Bill Walsh (American football coach)
 Walsh at San Jose State in 2007 | |||||||
| Position: | Head coach | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personal information | |||||||
| Born: | November 30, 1931 Los Angeles, California | ||||||
| Died: | July 30, 2007 (aged 75) Woodside, California | ||||||
| Career information | |||||||
| High school: | Hayward (CA) | ||||||
| College: | San Jose State | ||||||
| Career history | |||||||
| As a coach: | |||||||
| |||||||
| As an administrator: | |||||||
| |||||||
| Career highlights and awards | |||||||
| |||||||
| Career NFL statistics | |||||||
| |||||||
| Coaching stats at PFR | |||||||
William Ernest Walsh (November 30, 1931 – July 30, 2007) was an American professional and college football coach. He served as head coach of the San Francisco 49ers and the Stanford Cardinal, during which time he popularized the West Coast offense. After retiring from the 49ers, Walsh worked as a sports broadcaster for several years and then returned as head coach at Stanford for three seasons.
Walsh went 102–63–1 (wins-losses-ties) with the 49ers, winning 10 of his 14 postseason games along with six division titles, three NFC Championship titles, and three Super Bowls. He was named NFL Coach of the Year in 1981 and 1984. In 1993, he was elected to the Pro Football Hall of Fame.
Early life[]
Born in Los Angeles, Walsh played running back in the San Francisco Bay Area for Hayward High School in Hayward.[1] Walsh played quarterback at the College of San Mateo for two seasons. (Both John Madden and Walsh played and coached at the College of San Mateo early in their careers.) After playing at the College of San Mateo, Walsh transferred to San José State University, where he played tight end and defensive end. He also participated in intercollegiate boxing, winning the golden glove.
Walsh graduated from San Jose State with a bachelor's degree in physical education in 1955. After two years in the U.S. Army participating on their boxing team,[2] Walsh built a championship team at Washington High School in Fremont before becoming an assistant coach at Cal, Stanford and then the Oakland Raiders in 1966.[3]
Early coaching career[]
He served under Bob Bronzan as a graduate assistant coach on the Spartans football coaching staff and graduated with a master's degree in physical education from San Jose State in 1959.[4] His master's thesis was entitled Flank Formation Football -- Stress:: Defense. Thesis 796.W228f.[5]
Following graduation, Walsh coached the football and swim teams at Washington High School in Fremont, California.
Walsh was coaching in Fremont when he interviewed for an assistant coaching position with Marv Levy, who had just been hired as the head coach at the University of California, Berkeley. "I was very impressed, individually, by his knowledge, by his intelligence, by his personality, and hired him," Levy said. Levy and Walsh, two future NFL Hall of Famers, would never produce a winning season at Cal.
After coaching at Cal, Walsh did a stint at Stanford as an assistant coach, before beginning his pro coaching career.
Early professional coaching career[]
Walsh began his pro coaching career in 1966 as an assistant with the AFL's Oakland Raiders. As a Raider assistant, Walsh was trained in the vertical passing offense favored by Al Davis, putting Walsh in Davis' mentor Sid Gillman's coaching tree.
In 1967 Walsh was the head coach and general manager of the San Jose Apaches of the Continental Football League (CFL). Walsh led the Apaches to 2nd place in the Pacific Division. Prior to the start of the 1968 CFL season the Apaches ceased all football operations.
In 1968, Walsh moved to the AFL expansion Cincinnati Bengals, joining the staff of legendary coach Paul Brown. It was there that Walsh developed the philosophy now known as the "West Coast Offense", as a matter of necessity. Cincinnati's new quarterback, Virgil Carter, was known for his great mobility and accuracy but lacked a strong arm necessary to throw deep passes. Thus, Walsh modified the vertical passing scheme he had learned during his time with the Raiders, designing a horizontal passing system that relied on quick, short throws, often spreading the ball across the entire width of the field.[6] The new offense was much better suited to Carter's physical abilities; he led the league in pass completion percentage in 1971.
Walsh spent eight seasons as an assistant with the Bengals. Ken Anderson eventually replaced Carter as starting quarterback, and together with star wide receiver Isaac Curtis, produced a consistent, effective offensive attack. Initially, Walsh started out as the wide receivers coach from 1968 to 1970 before also coaching the quarterbacks from 1971 to 1975.
