Capital punishment in the United States

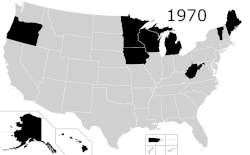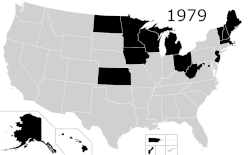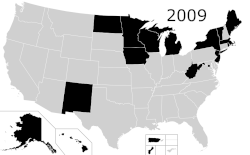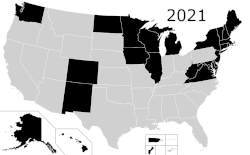
Capital punishment, also called the death penalty, is a legal penalty in the United States, with it being a legal punishment in 27 states, American Samoa,[b] the federal government, and the military.[1] Although it is a legal penalty in 27 states, only 21 states have the ability to execute death sentences, with the other 6, as well as the federal government, being subject to different types of moratoriums. The existence of capital punishment in the United States can be traced to early colonial Virginia. Along with Japan, Taiwan, and Singapore, the United States is one of four advanced democracies and the only Western nation that applies the death penalty regularly.[2][3][4][5][6] It is one of 54 countries worldwide applying it, and was the first to develop lethal injection as a method of execution, which has since been adopted by five other countries.[7] The Philippines has since abolished executions, and Guatemala has done so for civil offences, leaving the United States as one of four countries to still use this method (along with China, Thailand, and Vietnam). In Singapore and Japan, executions are carried out by long drop hanging.[8] In Taiwan, the preferred method of execution has long been by fatal gunshot; though never used, lethal injection was considered in the past and remains an option.[9][10][11] It is common practice worldwide for the condemned to be administered sedatives prior to execution, regardless of the method used.[12][13][14]
There were no executions in the United States between 1967 and 1977. In 1972, the Supreme Court of the United States struck down capital punishment statutes in Furman v. Georgia, reducing all pending death sentences to life imprisonment at the time.[15] Subsequently, a majority of states enacted new death penalty statutes, and the court affirmed the legality of capital punishment in the 1976 case Gregg v. Georgia. Since then, more than 7,800 defendants have been sentenced to death;[16] of these, more than 1,500 have been executed.[17][18] A total of at least 185 people who were sentenced to death since 1972 have since been exonerated.[19][20] As of December 16, 2020, 2,591 convicts are still on death row.[21][22]
The Trump administration's Department of Justice announced its plans to resume executions for federal crimes in 2019. On July 14, 2020, Daniel Lewis Lee became the first inmate executed by the federal government since 2003.[23] As of May 2021, there were 46 inmates on federal death row.[24] 13 federal death row inmates have been executed since federal executions resumed in July 2020. The last and most recent federal execution was of Dustin Higgs, who was executed on January 16, 2021. Higgs' execution was also the last under the presidency of Donald Trump.[25] It is currently unknown if federal executions will continue during the presidency of Joe Biden, although Biden does oppose capital punishment in the United States.[26]
Democrats introduced the Federal Death Penalty Abolition Act of 2021 on January 4, 2021. The bill is currently before the House Judiciary Committee.
History[]
Pre-Furman history[]

The first recorded death sentence in the British North American colonies was carried out in 1608 on Captain George Kendall,[27] who was executed by firing squad[28] at the Jamestown colony for spying on behalf of the Spanish government.[29] Executions in colonial America were also carried out by hanging. Bill of Rights adopted in 1789 included the Eighth Amendment which prohibited cruel and unusual punishment. The Fifth Amendment was drafted with language implying a possible use of the death penalty, requiring a grand jury indictment for "capital crime" and a due process of law for deprivation of "life" by the government.[30] The Fourteenth Amendment adopted in 1868 also requires a due process of law for deprivation of life by any states.
The Espy file,[31] compiled by M. Watt Espy and John Ortiz Smykla, lists 15,269 people executed in the United States and its predecessor colonies between 1608 and 1991. From 1930 to 2002, there were 4,661 executions in the U.S., about two-thirds of them in the first 20 years.[32] Additionally, the United States Army executed 135 soldiers between 1916 and 1955 (the most recent).[33][34][35]
Early abolition movement[]
Three states abolished the death penalty for murder during the 19th century: Michigan (which has never executed a prisoner since achieving statehood), in 1847, Wisconsin, in 1853 and Maine, in 1887. Rhode Island is also a state with a long abolitionist background, having repealed the death penalty in 1852, though it was theoretically available for murder committed by a prisoner between 1872 and 1984.
Other states which abolished the death penalty for murder before Gregg v. Georgia include Minnesota in 1911, Vermont in 1964, Iowa and West Virginia in 1965, and North Dakota in 1973. Hawaii abolished the death penalty in 1948 and Alaska in 1957, both before their statehood. Puerto Rico repealed it in 1929 and the District of Columbia in 1981. Arizona and Oregon abolished the death penalty by popular vote in 1916 and 1964 respectively, but both reinstated it, again by popular vote, some years later; Arizona reinstated the death penalty in 1918 and Oregon in 1978. In Oregon, the measure reinstating the death penalty was overturned by the Oregon Supreme Court in 1981, but Oregon voters again reinstated the death penalty in 1984.[36] Puerto Rico and Michigan are the only two U.S. jurisdictions to have explicitly prohibited capital punishment in their constitutions: in 1952 and 1964, respectively.
Constitutional law developments[]
Capital punishment was used by only 5 of 50 states in 2020. They were Alabama, Georgia, Missouri, Tennessee and Texas. Government executions, as reported by Amnesty International, took place in only 20 of the world's 195 countries. The federal government, however, which had not executed for 16 years prior, did so in 2020, pushed by Donald Trump and his nominee Attorney General William Barr. Executions for various crimes, especially murder and rape, occurred from the creation of the United States up to the beginning of the 1960s. Until then, "save for a few mavericks, no one gave any credence to the possibility of ending the death penalty by judicial interpretation of constitutional law", according to abolitionist Hugo Bedau.[37]
The possibility of challenging the constitutionality of the death penalty became progressively more realistic after the Supreme Court of the United States decided on Trop v. Dulles in 1958. The Supreme Court declared explicitly, for the first time, that the Eighth Amendment's cruel and unusual clause must draw its meaning from the "evolving standards of decency that mark the progress of a maturing society", rather than from its original meaning. Also in the 1932 case Powell v. Alabama, the court made the first step of what would later be called "death is different" jurisprudence, when it held that any indigent defendant was entitled to a court-appointed attorney in capital cases – a right that was only later extended to non-capital defendants in 1963, with Gideon v. Wainwright.
Capital punishment suspended (1972)[]
In Furman v. Georgia, the U.S. Supreme Court considered a group of consolidated cases. The lead case involved an individual convicted under Georgia's death penalty statute, which featured a "unitary trial" procedure in which the jury was asked to return a verdict of guilt or innocence and, simultaneously, determine whether the defendant would be punished by death or life imprisonment. The last pre-Furman execution was that of Luis Monge on June 2, 1967.
In a 5–4 decision, the Supreme Court struck down the impositions of the death penalty in each of the consolidated cases as unconstitutional in violation of the Eighth and Fourteenth Amendments of the United States Constitution. The Supreme Court has never ruled the death penalty to be per se unconstitutional. The five justices in the majority did not produce a common opinion or rationale for their decision, however, and agreed only on a short statement announcing the result. The narrowest opinions, those of Byron White and Potter Stewart, expressed generalized concerns about the inconsistent application of the death penalty across a variety of cases, but did not exclude the possibility of a constitutional death penalty law. Stewart and William O. Douglas worried explicitly about racial discrimination in enforcement of the death penalty. Thurgood Marshall and William J. Brennan Jr. expressed the opinion that the death penalty was proscribed absolutely by the Eighth Amendment as cruel and unusual punishment.
The Furman decision caused all death sentences pending at the time to be reduced to life imprisonment, and was described by scholars as a "legal bombshell".[15] The next day, columnist Barry Schweid wrote that it was "unlikely" that the death penalty could exist anymore in the United States.[38]
Capital punishment reinstated (1976)[]

Instead of abandoning capital punishment, 37 states enacted new death penalty statutes that attempted to address the concerns of White and Stewart in Furman. Some states responded by enacting mandatory death penalty statutes which prescribed a sentence of death for anyone convicted of certain forms of murder. White had hinted that such a scheme would meet his constitutional concerns in his Furman opinion. Other states adopted "bifurcated" trial and sentencing procedures, with various procedural limitations on the jury's ability to pronounce a death sentence designed to limit juror discretion.
On July 2, 1976, the U.S. Supreme Court decided Gregg v. Georgia[39] and upheld 7–2 a Georgia procedure in which the trial of capital crimes was bifurcated into guilt-innocence and sentencing phases. At the first proceeding, the jury decides the defendant's guilt; if the defendant is innocent or otherwise not convicted of first-degree murder, the death penalty will not be imposed. At the second hearing, the jury determines whether certain statutory aggravating factors exist, whether any mitigating factors exist, and, in many jurisdictions, weigh the aggravating and mitigating factors in assessing the ultimate penalty – either death or life in prison, either with or without parole. The same day, in Woodson v. North Carolina[40] and Roberts v. Louisiana,[41] the court struck down 5–4 statutes providing a mandatory death sentence.
Executions resumed on January 17, 1977, when Gary Gilmore went before a firing squad in Utah. Although hundreds of individuals were sentenced to death in the United States during the 1970s and early 1980s, only ten people besides Gilmore (who had waived all of his appeal rights) were actually executed prior to 1984.
