Bahrain International Circuit
  | |
| Location | Sakhir, Bahrain |
|---|---|
| Time zone | UTC+03:00 |
| Coordinates | 26°1′57″N 50°30′38″E / 26.03250°N 50.51056°ECoordinates: 26°1′57″N 50°30′38″E / 26.03250°N 50.51056°E |
| Capacity | 70,000 |
| FIA Grade | 1 (5 layouts) |
| Broke ground | December 2002 |
| Opened | 17 March 2004 |
| Construction cost | 56.2 million Dinars ($150 million) |
| Architect | Hermann Tilke |
| Major events | Current: Formula One Bahrain Grand Prix (2004–2010, 2012–present) FIA WEC 6 Hours of Bahrain (2012–2017, 2019–present) FIA F2 (2017–present) FIA F3 (2022) Former: World Series Formula V8 3.5 (2017) GP2 (2005, 2007, 2012–2015) GP2 Asia (2008–2010) GP3 (2015) V8 Supercars Desert 400 (2006–2008, 2010) FIA GT (2005) TCR International Series (2016–2017) (2005-2022) |
| Grand Prix Circuit (2005–present) | |
| Length | 5.412 km (3.363 mi) |
| Turns | 15 |
| Race lap record | 1:31.447[1] ( |
| Outer Circuit (2005–present) | |
| Length | 3.543 km (2.202 mi) |
| Turns | 11 |
| Race lap record | 0:55.404 ( |
| Endurance Circuit (2005–present) | |
| Length | 6.299 km (3.914 mi) |
| Turns | 23 |
| Race lap record | 1:58.287 ( |
| Paddock Circuit (2004–present) | |
| Length | 3.823 km (2.375 mi) |
| Turns | 10 |
| Race lap record | 1:24.910 ( |
| Oasis / Inner Circuit (2004–present) | |
| Length | 2.550 km (1.584 mi) |
| Turns | 8 |
| Race lap record | 1:03.819 ( |
| Original Grand Prix Circuit (2004) | |
| Length | 5.417 km (3.366 mi) |
| Turns | 15 |
| Race lap record | 1:30.252[1] ( |
The Bahrain International Circuit (Arabic: حلبة البحرين الدولية, romanized: Ḥalba al-Baḥrayn ad-Dawliyya) is a 5.412 km (3.363 mi) motorsport venue opened in 2004 and used for drag racing, GP2 Series (now FIA Formula 2), and the annual Formula One Bahrain Grand Prix. The 2004 Grand Prix was the first held in the Middle East. Beginning in 2006, Australian V8 Supercars raced at the BIC, with the event known as the Desert 400. However, the V8 Supercars did not return for the 2011 V8 Supercar season. 24 Hour endurance races are also hosted at BIC.[2] The circuit has a FIA Grade 1 license.[3] The circuit also has multiple layouts.
History[]

The construction of the Bahrain circuit was a national objective for Bahrain, initiated by the Crown Prince, Shaikh Salman bin Hamad Al Khalifa. The Crown Prince is the Honorary President of the Bahrain Motor Federation. TRL was asked to build the circuit, headed by Patrick Brogan.
Race organizers were worried that the circuit would not be complete in time for the 2004 Bahrain Grand Prix and attempted to cancel the event; however, Formula One supremo Bernie Ecclestone refused this request. In the end, the circuit was not quite fully complete, but was good enough for the grand prix to go ahead.[4]
After the 2004 race and ahead of the 2005 race the track was realigned at turn four, decreasing the circuit's overall length by 5 metres in total.[1]
In 2007 the circuit became the first Grand Prix circuit to be awarded the distinguished FIA Institute Centre of Excellence award, given for excellent safety, race marshal, and medical facilities, and for the high standards of technology required to maintain these.[5]
At the 2009 Grand Prix, BIC announced a collaboration with @bahrain to develop land next to the circuit. @bahrain is part of the Mumtalakat group of companies. @bahrain will dedicate more than 1 million square meters of business, entertainment and educational space with a value in excess of US$2bn (BHD 850million), making it one of the largest investment projects to take place in Bahrain in the past five years.[6]
In 2011 the circuit was scheduled to be the first GP of the season. However, due to civil unrest in the country the race had to be cancelled in March 2011. On 4 June the FIA announced that the race would be scheduled for 30 October, the original slot for the inaugural Indian Grand Prix, which would be shifted to a season-closing date on 11 December.[7] However, two days later following concerns from teams and other officials, the race organizers officially cancelled the race, choosing to focus their attention on the 2012 running. The 2012 Formula One calendar had the race scheduled for 22 April, the fourth of the season.
Construction and design[]
The circuit was designed by German architect Hermann Tilke, the same architect who designed the Sepang International Circuit in Malaysia. The main contractor for the project was Cebarco-WCT.[8] The circuit cost approximately 56.2 million Bahraini Dinars[9] (US$150 million) to construct.[10] It has six separate tracks, including a test oval and a drag strip.[10]
The circuit posed a unique problem. Positioned in the middle of a desert, there were worries that sand would blow onto the circuit and disrupt the race. However, organizers were able to keep the sand off the track by spraying an adhesive on the sand around the track.[11]
The surface of the track is made of graywacke aggregate, shipped to Bahrain from Bayston Hill quarry in Shropshire, England. The surface material is highly acclaimed by circuit bosses and Formula 1 drivers for the high level of grip it offers. The same aggregate material is used at the Yas Marina Circuit, venue of the Abu Dhabi Grand Prix.[12]
Shortly after the Formula One February 2014 testing, the first corner of the track was renamed after seven-time champion German driver Michael Schumacher in honour of his achievements and also in support after he suffered an almost fatal skiing accident late December 2013.[13]
Layouts[]