When Brown retired as head coach following the 1975 season and appointed Bill "Tiger" Johnson as his successor, Walsh resigned and served as an assistant coach for Tommy Prothro with the San Diego Chargers in 1976. In a 2006 interview,[7] Walsh claimed that during his tenure with the Bengals, Brown "worked against my candidacy" to be a head coach anywhere in the league. "All the way through I had opportunities, and I never knew about them," Walsh said. "And then when I left him, he called whoever he thought was necessary to keep me out of the NFL."
In 1977, Walsh was hired as the head coach at Stanford where he stayed for two seasons. His two Stanford teams were successful, posting a 9–3 record in 1977 with a win in the Sun Bowl, and 8–4 in 1978 with a win in the Bluebonnet Bowl. His notable players at Stanford included quarterbacks Guy Benjamin and Steve Dils, wide receivers James Lofton and Ken Margerum, linebacker Gordy Ceresino, in addition to running back Darrin Nelson. Walsh was the Pac-8 Conference Coach of the Year in 1977.
49ers head coach[]
He was appointed head coach of the San Francisco 49ers on January 9, 1979, one day after both his resignation from Stanford and team owner Edward J. DeBartolo, Jr.'s dismissal of Walsh's predecessor Fred O'Connor and general manager Joe Thomas.[8] The long-suffering 49ers went 2–14 in 1978, the season before Walsh's arrival and repeated the same dismal record in his first season. But Walsh got the entire organization to buy into his philosophy and vowed to turn around a miserable situation. He also drafted quarterback Joe Montana from Notre Dame in the third round. Despite their second consecutive 2–14 record, the 49ers were playing more competitive football.
In 1980, Steve DeBerg was the starting quarterback who got San Francisco off to a 3–0 start, but after a 59–14 blowout loss to Dallas in week 6, Walsh promoted Montana to starting QB. In a Sunday game, December 7 vs. the New Orleans Saints, Montana brought the 49ers back from a 35–7 halftime deficit to win 38–35 in overtime. The 49ers improved to 6–10, but more importantly, Walsh had them making great strides and they were getting better every week.
1981 championship[]
In 1981, key victories were two wins each over the Los Angeles Rams and the Dallas Cowboys. The Rams were only two seasons removed from a Super Bowl appearance, and had dominated the series with the 49ers since 1967, winning 23, losing 3 and tying 1. San Francisco's two wins over the Rams in 1981 marked the shift of dominance in favor of the 49ers that lasted until 1998 with 30 wins (including 17 consecutively) against only 6 defeats. The 49ers blew out the Cowboys in week 6 of the regular season. On Monday Night Football that week, the win was not included in the halftime highlights. Walsh felt that this was because the Cowboys were scheduled to play the Rams the next week in a Sunday night game and that showing the highlights of the 49ers' win would potentially hurt the game's ratings. However, Walsh used this as a motivating factor for his team, who felt they were disrespected.[9] The 49ers finished the regular season with a 13–3 record.
The 49ers faced the Cowboys again that same season in the NFC title game. The game was very close, and in the fourth quarter Walsh called a series of running plays as the 49ers marched down the field against the Cowboys' prevent defense, which had been expecting the 49ers to mainly pass. The 49ers came from behind to win the game on Dwight Clark's touchdown reception, known as The Catch, propelling Walsh to his first Super Bowl. Walsh would later write that the 49ers' two wins over the Rams showed a shift of power in their division, while the wins over the Cowboys showed a shift of power in the conference.
San Francisco won its first championship a year removed from back-to-back two-win seasons. The 49ers won Super Bowl XVI, defeating the Cincinnati Bengals 26–21 in Pontiac, Michigan. Under Walsh the team rose from the cellar to the top of the NFL in just two seasons.
