964): 239–60.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g F.W. Walbank, "Macedonia & Greece" in F. W. Walbank, A. E. Astin, M. W. Frederiksen , R. M. Ogilvie (ed.) Cambridge Ancient History 7.1: The Hellenistic World, p. 244,
- ^ Jump up to: a b P.J. Rhodes, p. 6.
- ^ Jump up to: a b F.W. Walbank, "Macedonia & Greece" in F. W. Walbank, A. E. Astin, M. W. Frederiksen , R. M. Ogilvie (ed.) Cambridge Ancient History 7.1: The Hellenistic World, p. 246.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c F.W. Walbank, "Macedonia & Greece" in F. W. Walbank, A. E. Astin, M. W. Frederiksen , R. M. Ogilvie (ed.) Cambridge Ancient History 7.1: The Hellenistic World, pp. 251–252.
- ^ Adams 2010, p. 222; Errington 1990, p. 173
- ^ Jump up to: a b Griffith, 1935, p. 105.
- ^ SEG 15:254
- ^ IG II² 1094
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2016-02-25. Retrieved 2016-02-17.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ Jump up to: a b c F.W. Walbank, "Macedonia & Greece" in F. W. Walbank, A. E. Astin, M. W. Frederiksen , R. M. Ogilvie (ed.) Cambridge Ancient History 7.1: The Hellenistic World p. 245.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Plut. Philo. 9
- ^ Anderson, 1967, p. 105.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Walbank, 1933, p. 148.
- ^ According to Errington, the reform was probably requested or influenced by Philip V of Macedon. At the time of Philopoemen's election, Philip was in a full-scale war and could not support or finance the League. He realized that the League had to become militarily self-sufficient but also kept in the Macedonian sphere, lest the Achaeans join Macedon's rivals. Philip V probably supported Philopoemen for strategos for the year 208/07 and in doing so was able to get what he wanted (Errington 1969, p. 63).
- ^ Errington 1969, p. 64.
- ^ Walbank, 1967, p. 286.
- ^ Griffith, 1935, p. 106.
- ^ C. Michael Hogan, 2008
- ^ SEG 1.74
- ^ B. Head, Historia Numorum, p. 418.
References[]
- Adams, Winthrop Lindsay (2010). "Alexander's Successors to 221 BC". In Roisman, Joseph; Worthington, Ian (eds.). A Companion to Ancient Macedonia. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 208–224. ISBN 978-1-4051-7936-2.
- Anderson, J.K (1967), "Philopoemen's Reform of the Achaean Army", CP, Vol.62, No.2, p. 104–106
- Benner, Steve M. (2008), "Achaian League Coinage of the 3rd through 1st Centuries B.C.E.", Classical Studies no. 7, CNG Inc.
- Errington, R.M (1969), Philopoemen
- Errington, Robert Malcolm (1990). A History of Macedonia. Translated by Catherine Errington. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-06319-8.
- Errington, Malcolm (1994). A History of Macedonia. Barnes Noble. ISBN 1-56619-519-5.
- Griffith, G.T (1935), The Mercenaries of the Hellenistic World
- Hansen, M. H. and Nielsen, T. H. (2004), An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis, Københavns universitet Polis centret, Danish National Research Foundation, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-814099-1
- Head, Duncan (1982), Armies of the Macedonian and Punic Wars 359–146 BC
- Hogan, C. M. (2008), Cydonia, The Modern Antiquarian, [1]
- Larsen, J. A. O. (1968), Greek Federal States, Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp. 215–240
- Morgan, J.D. (1981), "Sellasia Revisited", AJA, Vol.85, No.3, p. 328–330
- Rhodes, P.J. (1997), The Greek City States: A Source Book, Second Edition, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-85049-0
- Sabin; Van Wees; Whitby (eds.) (2007), The Cambridge History of Greek and Roman Warfare, Volume I
- Sage, Michael M. (1996), Warfare in Ancient Greece: A Sourcebook
- Walbank, F.W (1933), Aratos of Sicyon
- Walbank, F.W (1967), A Historical Commentary on Polybius, Volume III
- Walbank; Astin; Frederiksen; Ogilvie (1984), The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume VII, Part I"
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Achaean League. |
- "Hannibal and the Punic Wars". Archived from the original on 9 April 2004.
- Caspari, Maximilian Otto Bismarck (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. 1 (11th ed.). p. 141.Encyclopædia Britannica, 1911]
- "Achaean League". Columbia Encyclopedia (6th ed.).
- Achaean League
- Former confederations
- Military history of ancient Greece
- Greek city-state federations
- States and territories established in the 3rd century BC
- 280 BC
- 280s BC establishments
- States and territories disestablished in the 2nd century BC
- Ancient Achaea
- Ancient Arcadia
- Ancient Corinthia
- Ancient Argolis