"Grand Prix Circuit". Used in F1 in 2004–2009, and since 2012

"Endurance Circuit". Used in F1 in 2010
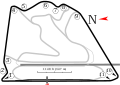
"Outer Circuit". Used in F1 in 2020 at the Sakhir Grand Prix[14]

"Paddock Circuit"

"Oasis / Inner Circuit"

A flat oval
A lap in a Formula One car[]
The DRS zone is on the pit straight at the Bahrain Grand Prix (starting 2012), so turn 1 ("Michael Schumacher turn") is the prime overtaking opportunity. The corner itself is incredibly tight; a typical F1 car must brake approximately 100 m (110 yd) before the corner and shift right down to gear one. The width of the track further adds to the overtaking possibilities.[15] Turns 2 and 3 are flat out and gaining a good exit can set up an overtaking opportunity into turn 4. The straight leading to turn 4 is very long with a DRS zone, and the track at the corner itself is incredibly wide, at about thirty metres.[15] Turns 5, 6 and 7 make up a high-speed left-right-left "S" section that leads into turn 8, a right-hand hairpin where taking a wide line can avoid the bump on the apex which unsettles the car.[16] Turns 9 and 10 are very challenging as they are two blind left-handers where cars must brake, downshift and turn simultaneously – they go from 205 km/h (127 mph) in gear 5 down to 63 km/h (39 mph) in gear 1 whilst trying to avoid locking up their inside front tyres.[15] The back straight leads down into turns 11, 12 and 13, a medium-speed complex of corners. Turn 11 is a fourth-gear left hander that leads immediately into the flat-out right hander of 12, then the third gear right-hander of turn 13 which requires a good exit to gain speed down the following straight. It is worth braking quite early for turn 14 to gain speed down the main straight.[16] If you brake about 100 m (110 yd) before the apex then it is easy to keep it tidy through the slow right hander and you can also put the power down early, and gain speed all the way through turn 15 and the main straight (which is the DRS zone).
The lap record (which only accounts for laps set in a race) on the current layout of the Grand Prix circuit was set in 2005 by Pedro de la Rosa at 1:31.447,[1] in what was the only fastest lap in his 104-race career.[17] Michael Schumacher set a faster time of 1:30.252 at the 2004 edition of the race, but alterations to turn 4 of the track meant that it was counted as a different layout from 2005 onwards.[1] The fastest time ever set at the track was produced by Lewis Hamilton during qualifying for the 2020 edition at 1:27.264, beating the previous record by Charles Leclerc, set during qualifying for the 2019 edition (1:27.866).[18]
Facilities[]
| Track[10] | Distance[10] | Grade[19] |
|---|---|---|
| Grand Prix track | 5.412 km (3.363 mi) | 1 |
| Oasis / Inner track | 2.554 km (1.587 mi) | 1 |
| Outer track | 3.543 km (2.202 mi) | 1 |
| Paddock Circuit | 3.823 km (2.376 mi) | 1 |
| Drag Strip | 1.2 km (0.7 mi) | n/a |
| Oval track | 2.500 km (1.553 mi) | n/a |
| Endurance Circuit | 6.299 km (3.914 mi) | 1 |
Formula One Grand Prix[]

