Boolean ring
In mathematics, a Boolean ring R is a ring for which x2 = x for all x in R,[1][2][3] that is, a ring that consists only of idempotent elements.[4][5] An example is the ring of integers modulo 2.
Every Boolean ring gives rise to a Boolean algebra, with ring multiplication corresponding to conjunction or meet ∧, and ring addition to exclusive disjunction or symmetric difference (not disjunction ∨,[6] which would constitute a semiring). Boolean rings are named after the founder of Boolean algebra, George Boole.
Notations[]
There are at least four different and incompatible systems of notation for Boolean rings and algebras:
- In commutative algebra the standard notation is to use x + y = (x ∧ ¬ y) ∨ (¬ x ∧ y) for the ring sum of x and y, and use xy = x ∧ y for their product.
- In logic, a common notation is to use x ∧ y for the meet (same as the ring product) and use x ∨ y for the join, given in terms of ring notation (given just above) by x + y + xy.
- In set theory and logic it is also common to use x · y for the meet, and x + y for the join x ∨ y. This use of + is different from the use in ring theory.
- A rare convention is to use xy for the product and x ⊕ y for the ring sum, in an effort to avoid the ambiguity of +.
Historically, the term "Boolean ring" has been used to mean a "Boolean ring possibly without an identity", and "Boolean algebra" has been used to mean a Boolean ring with an identity. The existence of the identity is necessary to consider the ring as an algebra over the field of two elements: otherwise there cannot be a (unital) ring homomorphism of the field of two elements into the Boolean ring. (This is the same as the old use of the terms "ring" and "algebra" in measure theory.[a])
Examples[]
One example of a Boolean ring is the power set of any set X, where the addition in the ring is symmetric difference, and the multiplication is intersection. As another example, we can also consider the set of all finite or cofinite subsets of X, again with symmetric difference and intersection as operations. More generally with these operations any field of sets is a Boolean ring. By Stone's representation theorem every Boolean ring is isomorphic to a field of sets (treated as a ring with these operations).
Relation to Boolean algebras[]
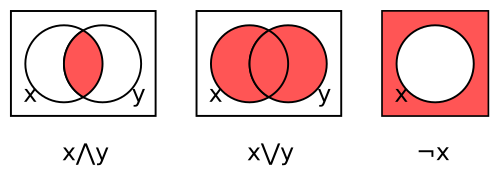
Since the join operation ∨ in a Boolean algebra is often written additively, it makes sense in this context to denote ring addition by ⊕, a symbol that is often used to denote exclusive or.
Given a Boolean ring R, for x and y in R we can define
- x ∧ y = xy,
- x ∨ y = x ⊕ y ⊕ xy,
- ¬x = 1 ⊕ x.
These operations then satisfy all of the axioms for meets, joins, and complements in a Boolean algebra. Thus every Boolean ring becomes a Boolean algebra. Similarly, every Boolean algebra becomes a Boolean ring thus:
- xy = x ∧ y,
- x ⊕ y = (x ∨ y) ∧ ¬(x ∧ y).
If a Boolean ring is translated into a Boolean algebra in this way, and then the Boolean algebra is translated into a ring, the result is the original ring. The analogous result holds beginning with a Boolean algebra.
A map between two Boolean rings is a ring homomorphism if and only if it is a homomorphism of the corresponding Boolean algebras. Furthermore, a subset of a Boolean ring is a ring ideal (prime ring ideal, maximal ring ideal) if and only if it is an order ideal (prime order ideal, maximal order ideal) of the Boolean algebra. The quotient ring of a Boolean ring modulo a ring ideal corresponds to the factor algebra of the corresponding Boolean algebra modulo the corresponding order ideal.
Properties of Boolean rings[]
Every Boolean ring R satisfies x ⊕ x = 0 for all x in R, because we know
- x ⊕ x = (x ⊕ x)2 = x2 ⊕ x2 ⊕ x2 ⊕ x2 = x ⊕ x ⊕ x ⊕ x
and since (R,⊕) is an abelian group, we can subtract x ⊕ x from both sides of this equation, which gives x ⊕ x = 0. A similar proof shows that every Boolean ring is commutative:
- x ⊕ y = (x ⊕ y)2 = x2 ⊕ xy ⊕ yx ⊕ y2 = x ⊕ xy ⊕ yx ⊕ y
and this yields xy ⊕ yx = 0, which means xy = yx (using the first property above).