Following the decision, the use of capital punishment in the United States soared.[42] This was in contrast to trends in other parts of advanced industrial democracies where the use of capital punishment declined or was prohibited.[42] Forty-seven European States, including Russia, are members of the Council of Europe,[43] and they all comply with the European Convention of Human Rights which prohibits capital punishment. The last execution in the UK took place in 1964,[44] and in 1977 in France.
Supreme Court narrows capital offenses[]
In 1977, the Supreme Court's Coker v. Georgia decision barred the death penalty for rape of an adult woman. Previously, the death penalty for rape of an adult had been gradually phased out in the United States, and at the time of the decision, Georgia and the U.S. Federal government were the only two jurisdictions to still retain the death penalty for this offense.
In the 1980 case Godfrey v. Georgia, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that murder can be punished by death only if it involves a narrow and precise aggravating factor.[45]
The U.S. Supreme Court has placed two major restrictions on the use of the death penalty. First, the case of Atkins v. Virginia, decided on June 20, 2002,[46] held that the execution of intellectually disabled inmates is unconstitutional. Second, in 2005, the court's decision in Roper v. Simmons[47] struck down executions for offenders under the age of 18 at the time of the crime.
In the 2008 case Kennedy v. Louisiana, the court also held 5–4 that the death penalty is unconstitutional when applied to non-homicidal crimes against the person, including child rape. Only two death row inmates (both in Louisiana) were affected by the decision.[48] Nevertheless, the ruling came less than five months before the 2008 presidential election and was criticized by both major party candidates Barack Obama and John McCain.[49]
Repeal movements and legal challenges[]
In 2004, New York's and Kansas' capital sentencing schemes were struck down by their respective states' highest courts. Kansas successfully appealed the Kansas Supreme Court decision to the United States Supreme Court, which reinstated the statute in Kansas v. Marsh (2006), holding it did not violate the U.S. Constitution. The decision of the New York Court of Appeals was based on the state constitution, making unavailable any appeal. The state lower house has since blocked all attempts to reinstate the death penalty by adopting a valid sentencing scheme.[50] In 2016, Delaware's death penalty statute was also struck down by its state supreme court.[51]
In 2007, New Jersey became the first state to repeal the death penalty by legislative vote since Gregg v. Georgia,[52] followed by New Mexico in 2009,[53][54] Illinois in 2011,[55] Connecticut in 2012,[56][57] and Maryland in 2013.[58] The repeals were not retroactive, but in New Jersey, Illinois and Maryland, governors commuted all death sentences after enacting the new law.[59] In Connecticut, the Connecticut Supreme Court ruled in 2015 that the repeal must be retroactive. In New Mexico, capital punishment for certain offenses is still possible for National Guard members in Title 32 status under the state's Code of Military Justice (NMSA 20-12), and for capital offenses committed prior to the repeal of the state's death penalty statute.[60][61]
Nebraska's legislature also passed a repeal in 2015, but a referendum campaign gathered enough signatures to suspend it. Capital punishment was reinstated by popular vote on November 8, 2016. The same day, California's electorate defeated a proposal to repeal the death penalty, and adopted another initiative to speed up its appeal process.[62]
On October 11, 2018, Washington state became the 20th state to abolish capital punishment when its state Supreme Court deemed the death penalty unconstitutional on the grounds of racial bias.[63]
New Hampshire became the 21st state to abolish capital punishment on May 30, 2019 when its state senate overrode Governor Sununu's veto by a vote of 16–8.[64]
Colorado became the 22nd state to abolish capital punishment when governor Jared Polis signed a repeal bill on March 23, 2020 and commuted all existing death sentences in the state to life without parole.[65]
Virginia became the 23rd state to abolish capital punishment, and the first Southern state to do so when governor Ralph Northam signed a repeal bill on March 24, 2021 and commuted all existing death sentences in the state to life without parole.[66][67]
Since Furman, 11 states have organized popular votes dealing with the death penalty through the initiative and referendum process. All resulted in a vote for reinstating it, rejecting its abolition, expanding its application field, specifying in the state constitution that it is not unconstitutional, or expediting the appeal process in capital cases.[36]
States that have abolished the death penalty[]
A total of 23 states, plus the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico have abolished the death penalty for all crimes. Below is a table of the states and the date that the state abolished the death penalty.[68][69][70][71][72][73][74][75] Michigan became the first English-speaking territory in the world to abolish capital punishment in 1847. Although treason remained a crime punishable by the death penalty in Michigan despite the 1847 abolition, no one was ever executed under that law, and Michigan's 1962 Constitutional Convention codified that the death penalty was fully abolished.[76] Vermont has abolished the death penalty for all crimes except treason.[77] One state (New Hampshire) abolished the death penalty for new crimes but still has one person remaining on death row for previous crimes.

| State/District/Territory | Year | Last execution |
|---|---|---|
| Alaska | 1957 | 1950 |
| Colorado | 2020 | 1997 |
| Connecticut | 2012 | 2005 |
| Delaware | 2016 | 2012 |
| District of Columbia | 1981 | 1957 |
| Hawaii | 1957 | 1947 |
| Illinois | 2011 | 1999 |
| Iowa | 1965 | 1963 |
| Maine | 1887 | 1885 |
| Maryland | 2013 | 2005 |
| Massachusetts | 1984 | 1947 |
| Michigan | 1963 | None |
| Minnesota | 1911 | 1906 |
| New Hampshire | 2019 | 1939 |
| New Jersey | 2007 | 1963 |
| New Mexico | 2009 | 2001 |
| New York | 2007 | 1964 |
| North Dakota | 1973 | 1905 |
| Rhode Island | 1984 | 1845 |
| Puerto Rico | 1929 | 1927 |
| Vermont | 1972 | 1954 |
| Virginia | 2021 | 2017 |
| Washington | 2018 | 2010 |
| West Virginia | 1965 | 1959 |
| Wisconsin | 1853 | 1851 |
Lethal injection era[]
In 1982, Texas carried out the first execution by lethal injection in world history and lethal injection subsequently became the preferred method throughout the country, displacing the electric chair.[78] From 1976 to 8 December 2016, there were 1,533 executions, of which 1,349 were by lethal injection, 163 by electrocution, 11 by gas inhalation, 3 by hanging, and 3 by firing squad.[79] The South had the great majority of these executions, with 1,249; there were 190 in the Midwest, 86 in the West, and only 4 in the Northeast. No state in the Northeast has conducted an execution since Connecticut, now abolitionist, in 2005. The state of Texas alone conducted 571 executions, over 1/3 of the total; the states of Texas, Virginia (now abolitionist), and Oklahoma combined make up over half the total, with 802 executions between them.[80] 17 executions have been conducted by the federal government.[81] Executions increased in frequency until 1999; 98 prisoners were executed that year. Since 1999, the number of executions has greatly decreased, and the 17 executions in 2020 were the fewest since 1991.[17] A 2016 poll conducted by Pew Research, found that support nationwide for the death penalty in the U.S. had fallen below 50% for the first time since the beginning of the post-Gregg era.[82]
The death penalty became an issue during the 1988 presidential election. It came up in the October 13, 1988, debate between the two presidential nominees George H. W. Bush and Michael Dukakis, when Bernard Shaw, the moderator of the debate, asked Dukakis, "Governor, if Kitty Dukakis [his wife] were raped and murdered, would you favor an irrevocable death penalty for the killer?" Dukakis replied, "No, I don't, and I think you know that I've opposed the death penalty during all of my life. I don't see any evidence that it's a deterrent, and I think there are better and more effective ways to deal with violent crime." Bush was elected, and many, including Dukakis himself, cite the statement as the beginning of the end of his campaign.[83]
In 1996, Congress passed the Antiterrorism and Effective Death Penalty Act to streamline the appeal process in capital cases. The bill was signed into law by President Bill Clinton, who had endorsed capital punishment during his 1992 presidential campaign.
