Arabinose

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Arabinose
| |
| Other names
Pectinose
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.182 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| Properties[1] | |
| C5H10O5 | |
| Molar mass | 150.13 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals as prisms or needles |
| Density | 1.585 g/cm3 (20 ºC) |
| Melting point | 164 to 165 °C (327 to 329 °F; 437 to 438 K) |
| 834 g/1 L (25 °C (77 °F)) | |
| -85.70·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 
1
1
0 |
| Related compounds | |
Related aldopentoses
|
Ribose Xylose Lyxose |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Arabinose is an aldopentose – a monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms, and including an aldehyde (CHO) functional group.
For biosynthetic reasons, most saccharides are almost always more abundant in nature as the "D"-form, or structurally analogous to D-glyceraldehyde.[note 1] However, L-arabinose is in fact more common than D-arabinose in nature and is found in nature as a component of biopolymers such as hemicellulose and pectin.[2]
The L-arabinose operon, also known as the araBAD operon, has been the subject of much biomolecular research. The operon directs the catabolism of arabinose in E. coli, and it is dynamically activated in the presence of arabinose and the absence of glucose.[3]
A classic method for the organic synthesis of arabinose from glucose is the Wohl degradation.[4]
D-Arabinose 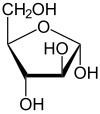
α-D-Arabinofuranose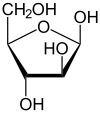
β-D-Arabinofuranose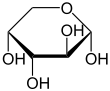
α-D-Arabinopyranose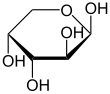
β-D-Arabinopyranose
Etymology[]
Arabinose gets its name from gum arabic, from which it was first isolated.[5]
Use in biology[]
In synthetic biology, arabinose is often used as a one-way or reversible switch for protein expression under the Pbad promoter in E. coli. This on-switch can be negated by the presence of glucose or reversed off by the addition of glucose in the culture medium which is a form of catabolite repression.[6]
Some organic acid tests check for the presence of arabinose, which may indicate overgrowth of intestinal yeast such as Candida albicans or other yeast/fungus species.[citation needed]
Use in foods[]
Originally commercialized as a sweetener, arabinose is an inhibitor of sucrase, the enzyme that breaks down sucrose into glucose and fructose in the small intestine.[7]
See also[]
Notes[]
- ^ The D/L nomenclature does not refer to the molecule's optical rotation properties but to its structural analogy to glyceraldehyde.
References[]
- ^ Weast, Robert C., ed. (1981). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (62nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. C-110. ISBN 0-8493-0462-8.
- ^ Holtzapple, M.T. (2003). HEMICELLULOSES. Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition. pp. 3060–3071. doi:10.1016/B0-12-227055-X/00589-7. ISBN 9780122270550.
- ^ Watson, James (2003). Molecular Biology of the Gene. p. 503.
- ^ Braun, Géza (1940). "D-Arabinose". Organic Syntheses. 20: 14.; Collective Volume, 3, p. 101
- ^ Merriam Webster Dictionary
- ^ Guzman LM, Belin D, Carson MJ, Beckwith J (July 1995). "Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose PBAD promoter". J. Bacteriol. 177 (14): 4121–30. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.629.9409. doi:10.1128/jb.177.14.4121-4130.1995. PMC 177145. PMID 7608087.
- ^ Krog-Mikkelsen, Inger; Hels, Ole; Tetens, Inge; Holst, Jens Juul; Andersen, Jens Rikardt; Bukhave, Klaus (2011-08-01). "The effects of L-arabinose on intestinal sucrase activity: dose-response studies in vitro and in humans". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 94 (2): 472–478. doi:10.3945/ajcn.111.014225. ISSN 1938-3207. PMID 21677059.
- Aldopentoses
- Glycerols