The 49ers won Super Bowl championships in the 1981, 1984 and 1988 seasons. Walsh served as 49ers head coach for 10 years, and during his tenure he and his coaching staff perfected the style of play known popularly as the West Coast offense.[10] Walsh was nicknamed "The Genius" for both his innovative play calling and design. Walsh would regularly script the first 10–15 offensive plays before the start of each game. In the ten years during which Walsh was the 49ers' head coach, San Francisco scored 3,714 points (24.4 per game), the most of any team in the league during that span.[11]
In addition to Joe Montana, Walsh drafted Ronnie Lott, Charles Haley, and Jerry Rice. He also traded a 2nd and 4th round pick in the 1987 draft for Steve Young. His success with the 49ers was rewarded with his election to the Pro Football Hall of Fame in 1993. Montana, Lott, Haley, Rice and Young were also elected to the Hall of Fame.
Coaching tree[]
Prominent assistant coaches[]
Many of Bill Walsh's assistant coaches went on to be head coaches themselves, including George Seifert, Mike Holmgren, Ray Rhodes, and Dennis Green. After Walsh's retirement from the 49ers, Seifert succeeded him as 49ers head coach, and guided San Francisco to victories in Super Bowl XXIV and Super Bowl XXIX. Holmgren won a Super Bowl with the Green Bay Packers, and made 3 Super Bowl appearances as a head coach: 2 with the Packers, and another with the Seattle Seahawks. These coaches in turn have their own disciples who have used Walsh's West Coast system, such as former Denver Broncos head coach Mike Shanahan and former Houston Texans head coach Gary Kubiak. Mike Shanahan was an offensive coordinator under George Seifert and went on to win Super Bowl XXXII and Super Bowl XXXIII during his time as head coach of the Denver Broncos. Kubiak was first a quarterback coach with the 49ers, and then offensive coordinator for Shanahan with the Broncos. In 2015, he became the Broncos' head coach and led Denver to victory in Super Bowl 50. Dennis Green trained Tony Dungy, who won a Super Bowl with the Indianapolis Colts, and Brian Billick with his brother-in law and linebackers coach Mike Smith. Billick won a Super Bowl as head coach of the Baltimore Ravens.
Mike Holmgren trained many of his assistants to become head coaches, including Jon Gruden and Andy Reid. Gruden won a Super Bowl with the Tampa Bay Buccaneers. Reid served as head coach of the Philadelphia Eagles from 1999 to 2012, and guided the Eagles to multiple winning seasons and numerous playoff appearances. Ever since 2013, Reid has served as head coach of the Kansas City Chiefs. He was finally able to win a Super Bowl, when his Chiefs defeated the San Francisco 49ers in Super Bowl LIV. In addition to this, Marc Trestman, former head coach of the Chicago Bears, served as Offensive Coordinator under Seifert in the 90's. Gruden himself would train Mike Tomlin, who led the Pittsburgh Steelers to their sixth Super Bowl championship, and Jim Harbaugh, whose 49ers would face his brother, John Harbaugh, whom Reid himself trained, and the Baltimore Ravens at Super Bowl XLVII, which marked the Ravens' second World Championship.
Bill Walsh was viewed as a strong advocate for African-American head coaches in the NFL and NCAA.[12] Thus, the impact of Walsh also changed the NFL into an equal opportunity for African-American coaches. Along with Ray Rhodes and Dennis Green, Tyrone Willingham became the head coach at Stanford, then later Notre Dame and Washington. One of Mike Shanahan's assistants, Karl Dorrell, went on to be the head coach at UCLA. Walsh directly helped propel Dennis Green into the NFL head coaching ranks by offering to take on the head coaching job at Stanford.
Bill Walsh coaching tree[]
Many former and current NFL head coaches trace their lineage back to Bill Walsh on his coaching tree, shown below.[13] Walsh, in turn, belonged to the coaching tree of American Football League great and Hall of Fame coach Sid Gillman of the AFL's Los Angeles/San Diego Chargers and Hall of Fame coach Paul Brown.