A study found that at least 34 of the 749 executions carried out in the U.S. between 1977 and 2001, or 4.5%, involved "unanticipated problems or delays that caused, at least arguably, unnecessary agony for the prisoner or that reflect gross incompetence of the executioner". The rate of these "botched executions" remained steady over the period.[84] A study published in The Lancet in 2005 found that in 43% of cases of lethal injection, the blood level of hypnotics in the prisoner was insufficient to ensure unconsciousness.[85] Nonetheless, the Supreme Court ruled in 2008 (Baze v. Rees), again in 2015 (Glossip v. Gross), and a third time in 2019 (Bucklew v. Precythe), that lethal injection does not constitute cruel and unusual punishment.[86][87]
On July 25, 2019, Attorney General William Barr ordered the resumption of federal executions after a 16-year hiatus, and set five execution dates for December 2019 and January 2020.[88][89][90][91] After the Supreme Court upheld a stay on these executions,[92] the stay was lifted in June 2020 and four executions were rescheduled for July and August 2020.[93] The federal government executed Daniel Lewis Lee on July 14, 2020. He became the first convict executed by the federal government since 2003.[23] Before Trump's term ended in January 2021, the federal government carried out a total of 13 executions.[94]
Women's history and capital punishment[]
In 1632, 24 years after the first recorded male execution in the colonies, Jane Champion became the first woman known to have been lawfully executed. She was sentenced to death by hanging after she was convicted of infanticide; around two-thirds of women executed in the 17th and early 18th centuries were convicted of child murder. A married woman, it is not known whether Champion's illicit lover, William Gallopin, also convicted of their child's murder, was also executed, although it appears he was so sentenced.[95][96] For the Puritans, infanticide was the worst form of murder.[97]
Women accounted for just one fifth of all executions between 1632 and 1759, in the colonial United States. Women were more likely to be acquitted, and the relatively low number of executions of women may have been impacted by the scarcity of female laborers. Slavery was not yet widespread in the 17th century mainland and planters relied mostly on Irish indentured servants. To maintain subsistence levels in those days everyone had to do farm work, including women.[98]
The second half of the 17th century saw the executions of 14 women and 6 men who were accused of witchcraft during the witch hunt hysteria and the Salem Witch Trials. While both men and women were executed, 80% of the accusations were towards women, so the list of executions disproportionately affected men by a margin of 6 (actual) to 4 (expected), i.e. 50% more men were executed than expected from the percentage of accused who were men.[99]
Other notable female executions include Mary Surratt, Margie Velma Barfield and Wanda Jean Allen. Mary Surratt was executed by hanging in 1865 after being convicted of co-conspiring to assassinate Abraham Lincoln.[100] Margie Velma Barfield was convicted of murder and when she was executed by lethal injection in 1984, she became the first woman to be executed since the ban on capital punishment was lifted in 1976.[101] Wanda Jean Allen was convicted of murder in 1989 and had a high-profile execution by lethal injection in January 2001. She was the first black woman to be executed in the US since 1954.[102] Allen's lawyers did not deny her guilt, but claimed that prosecutors capitalized on her low IQ, race and homosexuality in their representations of her as a murderer at trial. The tactic did not work.[103]
The federal government executes women infrequently. Ethel Rosenberg, convicted of espionage, was executed in the electric chair on June 19, 1953, and Bonnie Brown Heady, convicted of kidnapping and murder, was executed in the gas chamber later that same year on December 18. Since Heady, only one more woman has been executed: Lisa Montgomery, convicted of killing a pregnant woman and cutting out and kidnapping her baby, by lethal injection in Indiana on January 13, 2021. Her execution had been stayed while her lawyers argued that she suffered from mental health issues, but the Supreme Court lifted the stay.[104][105]
Juvenile capital punishment[]
In 1642, the first ever juvenile, Thomas Graunger, was sentenced to death in Plymouth Colony, Massachusetts, for bestiality. Since then, 361 other juveniles have been sentenced to the death penalty. Kent v. United States (1966), turned the tides for juvenile capital punishment sentencing when it limited the waiver discretion juvenile courts had. Before this case, juvenile courts had the freedom to waiver juvenile cases to criminal courts without a hearing, which did not make the waiving process consistent across states. Thoughts about abolishing the death penalty started happening between 1983 and 1986. In 1987, Thompson v. Oklahoma, the Supreme Court threw away Thompson's death sentence due to it being cruel and unusual punishment.[106]
It was not until Roper v. Simmons that the juvenile death penalty was abolished due to the United States Supreme Court finding that the execution of juveniles is in conflict with the Eighth Amendment and Fourteenth Amendment, which deal with cruel and unusual punishment. Prior to abolishing the juvenile death penalty in 2005, any juvenile aged 16 years or older could be sentenced to death in some states, the last of whom was Scott Hain, executed in Oklahoma in 2003 for burning two people to death in a robbery at age 17.[107] Since 2005, there have been no executions nor discussion of executing juveniles in the United States.
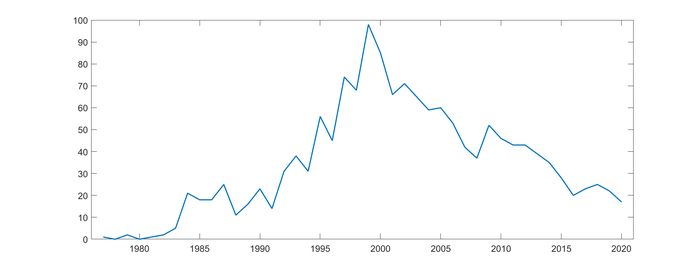
Execution statistics[]
| 1977 | 1978 | 1979 | 1980 | 1981 | 1982 | 1983 | 1984 | 1985 | 1986 | 1987 | 1988 | 1989 | 1990 | 1991 | 1992 | 1993 | 1994 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 21 | 18 | 18 | 25 | 11 | 16 | 23 | 14 | 31 | 38 | 31 |
| 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 |
| 56 | 45 | 74 | 68 | 98 | 85 | 66 | 71 | 65 | 59 | 60 | 53 | 42 | 37 | 52 | 46 | 43 | 43 |
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |||||||||
| 39 | 35 | 28 | 20 | 23 | 25 | 22 | 17 | 5 |
Capital crimes[]
Aggravated murder[]
Aggravating factors for seeking capital punishment of murder vary greatly among death penalty states. California has twenty-two.[108] Some aggravating circumstances are nearly universal, such as robbery-murder, murder involving rape of the victim, and murder of an on-duty police officer.[109]
Several states have included child murder to their list of aggravating factors, but the victim's age under which the murder is punishable by death varies. In 2011, Texas raised this age from six to ten.[110]
In some states, the high number of aggravating factors has been criticized on account of giving prosecutors too much discretion in choosing cases where they believe capital punishment is warranted. In California especially, an official commission proposed, in 2008, to reduce these factors to five (multiple murders, torture murder, murder of a police officer, murder committed in jail, and murder related to another felony).[111] Columnist Charles Lane went further, and proposed that murder related to a felony other than rape should no longer be a capital crime when there is only one victim killed.[112]
Aggravating factors in federal court[]
In order for a person to be eligible for a death sentence when convicted of aggravated first-degree murder, the jury or court (when there is not a jury) must determine at least one of sixteen aggravating factors that existed during the crime's commission. The following is a list of the 16 aggravating factors under federal law.[113]
- Murder while committing another felony.[114]
- Offender was convicted of a separate felony involving a firearm prior to the aggravated murder.
- Being convicted of a separate felony where death or life imprisonment was authorized prior to the aggravated murder.
- Being convicted of any separate violent felony prior to the aggravate murder.
- The offender put the lives of at least 1 or more other persons in danger of death during the commission of the crime.
- Offender committed the crime in an especially cruel, heinous, or depraved manner.
- Offender committed the crime for financial gain.
- Offender committed the crime for monetary gain.
- The murder was premeditated, involved planning in order to be carried out, or the offender showed early signs of committing the crime, such as keeping a journal of the crime's details[115] and posting things on the Internet.[116]
- Offender was previously convicted of at least two drug offenses.
- The victim would not have been able to defend themselves while being attacked.
- Offender was previously convicted of a federal drug offense.
- Offender was involved in a long-term business of selling drugs to minors.
- A high-ranking official was murdered, such as the President of the United States, the leader of another country, or a police officer.
- Offender was previously convicted of sexual assault or child rape.
- During the crime's commission, the offender killed or tried to kill multiple people.[117]
Crimes against the state[]
The opinion of the court in Kennedy v. Louisiana says that the ruling does not apply to "treason, espionage, terrorism, and drug kingpin activity, which are offenses against the State".[118]
Since no one is on death row for such offenses, the court has yet to rule on the constitutionality of the death penalty applied for them.
Treason, espionage and large-scale drug trafficking are all capital crimes under federal law. Treason is also punishable by death in six states (Arkansas, California, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Missouri). Large-scale drug trafficking is punishable by death in two states (Florida and Missouri),[119] and aircraft hijacking in two others (Georgia and Mississippi). Vermont has an invalidated pre-Furman statute allowing the electric chair for treason despite abolishing capital punishment in 1965.[120]
Legal process[]
The legal administration of the death penalty in the United States typically involves five critical steps: (1) prosecutorial decision to seek the death penalty (2) sentencing, (3) direct review, (4) state collateral review, and (5) federal habeas corpus.
Clemency, through which the Governor or President of the jurisdiction can unilaterally reduce or abrogate a death sentence, is an executive rather than judicial process.[121]
Decision to seek the death penalty[]
While judges in criminal cases can usually impose a harsher prison sentence than the one demanded by prosecution, the death penalty can be handed down only if the accuser has specifically decided to seek it.
In the decades since Furman, new questions have emerged about whether or not prosecutorial arbitrariness has replaced sentencing arbitrariness. A study by Pepperdine University School of Law published in Temple Law Review, surveyed the decision-making process among prosecutors in various states. The authors found that prosecutors' capital punishment filing decisions are marked by local "idiosyncrasies", and that wide prosecutorial discretion remains because of overly broad criteria. California law, for example, has 22 "special circumstances", making nearly all first-degree murders potential capital cases.[122]
A proposed remedy against prosecutorial arbitrariness is to transfer the prosecution of capital cases to the state attorney general.[123]
In 2017, Florida governor Rick Scott removed all capital cases from local prosecutor Aramis Ayala because she decided to never seek the death penalty no matter the gravity of the crime.[124]
Sentencing[]
Of the 27 states with the death penalty, 25 require the sentence to be decided by the jury, and 24 require a unanimous decision by the jury.
Two states don't use juries in death penalty cases. In Nebraska the sentence is decided by a three-judge panel, which must unanimously agree on death, and the defendant is sentenced to life imprisonment if one of the judges is opposed.[125] Montana is the only state where the trial judge decides the sentence alone.[126] The only state which does not require a unanimous jury decision is Alabama. At least 10 jurors must concur, and a retrial happens if the jury deadlocks.[127]
In all states in which the jury is involved, only death-qualified prospective jurors can be selected in such a jury, to exclude both people who will always vote for the death sentence and those who are categorically opposed to it. However, the states differ on what happens if the penalty phase results in a hung jury:[128][129]
- In four states (Arizona, California, Kentucky and Nevada), a retrial of the penalty phase will be conducted before a different jury (the common-law rule for mistrial).[130]
- In two states (Indiana and Missouri), the judge will decide the sentence.
