Bolkhovitinov DB-A
| DB-A | |
|---|---|

| |
| Role | Bomber |
| National origin | USSR |
| Designer | Viktor Bolkhovitinov |
| First flight | 2 May 1935 |
| Number built | 14 |
The Bolkhovitinov DB-A (Dal'niy Bombardirovshchik-Akademiya – long-range bomber, academy) was a heavy bomber aircraft designed and built in the USSR from 1934.
Development[]
Bolkhovitinov became the head of the VVIA design group at the VVA Zhukovsky ( - VVS academy Zhukovsky ) tasked with the design of a replacement for the Tupolev TB-3 heavy bomber. The resulting DB-A was advanced for its day, with stressed skin aluminium alloy construction throughout with clean lines, neatly cowled engines and trousered main undercarriage legs, with fully retracting main-wheels and tail-wheel. The split flaps, undercarriage, nose turret and bomb-bay doors were all operated by a pneumatic system recharged by engine-driven compressors. Flight trials began on 2 May 1935 at Khodinka piloted by and , factory tests were completed by April 1934 and NII testing was carried out in May and June 1935. The excellent performance demonstrated included, sustained flight at an altitude of 2,500 m (8,202 ft) with two engines shut down, and 4,500 km range.
A decision was made to fly nonstop from Moscow to the US, and the DB-A was modified to fly, at an overload weight of 34,700 kg (76,500 lb), carry enough fuel to fly 8,440 km (5,244 miles). The red-painted DB-A prototype under command of Sigizmund Levanevsky departed airport on 12 August 1937 on an attempt to fly to Fairbanks, Alaska. After 14 hours, 32 minutes, the crew sent a radio message that one engine had failed and gave a revised ETA for Fairbanks, but nothing further was heard from the DB-A, and the fate of the aircraft and crew remains a mystery.
A second aircraft with increased gross weight, improved airframe, re-designed nose and more power was completed and flown in March 1936 as the DB-2A. An order for 16 aircraft was placed late in 1937, with the designation DBA, but only twelve were completed due to the advent of the TB-7/Pe-8.
Variants[]
- DB-A – The initial prototype aircraft, with M-34RN engines, lost on a nonstop flight Moscow to Fairbanks, Alaska.
- DB-2A – The second prototype with many detail improvements and M-34RNV engines.
- DBA – Production aircraft ordered in 1937. Sixteen aircraft ordered, but only twelve completed, with M-34FRN engines plus turbo-chargers, rearwards retracting main undercarriage, gunners cockpits in the rear of the inner engine nacelles, and other modifications.
- TK-1 TK ( - heavy cruiser) – Projected escort bomber with 11 crew, 3xShVAK + 3,000 rounds, 5xShKAS + 11,000 rounds and underwing rockets.
Specifications (DBA)[]
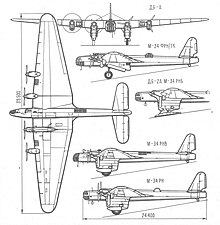
Data from Gunston, Bill. “The Osprey Encyclopaedia of Russian Aircraft 1875–1995”. London, Osprey. 1995. ISBN 1-85532-405-9
General characteristics
- Crew: 8
- Length: 24.4 m (80 ft 0.63 in)
- Wingspan: 39.5 m (129 ft 7 in)
- Wing area: 230 m2 (2,476 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 16,150 kg (35,605 lb)
- Gross weight: 22,000 kg (48,500 lb)
- Powerplant: 4 × M-34FRN + turbo-chargers , 671.1 kW (900 hp) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 316 km/h (196.4 mph, 170.7 kn)
- Range: 4,500 km (2,796 mi, 2,430 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 7,730 m (25,360 ft)
Armament
- 2 x ShKAS 7.62mm machine-guns in each of the inner nacelle gun positions.
- 1 x ShKAS 7.62mm machine-guns in nose and tail positions.
- 1 x ShVAK 20mm cannon in the dorsal turret.
- 5,000 kg of bombs in internal bomb-bay.
See also[]
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
- Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress
- Dornier Do 19
Related lists
- List of Interwar military aircraft
References[]
- Gunston, Bill. “The Osprey Encyclopaedia of Russian Aircraft 1875–1995”. London, Osprey. 1995. ISBN 1-85532-405-9
- Taylor, Michael J.H. . “ Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. Studio Editions. London. 1989. ISBN 0-517-69186-8
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bolkhovitinov DB-A. |
- 1930s Soviet bomber aircraft