Armadillidium depressum
| Armadillidium depressum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Armadillidium depressum specimen photographed in Oxford, UK. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Crustacea |
| Class: | Malacostraca |
| Superorder: | Peracarida |
| Order: | Isopoda |
| Suborder: | Oniscidea |
| Family: | Armadillidiidae |
| Genus: | Armadillidium |
| Species: | A. depressum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Armadillidium depressum | |
| |
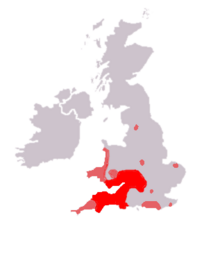
| Range[2][3] | |
| Synonyms [4] | |
|
Armadillidium gerstaeckeri Armadillidium virescens | |
Armadillidium depressum, the southern pill woodlouse[5] is a large, relatively common British species of woodlouse characterized by its "splayed" appearance.
Description[]
Armadillidium depressum may reach a length of 20 millimetres (0.71 in) compared to 18 millimetres for Armadillidium vulgare, and is capable of rolling into a ball when disturbed. Like Armadillidium nasatum, it can be distinguished from Armadillidium vulgare by the gap it leaves when enrolled, instead of completely enclosing.[2][6] Another distinguishing feature is that its pleon curve outwards, causing a splayed appearance. Otherwise, the appearance of A. depressum is very similar to A. vulgare in dark grey to black color.[2][5]
Armadillidium depressum maximum length is 20 millimetres, compared to A. vulgare 18 millimetres.[2]
Ecology[]
Like other woodlice, Armadillidium depressum feeds on dead plant matter, and lives for 3 years.[5] A. depressum can be seen all year long.[5]
Distribution[]
The majority of specimens of Armadillidium depressum are concentrated in southwest Britain, near the English channel, but small populations also occur in various towns scattered throughout England.[2] It is a synanthropic species, living on walls and under stones in towns and old houses.[2][5]
References[]
- ^ "Armadillidium depressum Brandt, 1833". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved August 2, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f Armadillidium depressum Brandt, 1833
- ^ http://www.nhm.ac.uk/nature-online/life/other-invertebrates/walking-with-woodlice/results/old/armadillidium_depressum.html
- ^ Helmut Schmalfuss (2003). "World catalog of terrestrial isopods (Isopoda: Oniscidea) — revised and updated version" (PDF). Stuttgarter Beiträge zur Naturkunde, Serie A. 654: 341 pp. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-02-24. Retrieved 2015-08-02.
- ^ a b c d e Southern Pill Woodlouse
- ^ http://www.eakringbirds.com/eakringbirds5/isopodinfocusarmadillidiumdepressum.htm
- Woodlice of Europe
- Crustaceans described in 1833
- Isopod stubs