The first Bahrain Grand Prix took place on 4 April 2004, making history as the first Formula One Grand Prix to be held in the Middle East. Bahrain fought off fierce competition from elsewhere in the region to stage the race, with Egypt, Lebanon and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) all hoping for the prestige of hosting a Formula One Grand Prix (the UAE would host a Grand Prix from 2009).
The Bahrain Grand Prix is usually the third race on the Formula One calendar, apart from the 2006 season, when Bahrain swapped places with the traditional opener, the Australian Grand Prix, which was pushed back to avoid a clash with the Commonwealth Games. In 2009, Bahrain was moved to the fourth race. For the 2010 season Bahrain was again the pre-season testing and season opener and Formula One cars drove the full 6.299 km (3.914 mi) "Endurance Circuit" to celebrate F1's 'diamond jubilee'. For 2011 however F1 was set to return to racing on the original layout used between 2004 and 2009.[20] The race was postponed and finally cancelled due to protests in the country but F1 returned to the track for the 2012 Bahrain Grand Prix. 2014 saw the track host its first ever Grand Prix under lights, as the race was scheduled as a night race to celebrate the tenth year of Formula 1 at the circuit. Subsequent editions of the race have also been held at night. In 2020 the circuit hosted two Grands Prix, the Bahrain and Sakhir Grands Prix, after the calendar was revised following the COVID-19 pandemic with the second using an alternative layout.[21]
Series hosted[]
The Bahrain International Circuit hosts a number of high-profile series, including the FIA Formula One World Championship, the FIA World Endurance Championship, the FIA Formula 2 Championship, FIA Formula 3 Championship, and Porsche Sprint Challenge Middle East.
In the past the circuit has hosted the FIA GT Championship, Speedcar Series, Australian V8 Supercars, GP2 Asia Series, and a one-off Bahrain Superprix involving Formula Three cars, following on from the collapsed Korea Super Prix. The first ever Formula BMW World Final took place in Bahrain.
Events[]
- Current
- January: Bahrain International Circuit 2000cc Challenge
- February: Bahrain International Circuit 2000cc Challenge
- March: Formula One Bahrain Grand Prix, FIA Formula 2 Championship Sakhir Formula 2 round, FIA Formula 3 Championship, Porsche Sprint Challenge Middle East
- April: Bahrain International Circuit 2000cc Challenge
- November: FIA World Endurance Championship 8 Hours of Bahrain, Porsche Sprint Challenge Middle East
- Former
- Bahrain Superprix (2004)
- Ferrari Challenge Asia-Pacific (2020)
- Ferrari Challenge Europe (2019)
- FIA GT Championship Bahrain Supercar 500 (2005)
- FIA GT Nations Cup (2018)
- Formula BMW World Final (2005)
- Formula One Sakhir Grand Prix (2020)
- Gulf 12 Hours (2021)
- GP2 Series Bahrain GP2 round (2005, 2007, 2012–2015)
- GP2 Asia Series (2008–2010)
- GP3 Series (2015)
- MRF Challenge Formula 2000 Championship (2013–2019)
- Porsche Supercup (2006–2010, 2012)
- Speedcar Series (2008–2009)
- TCR International Series (2016–2017)
- TCR Middle East Series (2017–2018)
- V8 Supercars Desert 400 (2006–2008, 2010)
- World Series Formula V8 3.5 (2017)
Lap records[]
The official fastest race lap records at the Bahrain International Circuit are listed as:
| Category | Driver | Vehicle | Time | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grand Prix Circuit: 5.412 km (2005–present) | ||||
| F1 | McLaren MP4-20 | 1:31.447 | 3 April 2005[22] | |
| LMP1 | Audi R18 | 1:41.511 | 19 November 2016[23] | |
| GP2 | Dallara GP2/11 | 1:43.166 | 20 November 2015[24] | |
| FIA F2 | Dallara F2 2018 | 1:43.848 | 19 March 2022 | |
| Formula V8 | Dallara T12 | 1:48.216 | 18 November 2017[25] | |
| GP3 | Dallara GP3/13 | 1:48.228 | 21 November 2015[26] | |
| LMP2 | Oreca 07 | 1:48.579 | 14 December 2019[23] | |
| LMH | Toyota GR010 Hybrid | 1:48.926 | 30 October 2021[27] | |
| FIA F3 | Dallara F3 2019 | 1:51.231 | 19 March 2022 | |
| GT1 | Maserati MC12 GT1 | 1:56.478 | 25 November 2005[28] | |
| LM GTE | Ferrari 488 GTE Evo | 1:56.942 | 14 December 2019[23] | |
| GT3 | McLaren 720S GT3 | 2:00.675 | 9 January 2021 | |
| V8 Supercars | Ford FG Falcon | 2:06.9097 | 27 February 2010[29] | |
| TCR International | Honda Civic Type R TCR (FK2) | 2:12.602 | 2 April 2016 | |