The property x ⊕ x = 0 shows that any Boolean ring is an associative algebra over the field F2 with two elements, in precisely one way. In particular, any finite Boolean ring has as cardinality a power of two. Not every unital associative algebra over F2 is a Boolean ring: consider for instance the polynomial ring F2[X].
The quotient ring R/I of any Boolean ring R modulo any ideal I is again a Boolean ring. Likewise, any subring of a Boolean ring is a Boolean ring.
Any localization of a Boolean ring R by a set is a Boolean ring, since every element in the localization is idempotent.
The maximal ring of quotients (in the sense of Utumi and Lambek) of a Boolean ring R is a Boolean ring, since every partial endomorphism is idempotent.[7]
Every prime ideal P in a Boolean ring R is maximal: the quotient ring R/P is an integral domain and also a Boolean ring, so it is isomorphic to the field F2, which shows the maximality of P. Since maximal ideals are always prime, prime ideals and maximal ideals coincide in Boolean rings.
Boolean rings are von Neumann regular rings.
Boolean rings are absolutely flat: this means that every module over them is flat.
Every finitely generated ideal of a Boolean ring is principal (indeed, (x,y) = (x + y + xy)).
Unification[]
Unification in Boolean rings is decidable,[8] that is, algorithms exist to solve arbitrary equations over Boolean rings. Both unification and matching in finitely generated free Boolean rings are NP-complete, and both are NP-hard in finitely presented Boolean rings.[9] (In fact, as any unification problem f(X) = g(X) in a Boolean ring can be rewritten as the matching problem f(X) + g(X) = 0, the problems are equivalent.)
Unification in Boolean rings is unitary if all the uninterpreted function symbols are nullary and finitary otherwise (i.e. if the function symbols not occurring in the signature of Boolean rings are all constants then there exists a most general unifier, and otherwise the minimal complete set of unifiers is finite).[10]
See also[]
- Ring sum normal form
Notes[]
- ^ When a Boolean ring has an identity, then a complement operation becomes definable on it, and a key characteristic of the modern definitions of both Boolean algebra and sigma-algebra is that they have complement operations.
References[]
- ^ Fraleigh (1976, p. 200)
- ^ Herstein (1975, p. 130)
- ^ McCoy (1968, p. 46)
- ^ Fraleigh (1976, p. 25)
- ^ Herstein (1975, p. 268)
- ^ https://math.stackexchange.com/q/1621618
- ^ B. Brainerd, J. Lambek (1959). "On the ring of quotients of a Boolean ring". Canadian Mathematical Bulletin. 2: 25–29. doi:10.4153/CMB-1959-006-x. Corollary 2.
- ^ Martin, U.; Nipkow, T. (1986). "Unification in Boolean Rings". In Jörg H. Siekmann (ed.). Proc. 8th CADE. LNCS. 230. Springer. pp. 506–513. doi:10.1007/3-540-16780-3_115. ISBN 978-3-540-16780-8.
- ^ Kandri-Rody, Abdelilah; Kapur, Deepak; Narendran, Paliath (1985). "An ideal-theoretic approach to word problems and unification problems over finitely presented commutative algebras". Rewriting Techniques and Applications. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 202. pp. 345–364. doi:10.1007/3-540-15976-2_17. ISBN 978-3-540-15976-6.
- ^ A. Boudet; J.-P. Jouannaud; M. Schmidt-Schauß (1989). "Unification of Boolean Rings and Abelian Groups". Journal of Symbolic Computation. 8 (5): 449–477. doi:10.1016/s0747-7171(89)80054-9.
Further reading[]
- Atiyah, Michael Francis; Macdonald, I. G. (1969), Introduction to Commutative Algebra, Westview Press, ISBN 978-0-201-40751-8
- Fraleigh, John B. (1976), A First Course In Abstract Algebra (2nd ed.), Addison-Wesley, ISBN 978-0-201-01984-1
- Herstein, I. N. (1975), Topics In Algebra (2nd ed.), John Wiley & Sons
- McCoy, Neal H. (1968), Introduction To Modern Algebra (Revised ed.), Allyn and Bacon, LCCN 68015225
- Ryabukhin, Yu. M. (2001) [1994], "Boolean ring", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press
External links[]
- John Armstrong, Boolean Rings
- Ring theory
- Boolean algebra


