Arecaidine
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
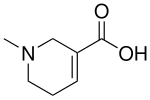
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Methylguvacine; Arecaine; N-Methylguvacine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 141.170 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Arecaidine is a bio-active alkaloid in areca nuts.[1] It is a competitive GABA uptake inhibitor.[2] Lime is said to hydrolyse arecoline to arecaidine[2]
References[]
- ^ Voigt, V; Laug, L; Zebisch, K; Thondorf, I; Markwardt, F; Brandsch, M (2013). "Transport of the areca nut alkaloid arecaidine by the human proton-coupled amino acid transporter 1 (hPAT1)". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 65 (4): 582–90. doi:10.1111/jphp.12006. PMID 23488788. S2CID 27577546.
- ^ a b Johnston, G. A. R.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, P.; Stephanson, A. (1975). "Betel nut constituents as inhibitors of γ-aminobutyric acid uptake". Nature. 258 (5536): 627–628. Bibcode:1975Natur.258..627J. doi:10.1038/258627a0. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 1207742. S2CID 4147760.
Categories:
- Alkaloids
- Carboxylic acids
- GABA reuptake inhibitors