- In the 19 other states, a hung jury results in a life sentence, even if only one juror opposed death. Federal law also provides that outcome.
The first outcome is referred as the "true unanimity" rule, while the third has been criticized as the "single-juror veto" rule.[131]
Direct review[]
If a defendant is sentenced to death at the trial level, the case then goes into a direct review.[132] The direct review process is a typical legal appeal. An appellate court examines the record of evidence presented in the trial court and the law that the lower court applied and decides whether the decision was legally sound or not.[133] Direct review of a capital sentencing hearing will result in one of three outcomes. If the appellate court finds that no significant legal errors occurred in the capital sentencing hearing, the appellate court will affirm the judgment, or let the sentence stand.[132] If the appellate court finds that significant legal errors did occur, then it will reverse the judgment, or nullify the sentence and order a new capital sentencing hearing.[134] Lastly, if the appellate court finds that no reasonable juror could find the defendant eligible for the death penalty, a rarity, then it will order the defendant acquitted, or not guilty, of the crime for which he/she was given the death penalty, and order him sentenced to the next most severe punishment for which the offense is eligible.[134] About 60 percent survive the process of direct review intact.[135]
State collateral review[]
At times when a death sentence is affirmed on direct review, supplemental methods to attack the judgment, though less familiar than a typical appeal, do remain. These supplemental remedies are considered collateral review, that is, an avenue for upsetting judgments that have become otherwise final.[136] Where the prisoner received his death sentence in a state-level trial, as is usually the case, the first step in collateral review is state collateral review, which is often called state habeas corpus. (If the case is a federal death penalty case, it proceeds immediately from direct review to federal habeas corpus.) Although all states have some type of collateral review, the process varies widely from state to state.[137] Generally, the purpose of these collateral proceedings is to permit the prisoner to challenge his sentence on grounds that could not have been raised reasonably at trial or on direct review.[138] Most often, these are claims, such as ineffective assistance of counsel, which requires the court to consider new evidence outside the original trial record, something courts may not do in an ordinary appeal. State collateral review, though an important step in that it helps define the scope of subsequent review through federal habeas corpus, is rarely successful in and of itself. Only around 6 percent of death sentences are overturned on state collateral review.[139]
In Virginia, state habeas corpus for condemned men are heard by the state supreme court under exclusive original jurisdiction since 1995, immediately after direct review by the same court.[140] This avoids any proceeding before the lower courts, and is in part why Virginia has the shortest time on average between death sentence and execution (less than eight years) and has executed 113 offenders since 1976 with only five remaining on death row as of June 2017.[141][142]
To reduce litigation delays, other states require convicts to file their state collateral appeal before the completion of their direct appeal,[143] or provide adjudication of direct and collateral attacks together in a "unitary review".[144]
Federal habeas corpus[]
After a death sentence is affirmed in state collateral review, the prisoner may file for federal habeas corpus, which is a unique type of lawsuit that can be brought in federal courts. Federal habeas corpus is a type of collateral review, and it is the only way that state prisoners may attack a death sentence in federal court (other than petitions for certiorari to the United States Supreme Court after both direct review and state collateral review). The scope of federal habeas corpus is governed by the Antiterrorism and Effective Death Penalty Act of 1996 (AEDPA), which restricted significantly its previous scope. The purpose of federal habeas corpus is to ensure that state courts, through the process of direct review and state collateral review, have done a reasonable job in protecting the prisoner's federal constitutional rights. Prisoners may also use federal habeas corpus suits to bring forth new evidence that they are innocent of the crime, though to be a valid defense at this late stage in the process, evidence of innocence must be truly compelling.[145] According to Eric Freedman, 21 percent of death penalty cases are reversed through federal habeas corpus.[139]
James Liebman, a professor of law at Columbia Law School, stated in 1996 that his study found that when habeas corpus petitions in death penalty cases were traced from conviction to completion of the case, there was "a 40 percent success rate in all capital cases from 1978 to 1995".[146] Similarly, a study by Ronald Tabak in a law review article puts the success rate in habeas corpus cases involving death row inmates even higher, finding that between "1976 and 1991, approximately 47 percent of the habeas petitions filed by death row inmates were granted".[147] The different numbers are largely definitional, rather than substantive: Freedam's statistics looks at the percentage of all death penalty cases reversed, while the others look only at cases not reversed prior to habeas corpus review.
A similar process is available for prisoners sentenced to death by the judgment of a federal court.[148]
The AEDPA also provides an expeditious habeas procedure in capital cases for states meeting several requirements set forth in it concerning counsel appointment for death row inmates.[149] Under this program, federal habeas corpus for condemned prisoners would be decided in about three years from affirmance of the sentence on state collateral review. In 2006, Congress conferred the determination of whether a state fulfilled the requirements to the U.S. attorney general, with a possible appeal of the state to the United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit. As of March 2016, the Department of Justice has still not granted any certifications.[150]
Section 1983[]
If the federal court refuses to issue a writ of habeas corpus, the death sentence ordinarily becomes final for all purposes. In recent times, however, prisoners have postponed execution through another avenue of federal litigation; the Civil Rights Act of 1871 – codified at 42 U.S.C. § 1983 – allows complainants to bring lawsuits against state actors to protect their federal constitutional and statutory rights.
While direct appeals are normally limited to just one and automatically stay the execution of the death sentence, Section 1983 lawsuits are unlimited, but the petitioner will be granted a stay of execution only if the court believes he has a likelihood of success on the merits.[151]
Traditionally, Section 1983 was of limited use for a state prisoner under sentence of death because the Supreme Court has held that habeas corpus, not Section 1983, is the only vehicle by which a state prisoner can challenge his judgment of death.[152] In the 2006 Hill v. McDonough case, however, the United States Supreme Court approved the use of Section 1983 as a vehicle for challenging a state's method of execution as cruel and unusual punishment in violation of the Eighth Amendment. The theory is that a prisoner bringing such a challenge is not attacking directly his judgment of death, but rather the means by which that the judgment will be carried out. Therefore, the Supreme Court held in the Hill case that a prisoner can use Section 1983 rather than habeas corpus to bring the lawsuit. Yet, as Clarence Hill's own case shows, lower federal courts have often refused to hear suits challenging methods of execution on the ground that the prisoner brought the claim too late and only for the purposes of delay. Further, the Court's decision in Baze v. Rees, upholding a lethal injection method used by many states, has narrowed the opportunity for relief through Section 1983.
Execution warrant[]
While the execution warrant is issued by the governor in several states, in the vast majority it is a judicial order, issued by a judge or by the state supreme court at the request of the prosecution.
The warrant usually sets an execution day. Some states instead provide a longer period, such as a week or 10 days to carry out the execution. This is designated to avoid issuing a new warrant in case of a last-minute stay of execution that would be vacated only few days or few hours later.[153]
Distribution of sentences[]

In recent years there has been an average of one death sentence for every 200 murder convictions in the United States.
Alabama has the highest per capita rate of death sentences. This is because Alabama was one of the few states that allowed judges to override a jury recommendation in favor of life imprisonment, a possibility it removed in March 2017.[154][155]
Among states[]
The distribution of death sentences among states is loosely proportional to their populations and murder rates. California, which is the most populous state, also has the largest death row, with over 700 inmates. Wyoming, which is the least populous state, has only one condemned man.
But executions are more frequent (and happen more quickly after sentencing) in conservative states. Texas, which is the second most populous state in the Union, carried out over 500 executions during the post-Furman era, more than a third of the national total. California has carried out only 13 executions during the same period, and has carried out none since 2006.[156][157][158]
Among races[]
African Americans made up 41% of death row inmates while making up only 12.6% of the general population. They have made up 34% of those actually executed since 1976. 54% of people wrongfully convicted and sentenced to death are black.[159]
Approximately 13.5% of death row inmates are of Hispanic or Latino descent, while they make up 17.4% of the general population.[160]
Approximately 1.81% of death row inmates are of Asian descent,[161] though Asians comprise an estimated 5.6% of the total population.[citation needed]
Among sexes[]
As of May 20, 2021, the Death Penalty Information Center reports that there are 51 women on death row. 17 women have been executed since 1976,[162] compared to 1,516 men during the same time period.[163]
Since 1608, 15,391 lawful executions are confirmed to have been carried out in jurisdictions of, or now of, the United States, of these, 575, or 3.6%, were women. Women account for 1⁄50 death sentences, 1⁄67 people on death row, and 1⁄100 people whose executions are actually carried out. While always comparatively rare, women are significantly less likely to be executed in the modern era than in the past. Of the 16 women executed on the state level, most took place in either Texas (6), Oklahoma (3) or Florida (2) and were demographically, 25% (4) African-American, with the rest (12) being white of any ethnicity. Historically, the states that have executed the most women are California, Texas and Florida; though unlike Texas and Florida, California has not executed a woman in the post-Furman era. The racial breakdown of women sentenced to death is 61% white, 21% black, 13% Latina, 3% Asian, and 2% American Indian.[162]
Methods[]


All 27 states with the death penalty for murder provide lethal injection as the primary method of execution. Vermont's remaining death penalty statute for treason provides electrocution as the method of execution.[77]
Some states allow other methods than lethal injection, but only as secondary methods to be used merely at the request of the prisoner or if lethal injection is unavailable.[164][165]
Several states continue to use the historical three-drug protocol: firstly an anesthetic, secondly pancuronium bromide, a paralytic, and finally potassium chloride to stop the heart.[166] Eight states have used a single-drug protocol, inflicting only an overdose of a single anesthetic to the prisoner.[166]
While some state statutes specify the drugs required, a majority do not, giving more flexibility to prison officers.[166]
Pressures from anti-death penalty activists and shareholders have made it difficult for correctional services to get the chemicals. Hospira, the only U.S. manufacturer of sodium thiopental, stopped making the drug in 2011.[167] In 2016, it was reported that more than 20 U.S. and European drug manufacturers including Pfizer (the owner of Hospira) had taken steps to prevent their drugs from being used for lethal injections.[167][168][169]
Since then, some states have used other anesthetics, such as pentobarbital, etomidate,[170] or fast-acting benzodiazepines like midazolam.[171] Many states have since bought lethal injection drugs from foreign furnishers, and most states have made it a criminal offense to reveal the identities of furnishers or execution team members.[167][172] In November 2015, California adopted regulations allowing the state to use its own public compounding pharmacies to make the chemicals.[173]
In 2009, Ohio approved the use of an intramuscular injection of 500 mg of hydromorphone (a 333-fold lethal overdose for an opioid-naive person)[174] and a supratherapeutic dose of midazolam as a backup means of carrying out executions when a suitable vein cannot be found for intravenous injection.[175][176]
Lethal injection was held to be a constitutional method of execution by the U.S. Supreme Court in three cases: Baze v. Rees (2008), Glossip v. Gross (2015), and Bucklew v. Precythe (2019).[177][178]
Offender-selected methods[]
In the following states, death row inmates with an execution warrant may choose to be executed by:[165]
- Electrocution in Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Kentucky, Mississippi, Oklahoma, South Carolina, and Tennessee.
