Beyond CMOS
Beyond CMOS refers to the possible future digital logic technologies beyond the CMOS scaling limits[1][2][3][4] which limits device density and speeds due to heating effects.[5]
Beyond CMOS is the name of one of the 7 focus groups in ITRS 2.0 (2013) and in its successor, the International Roadmap for Devices and Systems.

CPUs using CMOS were released from 1986 (e.g. 12 MHz Intel 80386). As CMOS transistor dimensions were shrunk the clock speeds also increased. Since about 2004 CMOS CPU clock speeds have leveled off at about 3.5 GHz.
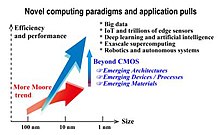
CMOS devices sizes continue to shrink – see Intel tick–tock and ITRS :
- 22nm Ivy Bridge in 2012
- first 14 nanometer processors shipped in Q4 2014.
- In May 2015, Samsung Electronics showed a 300 mm wafer of 10 nm FinFET chips.[7]
It is not yet clear if CMOS transistors will still work below 3 nm.[4] See 3 nanometer.
Comparisons of technology[]
About 2010 the (NRI) studied various circuits in various technologies.[2]
Nikonov benchmarked (theoretically) many technologies in 2012,[2] and updated it in 2014.[8] The 2014 benchmarking included 11 electronic, 8 spintronic, 3 , 2 ferroelectric, and 1 technology.[8]
The 2015 ITRS 2.0 report included a detailed chapter on Beyond CMOS,[9] covering RAM and logic gates.
Some areas of investigation[]
- tunnel junction devices, eg Tunnel field-effect transistor[10]
- indium antimonide transistors
- carbon nanotube FET, eg CNT Tunnel field-effect transistor
- graphene nanoribbons
- molecular electronics
- spintronics — many variants
- future low-energy electronics technologies, ultra-low dissipation conduction paths, including
- photonics and optical computing
- superconducting computing
- rapid single-flux quantum (RSFQ)
Superconducting computing and RSFQ[]
Superconducting computing includes several beyond-CMOS technologies that use superconducting devices, namely Josephson junctions, for electronic signals processing and computing. One variant called rapid single-flux quantum (RSFQ) logic was considered promising by the NSA in a 2005 technology survey despite the drawback that available superconductors require cryogenic temperatures. More energy-efficient superconducting logic variants have been developed since 2005 and are being considered for use in large scale computing.[11][12]
See also[]
- International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors
- International Roadmap for Devices and Systems
- Moore's law
- MOSFET scaling
- Nanostrain, a project to characterise piezoelectric materials for low power switches
- S-PULSE, the EU Shrink-Path of Ultra-Low Power Superconducting Electronics initiative
- Probabilistic complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (PCMOS)
References[]
- ^ Extending the road beyond CMOS. Hutchby 2002
- ^ a b c Nikonov, Dmitri E.; Young, Ian A. (September 2012). "Overview of Beyond-CMOS Devices and A Uniform Methodology for Their Benchmarking". arXiv:1302.0244 [cond-mat.mes-hall].
- ^ Bernstein; et al. (2011). "Device and Architecture Outlook for Beyond CMOS Switches". Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - ^ a b "Review of Advanced and Beyond CMOS FET Technologies for Radio Frequency Circuit Design. Carta 2011" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-02-23. Retrieved 2015-02-23.
- ^ Frank, D.J. (March 2002). "Power-constrained CMOS scaling limits". IBM Journal of Research and Development. 46 (2.3): 235–244. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.84.4043. doi:10.1147/rd.462.0235.
- ^ "Beyond CMOS" (PDF). The International Roadmap for Devices and Systems (2017 ed.). IEEE. 2018.
- ^ "Samsung vows to start 10nm chip production in 2016". 23 May 2015. Retrieved 16 July 2015.
- ^ a b Nikonov; Young (2015). "Benchmarking of Beyond-CMOS Exploratory – Devices for Logic Integrated Circuits". IEEE Journal on Exploratory Solid-State Computational Devices and Circuits. 1: 3–11. Bibcode:2015IJESS...1....3N. doi:10.1109/JXCDC.2015.2418033.
- ^ Beyond CMOS (PDF). International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors 2.0 (2015 ed.).
- ^ Seabaugh (September 2013). "The Tunneling Transistor". IEEE Spectrum. IEEE. 50 (10): 35–62. doi:10.1109/MSPEC.2013.6607013. S2CID 2729197.
- ^ Holmes, D.S.; Ripple, A.L.; Manheimer, M.A. (June 2013). "Energy-efficient superconducting computing—power budgets and requirements". IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 23 (3). 1701610. Bibcode:2013ITAS...2301610H. doi:10.1109/TASC.2013.2244634. S2CID 20374012.
- ^ Holmes, D.S.; Kadin, A.M.; Johnson, M.W. (December 2015). "Superconducting Computing in Large-Scale Hybrid Systems". Computer. 48 (12): 34–42. doi:10.1109/MC.2015.375. S2CID 26578755.
External links[]
- Electronics stubs
- Electronic design
- Digital electronics
- Logic families
- Integrated circuits