Alpine Racer
| Alpine Racer | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Developer(s) | Namco |
| Publisher(s) | Namco |
| Series | Alpine Racer |
| Platform(s) | Arcade |
| Release | |
| Genre(s) | Racing |
| Mode(s) | Single-player |
| Arcade system | Namco System 22 |
Alpine Racer[a] is a 1995 racing arcade game developed and published by Namco. The player uses a handlebar controller to move a skier down a course situated on a snow-covered mountain, the objective being to make it to the end of the course without falling off the slope or colliding with obstacles. It features three different courses to select, alongside a standard race mode and a time-attack mode where the player must pass through gates to replenish a time limit. It ran on the Namco System 22 arcade hardware.
Gameplay[]
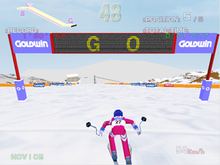
Alpine Racer is a racing video game based on the sport of alpine skiing.[2] It uses a handlebar controller for movement with rotating foot pedals to simulate real skis.[2] The player moves the on-screen skier down a course, while avoiding collision with obstacles, such as trees and rocks, or falling off the edge of the slope. Three different courses are selectable, each increasing in difficulty with the addition of fast-moving obstacles and sharper turns, alongside three difficulty levels: "Novice", "Intermediate", and "Expert".
Two gamemodes are present: "Race Mode" and "Time Trial Mode". In Race Mode, the player is pitted against five computer-controlled opponents to try and make it to the bottom of the course, the goal being to finish in first place. Finishing in first place will show the player a replay of their performance in the game. Time Trial Mode has the player going down a course solo; this mode adds a time limit that counts down as the game progresses, and will cause the game to end if it fully depletes. A second of time can be restored by passing through large gates found scattered across the course. In one of the courses, Pac-Man can be seen on a billboard sporting a Santa hat.[2]
Reception[]
| Publication | Score |
|---|---|
| AllGame | |
| Next Generation |
| Publication | Award |
|---|---|
| Amusement and Music Operators Association (AMOA) | Best New Equipment |
At the 1995 Amusement and Music Operators Association (AMOA) exposition in Illinois, Alpine Racer was given the "Best New Equipment" in the "Coin-Operated Arcade/Redemption Game" category based on executive vote.[5] In Japan, Game Machine listed it on their August 15, 1995 issue as being the most-popular dedicated arcade game at the time.[6] The game sold an estimated 2,000 arcade units worldwide, making it a highly sought-after cabinet by arcade collectors.[3][2] In 1996, Leisure Line reported it was the most-successful arcade game in Japan, topping Namco's own Tekken 2 and Sega's Virtua Cop 2.[7]
Alpine Racer was critically acclaimed. Play magazine called it a "superb" skiing simulator,[8] while Hobby Hi-Tech greatly appreciated its hardware and realism.[9] Many publications applauded the control style for being heavily unique compared to other games,[3][4][10] with Play saying that alongside its accurate portrayal of alpine skiing it made for a "brilliant" video game experience.[8] Next Generation, who gave the game a perfect score, identified the controls as being its strong point, saying that it gave a true sense of realism and was an accurate portrayal of actual skiing. Next Generation also stated that the "atypical approach and its success in execution" made Alpine Racer one of Namco's best coin-op games of the era, adding that its premise could also help attract players of both genders into arcades.[4] The graphics were also the subject of praise, with GameFan describing them as "nothing short of shocking" and Next Generation liking their attention to detail. Allgame appreciated the game's concept for making it stand out among other racing games.[3]
The Spanish magazine Ultima Generacion found the game to be far superior to many of Sega's racing games, such as Sega Rally, which they criticized for being based on preexisting ideas with little attempt towards an original concept. They commended Alpine Racer for its bizarre yet unique game idea, saying it could help attract more women and children into arcades for its appealing and interesting premise. Ultima Generacion also commended Namco's efforts at using the game to help break the common consensus at the time that arcades housed mostly violent titles unsuitable for younger players, which they said was thanks to its impressive arcade hardware and realism.[10] In an interview for Financial Times, Pac-Man creator Toru Iwatani stated that games such as Alpine Racer helped bring players into the "heart" of arcade games with unique controls instead of what he described as a "complex set of controls".[11] Video game historian Steve Kent cited Alpine Racer as a prime example of an arcade game which offered an experience that could never be recreated in the home.[12]
Legacy[]
Alpine Racer spawned a series of sequels and remakes. Alpine Racer 2 was released in 1996 for arcades, featuring three selectable skiers, new courses to race on, and a multiplayer mode made possible through linking multiple cabinets together.[13] A snowboard-themed spin-off game, Alpine Surfer, was released the same year.[14] A PlayStation 2 sequel was released in 2002, Alpine Racer 3, adding new gamemodes, selectable characters and other additions to the core gameplay, in addition of including Klonoa as a playable guest character.[15][16] A sequel for Japanese mobile phones, Alpine Racer EX, was released in 2007, followed by a "widescreen" version the same year.[17] Namco Networks produced an iOS remake of the original Alpine Racer in 2009,[18] which was subsequently ported to the Zeebo the same year.[19] A second arcade sequel, Super Alpine Racer, was released by Namco Bandai Games in 2014.[20]
In 2004, Harvard University sleep scientist Robert Stickgold used Tetris and Alpine Racer to study the relationship between learning and sleep.[21] He determined that patients who played Alpine Racer before sleeping, including those who suffered from anterograde amnesia, dreamed of skiing.[21]
Notes[]
References[]
- ^ Akagi, Masumi (13 October 2006). ナムコ Namco; Namco America; A. アーケードTVゲームリスト 国内•海外編 (1971-2005) (in Japanese) (1st ed.). Amusement News Agency. p. 53, 127, 145. ISBN 978-4-9902512-1-5.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Alpine Racer - Videogame by Namco". Killer List of Videogames. Archived from the original on 25 March 2019. Retrieved 28 December 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Alan Weiss, Brett (1998). "Alpine Racer - Review". Allgame. All Media. Archived from the original on 14 November 2014. Retrieved 27 December 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Hot Dog!". Next Generation. No. 10. Imagine Media. October 1995. p. 131.