- Gas chamber in Arizona and California.
- Firing squad in Mississippi, Oklahoma, South Carolina, and Utah.
In four states (Arizona, Kentucky, Tennessee and Utah), the alternative method is offered only to inmates sentenced to death for crimes committed prior to a specified date (usually when the state switched from the earlier method to lethal injection).
When an offender chooses to be executed by a means different from the state default method, which is always lethal injection, he/she loses the right to challenge its constitutionality in court. See Stewart v. LaGrand, 526 U.S. 115 (1999).
The last executions by methods other than injection are as follows (all chosen by the inmate):
| Method | Date | State | Inmate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrocution | 20 February 2020 | Tennessee | Nicholas Todd Sutton |
| Firing squad | 18 June 2010 | Utah | Ronnie Lee Gardner |
| Gas chamber | 3 March 1999 | Arizona | Walter Bernhard LaGrand |
| Hanging | 25 January 1996 | Delaware | Billy Bailey |
Backup methods[]
Depending on the state, the following alternative methods are statutorily provided in the event that lethal injection is either found unconstitutional by a court or unavailable for practical reasons:[164][165][179]
- Electrocution in Arkansas, Florida, Kentucky,[180] Mississippi, Oklahoma, South Carolina and Tennessee.
- Lethal gas in Alabama, California, Mississippi, Missouri, Oklahoma and Wyoming.
- Firing squad in Mississippi, Oklahoma, South Carolina, and Utah.
Three states (Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Utah) have added back-up methods recently in 2014 and 2015 (or have expanded their application fields) in reaction to the shortage of lethal injection drugs.[181]
Oklahoma and Mississippi are the only states allowing more than two methods of execution in their statutes, providing lethal injection, nitrogen hypoxia, electrocution and firing squad to be used in that order in the event that all earlier methods are unavailable. The nitrogen option was added by the Oklahoma Legislature in 2015 and has never been used in a judicial execution.[182] After struggling for years to design a nitrogen execution protocol and to obtain a proper device for it, Oklahoma announced in February 2020 it abandoned the project after finding a new reliable source of lethal injection drugs.[183]
Some states such as Florida have a larger provision dealing with execution methods unavailability, requiring their state departments of corrections to use "any constitutional method" if both lethal injection and electrocution are found unconstitutional. This was designed to make unnecessary any further legislative intervention in that event, but the provision applies only to legal (not practical) infeasibility.[184][185]
Federal executions[]
The method of execution of federal prisoners for offenses under the Violent Crime Control and Law Enforcement Act of 1994 is that of the state in which the conviction took place. If the state has no death penalty, the judge must choose a state with the death penalty for carrying out the execution.
The federal government has a facility (at U.S. Penitentiary Terre Haute) and regulations only for executions by lethal injection, but the United States Code allows U.S. Marshals to use state facilities and employees for federal executions.[186][187]
Execution attendance[]

The last public execution in the U.S. was that of Rainey Bethea in Owensboro, Kentucky, on August 14, 1936.
It was the last execution in the nation at which the general public was permitted to attend without any legally imposed restrictions. "Public execution" is a legal phrase, defined by the laws of various states, and carried out pursuant to a court order. Similar to "public record" or "public meeting", it means that anyone who wants to attend the execution may do so.
Around 1890, a political movement developed in the United States to mandate private executions. Several states enacted laws which required executions to be conducted within a "wall" or "enclosure", or to "exclude public view". Most state laws currently use such explicit wording to prohibit public executions, while others do so only implicitly by enumerating the only authorized witnesses.[188]
All states allow news reporters to be execution witnesses for information of the general public, except Wyoming which allows only witnesses authorized by the condemned.[189][190][191] Several states also allow victims' families and relatives selected by the prisoner to watch executions. An hour or two before the execution, the condemned is offered religious services and to choose their last meal (except in Texas which abolished it in 2011).
The execution of Timothy McVeigh on June 11, 2001, was witnessed by over 200 people, most by closed-circuit television.
Public opinion[]
This section is written like a personal reflection, personal essay, or argumentative essay that states a Wikipedia editor's personal feelings or presents an original argument about a topic. (July 2019) |
Gallup, Inc. has monitored support for the death penalty in the United States since 1937 by asking "Are you in favor of the death penalty for a person convicted of murder?" Gallup surveys documented a sharp increase in support for capital punishment between 1966 and 1994.[192] However, perhaps as the result of DNA exonerations of death row inmates reported in the national media in the late 1990s,[193] support began to wane, falling from 80% in 1994 to 56% in 2019. Moreover, approval varies substantially depending on the characteristics of the target and the alternatives posed, with much lower support for putting juveniles and the mentally ill to death (26% and 19%, respectively, in 2002).[192] Given the fact that attitudes toward capital punishment are often responsive to events, to characteristics of the target and to alternatives, many believe that the conventional wisdom—that death penalty attitudes are impervious to change—is flawed. Accordingly, any analysis of death penalty attitudes must account for the responsiveness of such attitudes, as well as their reputed resistance to change.[194]
Pew Research polls have demonstrated declining American support for the death penalty: 80% in 1974, 78% in 1996, 55% in 2014, and 49% in 2016.[195][196] The 2014 poll showed significant differences by race: 63% of whites, 40% of Hispanics and 36% of blacks, respectively, supported the death penalty in that year. However, in 2018, Pew's polls showed public support for the death penalty had increased to 54% from 49%. Since 2016, opinions among Republicans and Democrats have changed little, but the share of independents favoring the death penalty has increased by eight percentage points (from 44% to 52%).[197]
A 2010 poll by Lake Research Partners found that 61% of voters would choose a penalty other than the death sentence for murder.[198] When persons surveyed are given a choice between the death penalty and life without parole for persons convicted of capital crimes, support for execution has traditionally been significantly lower than in polling that asks only if a person does or does not support the death penalty. In Gallup's 2019 survey, support for the sentence of life without parole surpassed that for the death penalty by a margin of 60% to 36%.[192]
A 2014 study found that the belief that the death penalty helps victims' families to heal may be wrong; more often than finding closure, victims' families felt anger and wanted revenge, with potential side effects of depression, PTSD and a decreased satisfaction with life. Furthermore, the researchers found that a sense of compassion or remorse expressed from the perpetrator to the victim's family had a statistically significant positive effect on the family's ability to find closure.[199]
In November 2009, another Gallup poll found that 77% of Americans believed that the mastermind of the September 11 attacks, Khalid Sheikh Mohammed, should receive the death penalty if convicted, 12 points higher than the rate of general support for the death penalty upon Gallup's most recent poll at the time.[200] A similar result was found in 2001 when respondents were polled about the execution of Timothy McVeigh for the Oklahoma City bombing that killed 168 people.[201]
Debate[]
Capital punishment is a controversial issue, with many prominent organizations and individuals participating in the debate. Amnesty International and other groups oppose capital punishment on moral grounds.
Some law enforcement organizations, and some victims' rights groups support capital punishment.
The United States is one of the four developed countries that still practice capital punishment, along with Japan, Singapore, and Taiwan.