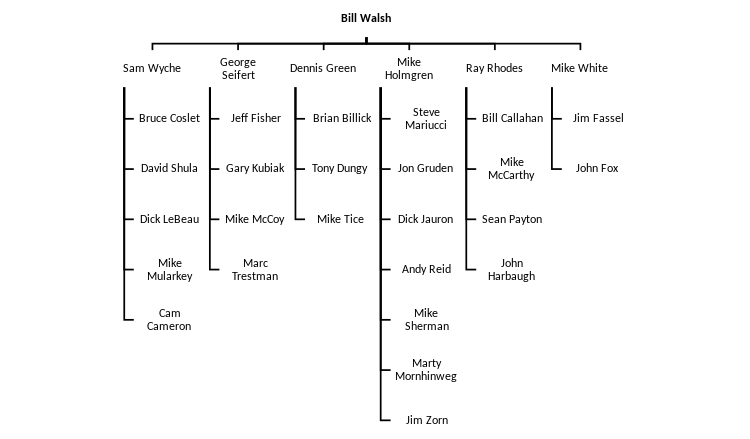
Tree updated through December 9, 2015.[14]
Later career[]
After leaving the coaching ranks immediately following his team's victory in Super Bowl XXIII, Walsh went to work as a broadcaster for NBC, teaming with Dick Enberg to form the lead broadcasting team, replacing Merlin Olsen.
During his time with NBC, rumors began to surface that Walsh would coach again in the NFL. There were at least two known instances.
First, according to a February 2015 article by Mike Florio of NBC Sports, after a 5–11 season in 1989, the Patriots fired Raymond Berry and unsuccessfully attempted to lure Walsh to Foxborough to become head coach and general manager. When that failed, New England promoted defensive coordinator Rod Rust; the team split its first two games and then lost 14 straight in 1990.[15]
Second, late in the 1990 season, Walsh was rumored to become Tampa Bay's next head coach and general manager after the team fired Ray Perkins and promoted Richard Williamson on an interim basis. Part of the speculation was fueled by the fact that Walsh's contract with NBC, which ran for 1989 and 1990, would soon be up for renewal, to say nothing of the pressure Hugh Culverhouse faced to increase fan support and to fill the seats at Tampa Stadium. However, less than a week after Super Bowl XXV, Walsh not only declined Tampa Bay's offer, but he and NBC agreed on a contract extension. Walsh would continue in his role with NBC for 1991.[16] Meanwhile, after unsuccessfully courting then-recently fired Eagles coach Buddy Ryan or Giants then-defensive coordinator Bill Belichick to man the sidelines for Tampa Bay in 1991, the Bucs stuck with Williamson. Under Williamson's leadership, Tampa Bay won only three games in 1991.
Walsh did return to Stanford as head coach in 1992, leading the Cardinal to a 10–3 record and a Pacific-10 Conference co-championship. Stanford finished the season with an upset victory over Penn State in the Blockbuster Bowl on January 1, 1993 and a #9 ranking in the final AP Poll. In 1994, after consecutive losing seasons, Walsh left Stanford and retired from coaching.
In 1996 Walsh returned to the 49ers as an administrative aide [17] Walsh was the Vice President and General Manager for the 49ers from 1999 to 2001 and was a special consultant to the team for three years afterwards.
In 2004, Walsh was appointed as special assistant to the athletic director at Stanford. In 2005, after then-athletic director Ted Leland stepped down, Walsh was named interim athletic director. He also acted as a consultant for his alma mater San Jose State University in their search for an Athletic Director and Head Football Coach in 2005.
Walsh was also the author of three books, a motivational speaker, and taught classes at the Stanford Graduate School of Business.
Walsh was a Board Member for the Lott IMPACT Trophy, which is named after Pro Football Hall of Fame defensive back Ronnie Lott, and is awarded annually to college football's Defensive IMPACT Player of the Year. Walsh served as a keynote speaker at the award's banquet.[18]
Awards and Honors[]
- 1989 – Golden Plate Award of the American Academy of Achievement[19][20]
- 1993 – Pro Football Hall of Fame[21]
- 1998 – San Jose State Hall of Fame and the SJSU Tower Award, the highest award given by SJSU[22]
Death[]
Bill Walsh died of leukemia on July 30, 2007 at his home in Woodside, California.[1]
Following Walsh's death, the playing field at the former Candlestick Park was renamed "Bill Walsh Field".[23] Additionally, the regular San Jose State versus Stanford football game was renamed the "Bill Walsh Legacy Game".[24]
Family[]
Walsh is survived by his wife Geri, his son Craig and his daughter Elizabeth. Walsh had another son, Steve, who died in 2002.