- ^ "US Arcades Get Ready for War". Next Generation. No. 12. Imagine Media. December 1995. p. 24.
- ^ "Game Machine's Best Hit Games 25 - 完成品夕イプのTVゲーム機 (Dedicated Videos)". Game Machine (in Japanese). No. 501. Amusement Press, Inc. 15 August 1995. p. 21.
- ^ "Test Report - Japanese Arcade Games". Leisure & Allied Industries. Leisure Line. March 1996. p. 58. Retrieved 27 December 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Alpine Racer". Paragon Publishing. Play. p. 75. Retrieved 16 October 2019.
- ^ Barral, Etienne (July 1995). "Historias Alternativas" (in Spanish) (3). Hobby Press. Hobby Hi-Tech. pp. 34–35. Retrieved 27 December 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Arcade - Alpine Racer" (10). Ultima Generacion. January 1996. pp. 28–30. Retrieved 27 December 2019.
- ^ Lewis, Leo (10 June 2015). "Toru Iwatani: Pac-Man and the real life of games design". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 27 December 2019. Retrieved 27 December 2019.
- ^ Boyer, Crispin (February 1998). "EGM Takes a Time-Tripping Look at the Evolution of Arcades". Electronic Gaming Monthly. No. 103. Ziff Davis. p. 92.
- ^ "Alpine Racer 2". Next Generation. No. 28. Imagine Media. April 1997. p. 132.
- ^ "Finals". Next Generation. No. 21. Imagine Media. September 1996. p. 162, 164.
- ^ IGN Staff (2 January 2002). "Will Alpine Racer 3 Come to the US?". IGN. Archived from the original on 28 December 2019. Retrieved 28 December 2019.
- ^ Saeki, Kenji (28 March 2003). "気軽に遊べてダイナミックな滑りを楽しめる 「アルペンレーサー3」". GAME Watch. Archived from the original on 6 June 2009. Retrieved 28 March 2003.
- ^ "バンダイナムコゲームス、EZアプリ「アルペンレーサーEX」「パニクルパネクル」を配信". ITmedia. 25 December 2008. Archived from the original on 28 December 2019. Retrieved 28 December 2019.
- ^ Patterson, Blake (27 February 2009). "Namco's SSX-Unlike 'Alpine Racer' Disappoints". TouchArcade. Archived from the original on 2 November 2019. Retrieved 28 December 2019.
- ^ "Zeebo console launches in Brazil, racks up a few publishers". Tech Crunch. 23 March 2009. Archived from the original on 31 August 2017. Retrieved 28 December 2019.
- ^ Inamoto, Tetsuya (14 February 2014). "[JAEPO2014]雪原を時速200kmで突っ走れ! 最大8人の体感スキーレース「スーパーアルペンレーサー」プレイレポート【ムービー追加】". 4Gamer.net. Aetas. Archived from the original on 26 January 2015. Retrieved 28 December 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Stickgold, Rober (2010). "Cognitive Replay of Visuomotor Learning at Sleep Onset: Temporal Dynamics and Relationship to Task Performance". Sleep. US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health. 33 (1): 59–68. doi:10.1093/sleep/33.1.59. PMC 2802248. PMID 20120621.
External links[]
- 1995 video games
- Arcade video games
- Bandai Namco Entertainment franchises
- Namco arcade games
- Namco System 22 games
- Namco games
- Skiing video games
- Video games developed in Japan