Religious groups are widely split on the issue of capital punishment.[202] The Fiqh Council of North America, a group of highly influential Muslim scholars in the United States, has issued a fatwa calling for a moratorium on capital punishment in the United States until various preconditions in the legal system are met.[203]
Reform Judaism has formally opposed the death penalty since 1959, when the Union of American Hebrew Congregations (now the Union for Reform Judaism) resolved "that in the light of modern scientific knowledge and concepts of humanity, the resort to or continuation of capital punishment either by a state or by the national government is no longer morally justifiable." The resolution goes on to say that the death penalty "lies as a stain upon civilization and our religious conscience." In 1979, the Central Conference of American Rabbis, the professional arm of the Reform rabbinate, resolved that, "both in concept and in practice, Jewish tradition found capital punishment repugnant" and there is no persuasive evidence "that capital punishment serves as a deterrent to crime."[204]
In October 2009, the American Law Institute voted to disavow the framework for capital punishment that it had created in 1962, as part of the Model Penal Code, "in light of the current intractable institutional and structural obstacles to ensuring a minimally adequate system for administering capital punishment". A study commissioned by the institute had said that experience had proved that the goal of individualized decisions about who should be executed and the goal of systemic fairness for minorities and others could not be reconciled.[205] As of 2017, 159 prisoners have been exonerated due to evidence of their innocence.[20][198][206]
Advocates of the death penalty say that it deters crime, is a good tool for prosecutors in plea bargaining,[207] improves the community by eliminating recidivism by executed criminals, provides "closure" to surviving victims or loved ones, and is a just penalty. Some advocates against the death penalty argue that "most of the rest of the world gave up on human sacrifice a long time ago."[208]
The murder rate is highest in the South (6.5 per 100,000 in 2016), where 80% of executions are carried out, and lowest in the Northeast (3.5 per 100,000), with less than 1% of executions. A report by the US National Research Council in 2012 stated that studies claiming a deterrent effect are "fundamentally flawed" and should not be used for policy decisions.[198] According to a survey of the former and present presidents of the country's top academic criminological societies, 88% of these experts rejected the notion that the death penalty acts as a deterrent to murder.[198]
Data shows that the application of the death penalty is strongly influenced by racial bias.[198] Furthermore, some opponents argue that it is applied in an arbitrary manner by a criminal justice system that has been shown to be biased through the systemic influence of socio-economic, geographic, and gender factors.[209] Another argument in the capital punishment debate is the cost.[198][210]
Various commentators predicted that the death penalty would likely have disappeared in the United States if Hillary Clinton had been elected U.S. president during the 2016 presidential race and thus allowed to appoint a left leaning Supreme Court Justice to replace the late Antonin Scalia.[citation needed] On the contrary, there was a surge in public support for capital punishment, as citizens in three states voted the same day for ballot measures supporting it. Many columnists came to the conclusion that it will remain indefinitely.[211][212][213]
Botched executions[]
One of the main arguments against the use of capital punishment in the United States is that there has been a long history of botched executions. University of Colorado Boulder Professor Michael L. Radelet described a "botched execution" as an execution that causes the prisoner to suffer for a long period of time before they die.[214] This has led to the argument that capital punishment is per se cruel and unusual punishment. The following is a short list of examples of botched executions that have occurred in the United States.
- William Kemmler was the first person executed in the electric chair, in 1890. After being pronounced dead after 17 seconds, he was found to be still alive. The current was applied a second time, for two minutes, to complete the death.[215]
- In Arizona, it took Joseph Wood two hours to die after being injected.[216]
- In Alabama, the execution of Doyle Hamm was called off after prison medical staff spent nearly three hours attempting to insert an IV that could be used to administer the lethal injection drugs. In the process, the execution team punctured Hamm's bladder and femoral artery, causing significant bleeding.[217][218]
- In Florida, Jesse Joseph Tafero had flames burst from his hair during an electrocution.[219]
- Wallace Wilkerson died after 27 minutes in pain after the firing squad failed to shoot him in the heart.[220] Because of this, the constitutionality of the use of the firing squad was questioned. The Supreme Court of the United States affirmed that the firing squad did not violate the Eighth Amendment in the case Wilkerson v. Utah (1879).[221]
- In New Mexico, Thomas Ketchum was decapitated when his body fell through the trap door during his hanging.[222]
- In Mississippi, Jimmy Lee Gray died after being in the gas chamber for nine minutes. During the procedure, Gray thrashed and banged his head against the metal pole behind his head while struggling to breathe.[223]
Austin Sarat, a professor of jurisprudence and political science at Amherst College, in his book Gruesome Spectacles: Botched Executions and America's Death Penalty, found that from 1890 to 2010, 276 executions were botched out of a total of 8,776, or 3.15%, with lethal injections having the highest rate. Sarat writes that between 1980 and 2010 the rate of botched executions was higher than ever: 8.53 percent.[224]
Clemency and commutations[]
In states with the death penalty, the governor usually has the discretionary power to commute a death sentence or to stay its execution. In some states the governor is required to receive an advisory or binding recommendation from a separate board. In a few states like Georgia, the board decides alone on clemency. At the federal level, the power of clemency belongs to the President of the United States.[225]
The largest number of clemencies was granted in January 2003 in Illinois when outgoing Governor George Ryan, who had already imposed a moratorium on executions, pardoned four death-row inmates and commuted the sentences of the remaining 167 to life in prison without the possibility of parole.[226] When Governor Pat Quinn signed legislation abolishing the death penalty in Illinois in March 2011, he commuted the sentences of the fifteen inmates on death row to life imprisonment.[55]
Previous post-Furman mass clemencies took place in 1986 in New Mexico, when Governor Toney Anaya commuted all death sentences because of his personal opposition to the death penalty. In 1991, outgoing Ohio Governor Dick Celeste commuted the sentences of eight prisoners, among them all four women on the state's death row. And during his two terms (1979–1987) as Florida's Governor, Bob Graham, although a strong death penalty supporter who had overseen the first post-Furman involuntary execution as well as 15 others, agreed to commute the sentences of six people on the grounds of doubts about guilt or disproportionality.
Moratorium on executions[]

All executions were suspended through the country between September 2007 and April 2008. At that time, the U.S. Supreme Court was examining the constitutionality of lethal injection in Baze v. Rees. This was the longest period with no executions in the United States since 1982. The Supreme Court ultimately upheld this method in a 7–2 ruling.
In addition to the states that have no valid death penalty statute, the following 13 states and 2 jurisdictions are noted that have an official moratorium, or have had no executions for more than ten years, as of 2021:
| State / Jurisdiction | Status | Moratorium status[227] |
|---|---|---|
| Federal government | by Attorney General | In 2021, Attorney General announced a moratorium pending review |
| Military | de facto | No executions since 1961 |
| American Samoa | de facto | No method of execution defined by law. No executions since gaining self-governance in 1949. There are currently no prisoners under sentence of death in the territory. |
| California | by Governor and court order | In 2019, Governor Gavin Newsom set a moratorium. There also has been a court ordered moratorium on executions in effect since 2006.[228][229] |
| Indiana | de facto | No executions since 2009 (excluding federal executions at Terre Haute) |
| Kansas | de facto | Kansas has had no executions since 1965. Kansas restored the death penalty in 1994 but no current death row inmates have exhausted their appeal processes. |
| Kentucky | by court order | In 2009, a judge suspended executions pending a new protocol[230] |
| Louisiana | de facto | No executions since 2010 (no involuntary executions since 2002) |
| Montana | by court order | In 2015, a judge ruled the state's lethal injection protocol is unlawful, stopping executions[231] |
| Nevada | de facto | No executions since 2006 |
| North Carolina | by implementers | Executions are suspended following a decision by the state's medical board that physicians cannot participate in executions, which is a requirement under state law. |
| Ohio | de facto | In 2020, Governor announced an informal moratorium |
| Oregon | by Governor | In 2011, Governor announced a moratorium and a review |
| Pennsylvania | by Governor | In 2015, Governor announced a moratorium pending review |
| South Carolina | de facto | No executions since 2011 |
| Utah | de facto | No executions since 2010 |
| Wyoming | de facto | Wyoming has had no executions since 1992. There are currently no prisoners under sentence of death in the state. |
Since 1976, four states have executed only condemned prisoners who voluntarily waived further appeals: Pennsylvania has executed three inmates, Oregon two, Connecticut one, and New Mexico one. In the latter state, Governor Toney Anaya commuted the sentences of all five condemned prisoners on death row in late 1986.[232]
In California, United States District Judge Jeremy Fogel suspended all executions in the state on December 15, 2006, ruling that the implementation used in California was unconstitutional but that it could be fixed.[233] California Governor Gavin Newsom declared an indefinite moratorium on March 13, 2019.[234]
On November 25, 2009, the Kentucky Supreme Court affirmed a decision by the Franklin County Circuit Court suspending executions until the state adopts regulations for carrying out the penalty by lethal injection.[235]
In November 2011, Oregon Governor John Kitzhaber announced a moratorium on executions in Oregon, canceling a planned execution and ordering a review of the death penalty system in the state.[236]
On February 13, 2015, Pennsylvania Governor Tom Wolf announced a moratorium on the death penalty. Wolf will issue a reprieve for every execution until a commission on capital punishment, which was established in 2011 by the Pennsylvania State Senate, produces a recommendation.[237] Effectively there was a moratorium in place, as the state had not executed anyone since Gary M. Heidnik in 1999.
On July 25, 2019, U.S. Attorney General William Barr announced that the federal government would resume executions using pentobarbital, rather than the three-drug cocktail previously used. Five convicted death row inmates were scheduled to be executed in December 2019 and January 2020.[238] On November 20, 2019, U.S. District Judge Tanya S. Chutkan issued a preliminary injunction preventing the resumption of federal executions. Plaintiffs in the case argued that the use of pentobarbital may violate the Federal Death Penalty Act of 1994.[239] The stay was lifted in June 2020 and four executions were rescheduled for July and August 2020.[93] On July 14, 2020, Daniel Lewis Lee was executed. He became the first convict executed by the federal government since 2003.[23] Overall, thirteen federal prisoners were executed during the presidency of Donald Trump between July 2020 and January 2021. The last convict executed was Dustin Higgs on January 16, 2021. On July 1, 2021, U.S. Attorney General Merrick Garland halted all federal executions pending review of the changes made under the Trump administration.[240]
See also[]
- Capital punishment by the United States federal government
- Capital punishment debate in the United States
- Felony murder and the death penalty in the United States
- List of death row inmates in the United States
- List of last executions in the United States by crime
- List of offenders executed in the United States in 2021
- List of offenders scheduled to be executed in the United States
- List of United States Supreme Court decisions on capital punishment
- Lists of people executed in the United States
Notes[]
- ^ Map only displays the status of the death penalty for crimes committed in the present and future. Some abolitionist states may still allow one to be sentenced to death for crimes committed before the abolition of the capital punishment in that state. Also includes laws where abolition has not yet taken effect, but an act to abolish it has been enacted.
