Battle of Ichi-no-Tani
| Battle of Ichi-no-Tani | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Genpei War | |||||||
 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Minamoto clan | Taira clan | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Minamoto no Yoshitsune Minamoto no Noriyori |
Taira no Tadanori Taira no Shigehira Taira no Noritsune Taira no Narimori Taira no Michimori | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 3000[1] | 5000[1] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 1000[1] | |||||||

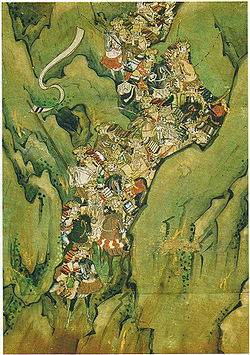
Ichi-no-Tani (一ノ谷) was a Taira defensive position at Suma, to the west of present-day Kobe, Japan. It sat on a very narrow strip of shore, between mountains on the north, and the sea to the south. This made it quite defensible, but also made it difficult to maneuver troops inside the fortress. The Taira suffered a crucial defeat to the forces of Yoshitsune and Noriyori.[1]
Yoshitsune split his force in two. Noriyori's force attacked the Taira at Ikuta Shrine, in the woods a short distance to the east. A second detachment, no more than a hundred horsemen under Yoshitsune, attacked the Taira at Ichinotani from the mountain ridge to the north. At the chosen hour, the Minamoto forces attacked causing confusion amongst the Taira who neither deploy nor retreat. Only about 3000 Taira escaped to Yashima, while Tadanori was killed and Shigehira captured.[1] Also killed from the Taira clan were Lord Michimori, Tsunemasa, Atsumori, Moromori, Tomoakira, Tsunetoshi, and Moritoshi.[2]: 117, 123
Ichi-no-Tani is one of the most famous battles of the Genpei War, in large part due to the individual combats that occurred here.[3] Benkei, probably the most famous of all warrior monks, fought alongside the Minamoto Yoshitsune here, and many of the Taira's most important and powerful warriors were present as well.[4]
The death of Taira no Atsumori at the hand of Kumagai no Naozane is a particularly famous passage in Heike Monogatari.[2] It has been dramatized in noh and kabuki, and in popular fiction, Oda Nobunaga is often portrayed as performing the noh at his own death (ningen goju nen geten no uchi wo kurabureba, yumemaboroshi no gotoku nari). The death of Atsumori is arguably among the most celebrated acts of single combat in all of Japanese history.
Ichi-no-Tani is also the last recorded instance in which crossbows were used in a Japanese siege.
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Sansom, George (1958). A History of Japan to 1334. Stanford University Press. pp. 298–299. ISBN 0804705232.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Sato, Hiroaki (1995). Legends of the Samurai. Overlook Duckworth. p. 117. ISBN 9781590207307.
- ^ Turnbull, Stephen (1998). The Samurai Sourcebook. Cassell & Co. p. 204. ISBN 1854095234.
- ^ Turnbull, Stephen (1977). The Samurai, A Military History. MacMillan Publishing Co., Inc. pp. 66–71. ISBN 0026205408.
- 1180s in Japan
- 1184 in Asia
- Battles of the Genpei War
- Conflicts in 1184