Aesculus flava
| Aesculus flava | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Sapindaceae |
| Genus: | Aesculus |
| Species: | A. flava
|
| Binomial name | |
| Aesculus flava | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Aesculus octandra | |
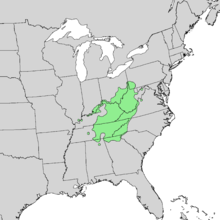
Aesculus flava, the yellow buckeye, common buckeye, or sweet buckeye, is a species of deciduous tree. It is native to the Ohio Valley and Appalachian Mountains of the Eastern United States.[2] It grows in mesophytic forest or floodplains, generally in acid to circumneutral soil, reaching a height of 20m to 48m (65 ft to 154 ft).
Description[]
The leaves are palmately compound with five (rarely seven) leaflets, 10–25 cm long and broad. The flowers are produced in panicles in spring, yellow to yellow-green, each flower 2–3 cm long with the stamens shorter than the petals (unlike the related A. glabra (Ohio buckeye), where the stamens are longer than the petals). The twigs have a faintly rank odor, but much less so than the Ohio buckeye, A. glabra. The fruit is a smooth (spineless), round or oblong capsule 5–7 cm diameter, containing 1-3 nut-like seeds, 2.5-3.5 cm diameter, brown with a whitish basal scar. The fruit is poisonous to humans but can be made edible through a leaching process.
Cultivation[]
Aesculus flava is cultivated as an ornamental tree. The tree's showy yellow flowers and good autumn color are attractive in larger gardens and in parks.[3]
This plant has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit.[4]
Uses[]
Native Americans roasted and soaked the poisonous seeds to remove the toxic element and consume them as food.[5]
Photo gallery[]

Leaf 
Bark 
Spring bud break 
Fruit
References[]
- ^ "Aesculus flava". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019. 2019. Retrieved 17 June 2019.
- ^ "Aesculus Octandra Range Map" (PDF). United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2008-03-06.
- ^ Missouri Botanical Garden horticultural treatment: Aesculus flava . accessed 1.31.2013
- ^ "RHS Plant Selector - Aesculus flava". Retrieved 23 February 2020.
- ^ Little, Elbert L. (1980). The Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Trees: Eastern Region. New York: Knopf. p. 586. ISBN 0-394-50760-6.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Aesculus flava. |
- Yellow Buckeye Diagnostic images, Morton Arboretum acc. 12-U*1
- Bioimages.vanderbilt.edu — Aesculus flava photo gallery
- Ohio Buckeye Trivia Cards tell about the buckeye, buckeye tree, buckeye history, buckeye folklore and more.
- IUCN Red List least concern species
- Aesculus
- Flora of the Appalachian Mountains
- Trees of the Eastern United States
- Trees of the Southeastern United States
- Trees of the Northeastern United States
- Natural history of the Great Smoky Mountains
- Garden plants of North America
- Ornamental trees
- Trees of the Great Lakes region (North America)