- ^ Although capital punishment is, in theory, a legal punishment, there are currently no statutes that govern the execution of a sentence of death, resulting in a situation where life imprisonment is the de facto highest punishment in American Samoa.
References[]
- ^ "States and capital punishment". National Conference of State Legislatures. Retrieved June 23, 2017.
- ^ Leigh B. Bienen (2010). Murder and Its Consequences: Essays on Capital Punishment in America (2 ed.). Northwestern University Press. p. 143. ISBN 978-0-8101-2697-8.
- ^ Elisabeth Reichert (2011). Social Work and Human Rights: A Foundation for Policy and Practice. Columbia University Press. p. 89. ISBN 978-0-231-52070-6.
- ^ Russil Durrant (2013). An Introduction to Criminal Psychology. Routledge. p. 268. ISBN 978-1-136-23434-7.
- ^ Clifton D. Bryant; Dennis L. Peck (2009). Encyclopedia of Death & Human Experience. Sage Publications. p. 144. ISBN 978-1-4129-5178-4.
- ^ Cliff Roberson (2015). Constitutional Law and Criminal Justice, Second Edition. CRC Press. p. 188. ISBN 978-1-4987-2120-2.
- ^ "Lethal injection". capitalpunishmentuk.org. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
China...Guatemala, Philippines, Thailand...Vietnam
- ^ "A secret theater: inside japan's capital punishment system". www.japansociety.org. Japan Society. Retrieved June 16, 2020.
- ^ "A fight to the death: stopping the death penalty in Taiwan | Capital punishment | The Guardian". amp.theguardian.com.
- ^ Presse, AFP-Agence France. "Taiwan's New Execution Guidelines Slammed By Rights Groups". www.barrons.com.
- ^ "New law requires prisoners being executed to wear hood - Focus Taiwan". focustaiwan.tw.
- ^ "The brutal way Saudi Arabia treats the people it is going to execute". The Independent. October 13, 2015.
- ^ "The confronting truth behind executions". NewsComAu. February 17, 2015.
- ^ Writer - 11/05/06, ANDREW WELSH-HUGGINS- Associated Press. "States give sedatives to inmates before execution". Helena Independent Record.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Barry Latzer (2010), Death Penalty Cases: Leading U.S. Supreme Court Cases on Capital Punishment, Elsevier, p.37.
- ^ "Death Sentences in the United States From 1977 By State and By Year". Death Penalty Information Center. Retrieved April 24, 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Execution Statistics Summary – State and Year". people.smu.edu/rhalperi/. Retrieved January 26, 2017.
- ^ "Georgia inmate is the 1,500th person executed in the US since the death penalty was reinstated". edition.cnn.com. June 21, 2019. Retrieved June 21, 2019.
- ^ "Innocence: List of Those Freed From Death Row". Death Penalty Information Center. Archived from the original on May 13, 2019. Retrieved May 13, 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Dwyer-Moss, Jessica (2013) "Flawed Forensics and the Death Penalty: Junk Science and Potentially Wrongful Executions", Seattle Journal for Social Justice: Vol. 11 : Iss. 2, Article 10. (p.760)
- ^ "The Death Penalty in 2020: Year End Report" (PDF). Death Penalty Information Center. Retrieved February 2, 2021.
- ^ Research, CNN Editorial. "Death Penalty Fast Facts". CNN.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "US Executes First Federal Prisoner, Convicted Of Murder, In 17 Years". www.ndtv.com. Retrieved July 14, 2020.
- ^ "List of Federal Death-Row Prisoners". deathpenaltyinfo.org. Death Penalty Information Center. Retrieved May 11, 2021.
- ^ Allen, Jonathan; Acharya, Bhargav (January 16, 2021). "U.S. carries out 13th and final execution under Trump administration". Reuters. Retrieved January 16, 2021.
- ^ "Joe Biden's Criminal Justice Policy | Joe Biden". Joe Biden for President.
- ^ Death Penalty Information Center (2010). "Part I: History of the Death Penalty, Death Penalty Information Center". Retrieved April 12, 2011.
- ^ david waksman. "Is there a Death Penalty in America?". Archived from the original on December 30, 2013. Retrieved December 28, 2013.
- ^ "History of the Death Penalty in America". Antideathpenalty.org. Archived from the original on November 16, 2011. Retrieved December 1, 2011.
- ^ "BAZE v. REES (No. 07-5439) [April 16, 2008] Justice Scalia, with whom Justice Thomas joins, concurring in the judgment". law.cornell.edu. Retrieved April 7, 2016.
- ^ "Espy file". Deathpenaltyinfo.org. Archived from the original on September 5, 2008. Retrieved December 1, 2011.
- ^ Department of Justice Archived December 11, 2009, at the Wayback Machine of the United States of America
- ^ "The U.S. Military Death Penalty". Deathpenaltyinfo.org. Archived from the original on May 22, 2008. Retrieved December 1, 2011.
- ^ John A. Bennett
- ^ "Executions in the Military". Deathpenaltyinfo.org. Archived from the original on August 8, 2008. Retrieved December 1, 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Death penalty on the ballot". ballotpedia.org. Retrieved April 6, 2016.
- ^ The Courts, the Constitution, and Capital Punishment 118 (1977)
- ^ "The Free Lance-Star – Google News Archive Search". news.google.com.
- ^ Gregg v. Georgia, 428 U.S. 153 (1976)
- ^ Woodson v. North Carolina, 428 U.S. 280 (1976)
- ^ Roberts v. Louisiana, 428 U.S. 325 (1976), 431 U.S. 633 (1977)
- ^ Jump up to: a b Steiker, Carol S.; Steiker, Jordan M. (January 13, 2020). "The Rise, Fall, and Afterlife of the Death Penalty in the United States". Annual Review of Criminology. 3 (1): 299–315. doi:10.1146/annurev-criminol-011518-024721. ISSN 2572-4568.
- ^ The sole European states which are not in the Council of Europe are: Belarus, Kazakhstan and the Vatican City).
- ^ Amnesty International report [1]
- ^ "Godfrey v. Georgia". supreme.justia.com. Retrieved March 24, 2016.
- ^ "DARYL RENARD ATKINS, PETITIONER v. VIRGINIA". June 20, 2002. Retrieved August 6, 2006.
- ^ Roper v. Simmons, 543 U.S. 551 (2005)
- ^ Mears, Bill (June 25, 2008). "Child rapists can't be executed, Supreme Court rules". CNN. Retrieved May 7, 2017.
- ^ Sara Kugler (June 25, 2008). "Obama Disagrees With High Court on Child Rape Case". ABC News. Archived from the original on May 24, 2009. Retrieved May 7, 2017.
- ^ Powell, Michael (April 13, 2005). "In N.Y., Lawmakers Vote Not to Reinstate Capital Punishment". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on May 14, 2019. Retrieved May 14, 2019.
NEW YORK, April 12 – New York's death penalty is no more. A legislative committee tossed out a bill Tuesday aimed at reinstating the state's death penalty, which a court had suspended last year. It was an extraordinary bit of drama, not least because a top Democrat who once strongly supported capital punishment led the fight to end it.
- ^ "Top court: Delaware's death penalty law unconstitutional". August 2, 2016. Archived from the original on July 1, 2017. Retrieved May 14, 2019.
- ^ Richburg, Keith B. (December 14, 2007). "N.J. Approves Abolition of Death Penalty; Corzine to Sign". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on May 14, 2019. Retrieved May 14, 2019.
- ^ (in English) Maria Medina, « Governor OK with Astorga capital case »
- ^ "New Mexico governor bans death penalty". Agence France-Presse. March 18, 2009. Archived from the original on April 18, 2010. Retrieved December 23, 2009.
New Mexico Governor Bill Richardson made his state the 15th in the nation to outlaw capital punishment when he signed a law abolishing the death penalty, his office said.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Quinn signs death penalty ban, commutes 15 death row sentences to life". Chicago Tribune. March 9, 2011. Retrieved March 9, 2011.
- ^ "RECENT LEGISLATION: Death Penalty Repeal Passes Second Connecticut House, Awaits Governor's Signature | Death Penalty Information Center". Deathpenaltyinfo.org. April 12, 2012. Archived from the original on May 14, 2019. Retrieved May 14, 2019.
- ^ "Connecticut governor signs bill to repeal death penalty". FOX News Network, LLC. April 25, 2012. Archived from the original on May 14, 2019. Retrieved May 14, 2019.
- ^ Wagner, John (March 16, 2013). "Md. General Assembly repeals death penalty". The Washington Post. Retrieved May 14, 2019.
- ^ "Clemency". deathpenaltyinfo.org. Retrieved April 6, 2016.
