Asian short-toed lark
| Asian short-toed lark | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Alaudidae |
| Genus: | Alaudala |
| Species: | A. cheleensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Alaudala cheleensis R. Swinhoe, 1871
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
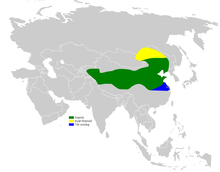
The Asian short-toed lark (Alaudala cheleensis) is a lark in the family Alaudidae. The species was first described by Robert Swinhoe in 1871. It is found from south-central to eastern Asia.
Taxonomy and systematics[]
Formerly or presently, some authorities have considered the Asian short-toed lark to belong to the genus Calandrella or to be a subspecies of the lesser short-toed lark. Alternate names for the Asian short-toed lark include the Asiatic short-toed lark, eastern short-toed lark (a name also used by the steppe greater short-toed lark), grey short-toed lark, Mongolian short-toed lark (not to be confused with the species of the same name, Calandrella dukhunensis), salined lark and salt-marsh lark.
A molecular phylogenetic study published in 2020 compared the nuclear and mitochondrial DNA from the sand, Asian short-toed, and Mediterranean short-toed larks. The study analysed samples from 130 individuals that represented 16 of the 18 recognised subspecies. The resulting phylogenetic tree indicated that neither the Asian short-toed lark, nor the lesser short-toed lark as currently defined are monophyletic. Most of the subspecies were also found to be non-monophyletic. The authors refrained from proposing a revised taxonomy until additional studies had been completed comparing the vocalizations, sexual behaviour and ecology.[1]
Subspecies[]
Six subspecies are recognized:[2]
- A. c. leucophaea - (Severtsov, 1873): Originally described as a separate species in the genus Calandrella. Found from Kazakhstan to Turkmenistan
- A. c. seebohmi - Sharpe, 1890: Originally described as a separate species. Found in north-western China
- A. c. tuvinica - (Stepanyan, 1975): Found in north-western Mongolia and southern Russia
- A. c. cheleensis - R. Swinhoe, 1871: Found in south-central Siberia, north-eastern Mongolia and north-eastern China
- A. c. kukunoorensis - Przewalski, 1876: Found in west-central China
- A. c. beicki - (Meise, 1933): Found in southern Mongolia and north-central China
References[]
- ^ Ghorbani, F.; Aliabadian, M.; Zhang, R.; Irestedt, M.; Hao, Y.; Sundev, G.; Lei, F.; Ma, M.; Olsson, U.; Alström, P. (2020). "Densely sampled phylogenetic analyses of the Lesser Short-toed Lark (Alaudala rufescens) — Sand Lark (A. raytal) species complex (Aves, Passeriformes) reveal cryptic diversity". Zoologica Scripta. 49 (4): 427–439. doi:10.1111/zsc.12422.
- ^ Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (2020). "Nicators, reedling, larks". IOC World Bird List Version 10.1. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Alaudala cheleensis. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Alaudala cheleensis. |
- Alaudala
- Birds of India
- Birds of Pakistan
- Birds described in 1871
- Alaudidae stubs