Armed Forces of South Russia
This article includes a list of references, related reading or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (February 2013) |
| Armed Forces of South Russia | |
|---|---|
| Вооружённые силы Юга России | |
 Most territory controlled by South Russian forces as of October 1919 | |
| Active | 8 January 1919 – April 1920 |
| Country | South Russia |
| Allegiance | |
| Size | 85,000 (January 1919) 160,000 (July 1919) 270,000 (October 1919) |
| Engagements | |
| Commanders | |
| Commander-in-Chief | Anton Denikin |
The Armed Forces of South Russia (AFSR) (Russian: Вооружённые силы Юга России, romanized: Vooruzhyonniye sily Yuga Rossii, VSYuR) were the unified military forces of the White movement in southern Russia between 1919 and 1920.
The Armed Forces of South Russia were formed on 8 January 1919, incorporating the Volunteer Army (which was renamed the Caucasian Volunteer Army). In addition, the AFSR included the Don Army, the Crimean-Azov Army, the Forces of Northern Caucasus and the Turkestan Army.
In January 1919, it numbered 51,000 Infantry, 34,000 Cavalry, 204 Field guns, 682 machine guns and 6 armoured trains. By July 1919 it had grown to 104,000 Infantry, 56,000 Cavalry, 600 Field guns, 1,500 machine guns, 19 aircraft, 34 armoured trains, 1 Cruiser, 5 Destroyers, 4 Submarines and 20 Gunboats.[citation needed] By October, after heavy losses and the transfer of units to other armies, the armies' strength fell drastically.[dubious ]
On 22 May 1919, the Caucasian Volunteer Army was split into two formations: the Caucasus Army, and the Volunteer Army. The Caucasus Army disbanded on January 29, 1920 and was replaced by the short-lived Kuban Army. Troops of the Kuban Army ended up surrendering by April 18–20, 1920 to the Red Army. The Volunteer Army continued to exist from May 22, 1919 until March 26/27, 1920, when the remaining troops were evacuated from Novorossiysk to Crimea. Most then merged there with Wrangel's forces.
In early April 1920, Anton Denikin, commander-in-chief of the AFSR, delegated all authority to Pyotr Wrangel, who took command of the so-called Russian Army, which included all remaining units of the AFSR after its defeat in Northern Caucasus.
Order of Battle of the AFSR, early 1919[]
![]() Volunteer Army (known as Caucasian Volunteer Army from January 23 – May 22, 1919), commanded by Gen. Anton Denikin (April 1918 – April 1920)
Volunteer Army (known as Caucasian Volunteer Army from January 23 – May 22, 1919), commanded by Gen. Anton Denikin (April 1918 – April 1920)
- 1st Army Corps (Gen. Kutepov)
- 2nd Army Corps (Gen. Mikhail Promtov)
- 5th Cavalry Corps (Gen. )
- 3rd Kuban Cavalry Corps (Lt. Gen. Shkuro)
- Kyiv Army Group (Gen. Bredov)
![]() Caucasus Army (split from Caucasian Volunteer Army on May 22, 1919), commanded by Lt. Gen. Pyotr Wrangel (May 21 – December 8, 1919) and Lt. Gen. Viktor Pokrovsky (December 9, 1919 – February 8, 1920)
Caucasus Army (split from Caucasian Volunteer Army on May 22, 1919), commanded by Lt. Gen. Pyotr Wrangel (May 21 – December 8, 1919) and Lt. Gen. Viktor Pokrovsky (December 9, 1919 – February 8, 1920)
- 1st Kuban Corps (Lt. Gen. Viktor Pokrovsky)
- 2nd Kuban Corps (Gen. Ulaguy, later Gen. Nahumenko)
- 4th Kuban Corps (Gen. Shatilov, later Gen. Toporkov)
![]() Don Army (joined AFSR on 23 February 1919), commanded by Gen. Vladimir Sidorin (February 1919 and April 1920)
Don Army (joined AFSR on 23 February 1919), commanded by Gen. Vladimir Sidorin (February 1919 and April 1920)
- Northern Group (Starshina Semiletov)
- Southern Group (Gen. S. Denisov)
- Trans-Don (Zadonskaya) Group (Col. Bykadorov)
Turkestan Army (formed on 22 January 1919), commanded by Ippolit Savitsky (April – July 1919), Aleksander Borovsky (July – October 1919) and Boris Kazanovich (October 1919 – February 1920).
- Transcaspian Composite Inf. Division (Maj. Gen. Lazarev)
- Turkestan Rifle Division (Maj. Gen. Litvinov)
- Cavalry Division (Maj. Gen. Oraz-Khan Sedar)
Gallery[]
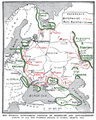
Military map of March 1919 after the Armistice of Mudros

Volunteer Army recruitment poster saying "Why are you not in the army?"

Volunteer Army soldiers and officers next to a train in January 1918

Volunteer Army Mark V tank named "General Drozdovsky" in 1919

Volunteer Army armoured train "United Russia" on its way towards Tsaritsyn, June 1919

Local citizens welcome Denikin and officers to Tsaritsyn on 1 July 1919

Denikin and Wrangel during an AFSR parade in Tsaritsyn in July 1919

Don Army troops and Major General Vladimir Sidorin (center) with a Mark V tank in 1919

Don Army Austin Armoured Car named "Ataman Bogayevsky" in 1919

AFSR 2nd Infantry Division soldiers in Sochi, 1919
See also[]
- Don Republic
- Kuban People's Republic
- South Russia (1919–1920)
- South Russian Government (Denikin)
- Government of South Russia (Wrangel)
Sources[]
- Н.Е.Какурин, И.И.Вацетис "Гражданская война. 1918-1921" (N.E.Kakurin, I.I.Vacietis "Civil War. 1918-1921") - Sankt-Peterburg, "Polygon" Publishing House, 2002. ISBN 5-89173-150-9
- Military history of Russia
- Military units and formations of White Russia (Russian Civil War)
- Counter-revolutionaries