| Outer Circuit: 3.543 km (2005–present) | ||||
| F1 | Mercedes-AMG F1 W11 EQ Performance | 0:55.404 | 6 December 2020 | |
| FIA F2 | Dallara F2 2018 | 1:04.087 | 5 December 2020 | |
| Endurance Circuit: 6.299 km (2005–present) | ||||
| F1 | Ferrari F10 | 1:58.287 | 14 March 2010 | |
| GP2 Asia | Dallara GP2/08 | 2:09.823 | 13 March 2010 | |
| Paddock Circuit: 3.823 km (2004–present) | ||||
| V8 Supercars | Ford BA Falcon | 1:24.910 | 24 November 2006[30] | |
| Grand Prix Circuit: 5.417 km (2004) | ||||
| F1 | Ferrari F2004 | 1:30.252 | 4 April 2004 | |
See also[]
References[]
- ^ a b c d e "Race Preview". FIA Communications Department. Archived from the original on 2 April 2016. Retrieved 3 April 2016.
- ^ "24 hour Race of Bahrain 15–16 December 2006". bahraingp.com.bh. n.d. Retrieved 11 September 2009.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "LIST OF FIA LICENSED CIRCUITS" (PDF). FIA. 6 February 2015. Retrieved 28 May 2015.
- ^ "Bahrain 'tried to stop GP'". BBC News. 25 March 2004. Retrieved 13 April 2007.
- ^ "Bahrain named Centre of Excellence by FIA". Formula1.com. 13 April 2007. Archived from the original on 15 April 2007. Retrieved 13 April 2007.
- ^ "Jobs 'for generations to come'". gulf-daily-news.com. 26 April 2009. Retrieved 27 August 2009.
- ^ "F1plus: Bahrain Grand Prix reinstated; race will take place on October the 30th". F1plus.com. 4 June 2011. Archived from the original on 24 March 2012. Retrieved 4 June 2011.
- ^ "Cybarco takes on $155 million Bahrain F1 circuit". xak.com. 4 June 2011. Archived from the original on 15 April 2012. Retrieved 4 June 2011.
- ^ "Bahrain International Circuit". Archived from the original on 28 June 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ a b c d "Bahrain International Circuit Info". Bahrain International Circuit. Archived from the original on 3 January 2007. Retrieved 17 December 2006.
- ^ "Schumacher admits sand fear". BBC News. 29 March 2004. Retrieved 13 April 2007.
- ^ "From Shropshire to Abu Dhabi GP". BBC. 30 October 2009. Archived from the original on 2 November 2009. Retrieved 30 October 2009.
- ^ "Michael Schumacher has Bahrain corner named in his honour". BBC. 2 February 2014. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ^ "F1 to use Bahrain's 'outer track' for Sakhir Grand Prix, sub-60s laps expected". Formula1.com. 28 August 2020. Retrieved 28 August 2020.
- ^ a b c "Bahrain track guide". F1 Fanatic. Retrieved 19 December 2012.
- ^ a b "Car setups for Formula One". Retrieved 19 December 2012.
- ^ "In numbers - the Bahrain Grand Prix". formula1.com. Formula One World Championship Limited. 31 March 2016. Archived from the original on 3 April 2016. Retrieved 3 April 2016.
- ^ "Formula 1 Gulf Air Bahrain Grand Prix 2020 – Qualifying". Formula1.com. 28 November 2020. Retrieved 28 November 2020.
- ^ "LIST OF FIA LICENSED CIRCUITS" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 May 2012. Retrieved 22 April 2012.
- ^ "Sakhir reverts to old layout for 2011". ESPN UK. Archived from the original on 20 December 2013. Retrieved 3 April 2016.
- ^ "Formula 1 to return to Turkey as four more races are added to the 2020 F1 calendar". www.formula1.com. Retrieved 22 September 2020.
- ^ McDonagh, Connor (2 April 2021). "Who holds the lap record for each circuit on the F1 2021 calendar?". Crash.net. Retrieved 31 August 2021.
- ^ a b c "2020 8 Hours of Bahrain Classification" (PDF). Retrieved 3 March 2021.
- ^ "2015 GP2 Series Bahrain Session Facts". Retrieved 3 March 2021.
- ^ "2017 World Series Formula V8 3.5 Bahrain Session Facts". Retrieved 3 March 2021.
- ^ "2015 GP3 Series Bahrain Session Facts". Retrieved 3 March 2021.
- ^ "FIA WEC 2021 Bapco 6 Hours of Bahrain Race Final Classification by Category" (PDF). Retrieved 31 October 2021.
- ^ "FIA GT Championship Bahrain 2005". Retrieved 30 March 2021.
- ^ "Desert 400 - 2010 V8 Supercar Championship - Races 3 & 4 V8 SUPERCARS - Race 4". Natsoft. Retrieved 31 August 2021.
- ^ "Gulf Air Desert 400 - 2008 V8 Supercar Championship Round 12 V8 SUPERCARS - Race 3". Natsoft. 22 November 2008. Retrieved 31 August 2021.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bahrain International Circuit. |
- Bahrain International Circuit on Twitter
- Formula One circuits
- Bahrain Grand Prix
- Motorsport venues in Bahrain
- Drag racing venues
- Supercars Championship circuits
- Racing circuits designed by Hermann Tilke