Head coaching record[]
College[]
| Year | Team | Overall | Conference | Standing | Bowl/playoffs | Coaches# | AP° | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stanford Cardinal (Pacific-8/Pacific-10 Conference) (1977–1978) | |||||||||
| 1977 | Stanford | 9–3 | 5–2 | T–2nd | W Sun | 15 | 15 | ||
| 1978 | Stanford | 8–4 | 4–3 | T–4th | W Bluebonnet | 16 | 17 | ||
| Stanford Cardinal (Pacific-10 Conference) (1992–1994) | |||||||||
| 1992 | Stanford | 10–3 | 6–2 | T–1st | W Blockbuster† | 9 | 9 | ||
| 1993 | Stanford | 4–7 | 2–6 | T–8th | |||||
| 1994 | Stanford | 3–7–1 | 2–6 | T–8th | |||||
| Stanford: | 34–24–1 | 19–19 | |||||||
| Total: | 34–24–1 | ||||||||
| National championship Conference title Conference division title or championship game berth | |||||||||
| |||||||||
NFL[]
| Team | Year | Regular Season | Post Season | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Won | Lost | Ties | Win % | Finish | Won | Lost | Win % | Result | ||
| SF | 1979 | 2 | 14 | 0 | .125 | 4th in NFC West | — | — | — | — |
| SF | 1980 | 6 | 10 | 0 | .375 | 3rd in NFC West | — | — | — | — |
| SF | 1981 | 13 | 3 | 0 | .812 | 1st in NFC West | 3 | 0 | 1.000 | Super Bowl XVI champions |
| SF | 1982 | 3 | 6 | 0 | .333 | 11th in NFC | — | — | — | — |
| SF | 1983 | 10 | 6 | 0 | .625 | 1st in NFC West | 1 | 1 | .500 | Lost to Washington Redskins in NFC Championship Game |
| SF | 1984 | 15 | 1 | 0 | .938 | 1st in NFC West | 3 | 0 | 1.000 | Super Bowl XIX champions |
| SF | 1985 | 10 | 6 | 0 | .625 | 2nd in NFC West | 0 | 1 | .000 | Lost to New York Giants in NFC Wild Card Game |
| SF | 1986 | 10 | 5 | 1 | .656 | 1st in NFC West | 0 | 1 | .000 | Lost to New York Giants in NFC Divisional Game |
| SF | 1987 | 13 | 2 | 0 | .867 | 1st in NFC West | 0 | 1 | .000 | Lost to Minnesota Vikings in NFC Divisional Game |
| SF | 1988 | 10 | 6 | 0 | .625 | 1st in NFC West | 3 | 0 | 1.000 | Super Bowl XXIII champions |
| SF Total | 92 | 59 | 1 | .609 | 10 | 4 | .714 | |||
| Total[25] | 92 | 59 | 1 | .609 | 10 | 4 | .714 | |||
Books[]
- Bill Walsh and Glenn Dickey, Building a Champion: On Football and the Making of the 49ers. St Martin's Press, 1990. (ISBN 0-312-04969-2).
- Bill Walsh, Brian Billick and James A. Peterson, Finding the Winning Edge. Sports Publishing, 1998. (ISBN 1-571-67172-2).
- Bill Walsh with Steve Jamison and Craig Walsh, The Score Takes Care of Itself: My Philosophy of Leadership. Penguin Group Publishing, 2009 (ISBN 978-1-59184-266-8).
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Fitzgerald, Tom (July 30, 2007). "Former 49er head coach Bill Walsh dies". San Francisco Chronicle. Archived from the original on November 12, 2007.
- ^ "The Story of the 1988 49ers". America's Game. March 8, 2007. NFL Network.
- ^ Newhouse, Dave (July 31, 2007). "Bill Walsh: Nov. 30, 1931 – July 30, 2007". Vallejo Times Herald. Vallejo, California.
- ^ "San Jose State Legend Bill Walsh Dies" (Press release). San Jose State University. July 30, 2007. Archived from the original on January 10, 2011. Retrieved October 1, 2007.
