Anti-rolling gyro
Ship stabilizing gyroscopes are a technology developed in the 19th century and early 20th century and used to stabilize roll motions in ocean-going ships. It lost favor in this application to hydrodynamic roll stabilizer fins because of reduced cost and weight. However, since the 1990s, there is renewed interest in the device for low-speed roll stabilization of vessels (Seakeeper, Quick MC2, etc.). Unlike traditional fins, the gyroscope does not rely on the forward speed of the ship to generate a roll stabilizing moment and therefore can stabilize motor yachts while at anchor. However, the latest generation of "zero speed" fins stabilizers (CMC, Humphree, etc.) can stabilize yachts while at anchor thanks to their eccentricity with respect of the shaft.
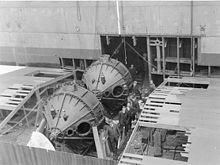
The World War I transport USS Henderson, completed in 1917, was the first large ship with gyro stabilizers. It had two 25-ton, 9-foot (2.7 m) diameter flywheels mounted near the center of the ship, spun at 1100 rpm by 75 hp (56 kW) AC motors. The gyroscopes' cases were mounted on vertical bearings. When a small sensor gyroscope on the bridge sensed a roll, a servomotor would rotate the gyros about a vertical axis in a direction so their precession would counteract the roll. In tests this system was able to reduce roll to 3 degrees in the roughest seas.
One of the most famous ships to first use an anti-rolling gyro was the Italian passenger liner SS Conte di Savoia, which first sailed in November 1932. It had three flywheels which were 13 feet in diameter and weighed 108 tons.[1]
The ship gyroscopic stabilizer typically operates by constraining the gyroscope's roll axis and allowing it to "precess" either in the pitch or the yaw axes. Allowing it to precess as the ship rolls causes its spinning rotor to generate a counteracting roll stabilizing moment to that generated by the waves on the ship's hull. Its ability to effectively do this is dependent on a range of factors that include its size, weight, and angular momentum. It is also affected by the roll period of the ship. Effective ship installations require rotors having a weight of approximately 3% to 5% of a vessel's displacement.
Unlike hydrodynamic roll stabilizing fins, the ship gyroscopic stabilizer can only produce a limited roll stabilizing moment that may be exceeded as the wave height increases. Otherwise, it is not unusual for the manufacturer to recommend that the unit not be used at sea in large waves.
Instead of providing stabilization, the same technology can be used in an active way to control the orientation, as control moment gyroscopes do in spacecraft, to provide attitude control.
See also[]
References[]
- ^ "Italian Liner To Defy The Waves" Popular Mechanics, April 1931.
External links[]
- Gyroscopes
- Watercraft components