- ^ Daniel Brown, Jon Wilner and Mack Lundstrom (July 31, 2007). "Coaching legend Bill Walsh dies at 75". San Jose Mercury News. Retrieved October 1, 2007.
- ^ Doc Bear (May 27, 2009). "Bill Walsh, Bill Parcells and the Rise of the Left Tackle". MileHighReport.com.
- ^ Sam Farmer (December 22, 2006). "Living Legend". Los Angeles Times. p. D1.
- ^ "Bill Walsh Is Named 49er Coach," The Associated Press (AP), Tuesday, January 9, 1979. Retrieved November 20, 2020
- ^ Walsh, Bill (2009). The Score Takes Care of Itself: My Philosophy of Leadership. Penguin Group. p. 169.
- ^ Goldstein, Richard (July 31, 2007). "Bill Walsh, Innovator of West Coast Offense, Dies at 75". The New York Times. Retrieved January 31, 2018.
- ^ "Pro-Football-Reference.com: In multiple seasons, from 1979 to 1988, in the Regular Season, requiring Underdog By >= 0, sorted by descending Points For".
- ^ Glenn Dickey (January 14, 2002). "It's past time". ProFootballWeekly.com. Archived from the original on November 21, 2006.
- ^ Pasquarelli, Len (October 17, 2002). "An offense by any other name ..." ESPN.com. Retrieved March 12, 2009.
- ^ Beaton, Andrew and Camden Hu (December 9, 2015). "The NFL Coaching Tree". WSJ.com. Retrieved December 26, 2020.
- ^ "Recalling the Raymond Berry era and New England's failed run at Bill Walsh". ProFootballTalk.com. February 26, 2015. Retrieved August 8, 2020.
- ^ "Walsh Won't Leave TV for Bucs". Chicago Tribune. January 31, 1991. Archived from the original on November 15, 2018. Retrieved August 8, 2020.
- ^ Plaschke, Bill (January 24, 1996). "Adding Walsh to the 49ers Could Stir up Trouble". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved August 8, 2020.
- ^ Donovan, Pete (August 15, 2011). "'You are looking live at...': Brent Musburger to Speak at Newport Beach Event". Lott IMPACT Trophy. Archived from the original on May 27, 2012. Retrieved August 8, 2020.
- ^ "Golden Plate Awardees of the American Academy of Achievement". www.achievement.org. American Academy of Achievement.
- ^ Nix, Shann (June 26, 1989). "Looking Up to The Stars Where 50 top celebs dazzle 400 students" (PDF). Coronado Journal. San Francisco Chronicle.
- ^ "Class of 1993 Pro Football Hall of Fame". Pro Football Hall of Fame.
- ^ "Past San Jose Sports Hall of Fame Inductees". Inside the Spartans.
- ^ "Mayor announces name change at public memorial service". ESPN. August 10, 2007. Retrieved November 11, 2007.
- ^ Michelle Smith (September 12, 2007). "Walsh's legacy all over this game". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved November 11, 2007.
- ^ "Bill Walsh Record, Statistics, and Category Ranks - Pro-Football-Reference.com". Pro-Football-Reference.com.
External links[]
- Bill Walsh at the Pro Football Hall of Fame
- 1931 births
- 2007 deaths
- 20th-century American memoirists
- American motivational writers
- College football announcers
- California Golden Bears football coaches
- Cincinnati Bengals coaches
- Continental Football League coaches
- National Football League announcers
- National Football League general managers
- Notre Dame Fighting Irish football announcers
- Oakland Raiders coaches
- San Diego Chargers coaches
- San Francisco 49ers executives
- San Francisco 49ers head coaches
- San Mateo Bulldogs football players
- San Jose State Spartans football players
- San Jose State Spartans football coaches
- Stanford Cardinal football coaches
- High school football coaches in California
- Pro Football Hall of Fame inductees
- Super Bowl-winning head coaches
- People from Woodside, California
- Sportspeople from Hayward, California
- Sportspeople from Los Angeles
- Coaches of American football from California
- Players of American football from California
- Deaths from leukemia
- Deaths from cancer in California