- ^ 2016 New Mexico Statutes Chapter 20 – Military Affairs Article 12 – Code of Military Justice, JUSTIA US Law, Retrieved Mar 15, 2019
- ^ "Connecticut's highest court overturns its death penalty". cnn.com/. Retrieved April 6, 2016.
- ^ "Voters in California, Oklahoma, and Nebraska chose to preserve and strengthen the death penalty". news.vice.com. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ http://www.courts.wa.gov: PDF
- ^ "Senate overrides Sununu ending death penalty in New Hampshire". Concord Monitor. May 30, 2019. Retrieved May 30, 2019.
- ^ "Governor signs bill abolishing Colorado's death penalty, commutes sentences of state's 3 death row inmates". The Colorado Sun. March 23, 2020.
- ^ Schneider, Gregory S. (March 24, 2021). "Virginia abolishes the death penalty, becoming the first Southern state to ban its use". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on March 24, 2021. Retrieved March 24, 2021.
- ^ Kelley, Alexandra (March 24, 2021). "Virginia officially first Southern state to abolish the death penalty". The Hill. Retrieved March 24, 2021.
- ^ Arango, Tim (March 13, 2019). "California Death Penalty Suspended; 737 Inmates Get Stay of Execution (Published 2019)" – via NYTimes.com.
- ^ "31 States with the Death Penalty and 21 States with Death Penalty Bans - Death Penalty - ProCon.org". deathpenalty.procon.org. Retrieved May 2, 2018.
- ^ "Washington joins long list of states reconsidering or abolishing the death penalty". Public Radio International. Retrieved May 2, 2018.
- ^ "The day Michigan became 1st state to ban death penalty". Detroit Free Press. Retrieved May 2, 2018.
- ^ "Delaware | Death Penalty Information Center". deathpenaltyinfo.org. Retrieved May 2, 2018.
- ^ "Minnesota Capital Punishment Laws – FindLaw". Findlaw. Retrieved May 2, 2018.
- ^ "Washington State Strikes Down Death Penalty, Citing Racial Bias". NPR.org. Retrieved October 11, 2018.
- ^ "Colorado abolishes death penalty; governor commutes sentences of 3 on death row". The Denver Post. March 23, 2020. Retrieved March 24, 2020.
- ^ "Michigan: General Information". Death Penalty Information Center. Retrieved January 8, 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Vermont Laws". legislature.vermont.gov.
- ^ "Life and Death Row: How the lethal injection kills: The lethal injection has been the primary means of executing condemned Americans for decades - but its use remains controversial." Bryant, Ben, The BBC (March 5, 2018). https://www.bbc.co.uk/bbcthree/article/cd49a818-5645-4a94-832e-d22860804779. Retrieved March 14, 2021.
- ^ "USA Executions 2016 (as of 12/8/16)". people.smu.edu. Retrieved March 16, 2017.
- ^ "Number of Executions by State and Region Since 1976 – Death Penalty Information Center". deathpenaltyinfo.org.
- ^ "Executions Under the Federal Death Penalty". Death Penalty Information Center. Retrieved March 14, 2021.
- ^ Pew Research SEPTEMBER 29, 2016, "Support for death penalty lowest in more than four decades." BY J. BAXTER OLIPHANT. https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2016/09/29/support-for-death-penalty-lowest-in-more-than-four-decades/. Retrieved March 14, 2021.
- ^ "Obama's non-Dukakis answer". nbcnews.com. Retrieved April 8, 2016.
- ^ Borg and Radelet, pp. 144–147
- ^ Van Norman p. 287
- ^ Paternoster, R. (September 18, 2012). Capital Punishment. Oxford Handbooks Online. Retrieved June 15, 2016, from http://www.oxfordhandbooks.com/view/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780195395082.001.0001/oxfordhb-9780195395082-e-24.
- ^ https://www.supremecourt.gov/opinions/18pdf/17-8151_new_0pm1.pdf
- ^ Tammy Kupperman; Ariane de Vogue; Vernocia Stracqualursi (July 25, 2019), "Barr directs federal government to reinstate death penalty, schedule the execution of 5 death row inmates", CNN, retrieved July 25, 2019
- ^ "AG Barr orders reinstatement of the federal death penalty". NBC News.
- ^ Brownlee, Chip (July 25, 2019). "The Federal Government Plans to Revive the Death Penalty After 16 Years". Slate Magazine.
- ^ "US justice department resumes use of death penalty and schedules five executions". The Guardian. July 25, 2019.
- ^ "Supreme Court keeps federal executions on hold". NBC News.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "AP Exclusive: New dates set to begin federal executions". apnews.com. Associated Press. Retrieved June 16, 2020.
- ^ Michael Tarm & Michael Kunzelman, Trump administration carries out 13th and final execution, Associated Press (January 15, 2021). Retrieved March 14, 2021.
- ^ Baker, David V. (2016). Women and Capital Punishment in the United States: An Analytical History. Jefferson, NC: McFarland. p. 75. ISBN 9780786499502.
- ^ "Part I: History of the Death Penalty | Death Penalty Information Center". deathpenaltyinfo.org. Retrieved November 8, 2017.
- ^ Jones, Ann (2009) [1980]. Women Who Kill. New York, NY: The Feminist Press at the City University of New York. p. 76ff. ISBN 9781558616073. (Originally published by Holt, Rinehart and Winston)
- ^ Baker, David V. (2016). Women and Capital Punishment in the United States: An Analytical History.
- ^ Karlsen, Carol F. (April 17, 1998). The Devil in the Shape of a Woman: Witchcraft in Colonial New England. W. W. Norton & Company. p. 274. ISBN 9780393347197.
- ^ "Mary Surratt's Story – Surratt House Museum". www.surrattmuseum.org. Archived from the original on November 4, 2017. Retrieved November 8, 2017.
- ^ "Velma Margie Barfield #29". www.clarkprosecutor.org. Retrieved November 8, 2017.
- ^ "Wanda Jean Allen #687". www.clarkprosecutor.org. Retrieved November 8, 2017.
- ^ Baker, David V. (December 31, 2015). Women and Capital Punishment in the United States: An Analytical History. McFarland. ISBN 9781476622880.
- ^ Croft, Jay (October 17, 2020). "US government to execute first woman since 1953". CNN. Retrieved October 17, 2020.
- ^ Jeltsen, Melissa (January 12, 2021). "Only Woman On Federal Death Row Spared Execution For Now". HuffPost. Retrieved January 12, 2021.
- ^ Cothern, Lynn (November 2000). "Juveniles and the Death Penalty" (PDF). Coordinating Council on Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention: 1–16 – via NCJRS.
- ^ Maier, Shana (2017). The Encyclopedia of Corrections. John Wiley and Sons Inc.
- ^ "California Penal Code § 190.2". California Office of Legislative Counsel. Retrieved March 16, 2019.
- ^ "AGGRAVATING FACTORS FOR CAPITAL PUNISHMENT BY STATE". Retrieved April 28, 2017.
- ^ "AN ACT relating to the murder of a child as a capital offense". legis.state.tx.us. Retrieved March 24, 2016.
- ^ "Official recommendations on the fair administration of the death penalty in california". ccfaj.org. Archived from the original on March 14, 2016. Retrieved March 24, 2016.
- ^ Charles Lane (2010), Stay of Execution: Saving the Death Penalty from Itself, Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, p.110-111
- ^ "18 U.S. Code § 3592 – Mitigating and aggravating factors to be considered in determining whether a sentence of death is justified". LII / Legal Information Institute. Retrieved May 4, 2018.
- ^ "Felony-Murder Rule". TheFreeDictionary.com. Retrieved May 4, 2018.
- ^ Cullen, Dave (April 20, 2004). "The Depressive and the Psychopath". Slate. ISSN 1091-2339. Retrieved May 3, 2018.
- ^ "Nikolas Cruz, Florida Shooting Suspect, Showed 'Every Red Flag'". The New York Times. February 15, 2018. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved May 4, 2018.
- ^ "Serial Killers vs. Mass Murderers – Crime Museum". Crime Museum. Retrieved May 4, 2018.
- ^ Kennedy v. Louisiana, 554 U.S. 407, 437 (2007); see also Greenhouse, Linda (June 26, 2008). "Supreme Court Rejects Death Penalty for Child Rape". The New York Times. Retrieved March 11, 2011.
The court went beyond the question in the case to rule out the death penalty for any individual crime – as opposed to "offenses against the state", such as treason or espionage – "where the victim's life was not taken.
- ^ "Death Penalty for Offenses Other Than Murder". Death Penalty Information Center. 2008. Archived from the original on February 21, 2008. Retrieved January 28, 2008.
- ^ "§ 3401. Definition and punishment of treason". legislature.vermont.gov. Retrieved December 9, 2016.
- ^ See generally Separation of powers.
- ^ "Unpredictable Doom and Lethal Injustice: An Argument for Greater Transparency in Death Penalty Decisions". Journalist's Resource.org.
- ^ Adam M. Gershowitz. "Statewide Capital Punishment: The Case for Eliminating Counties' Role in the Death Penalty". Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- ^ Kristen M. Clark. "Florida Supreme Court backs Gov. Scott in Orlando death-penalty dispute". Retrieved May 10, 2020.
- ^ "2014 Nebraska Revised Statutes – Chapter 29 – CRIMINAL PROCEDURE – 29-2521 – Sentencing determination proceeding". law.justia.com. Retrieved April 16, 2017.
- ^ "46-18-301. Hearing on imposition of death penalty". leg.mt.gov. Retrieved April 16, 2017.
- ^ "SB 16 To amend Sections 13A-5-45, 13A-5-46, and 13A-5-47, Code of Alabama 1975, relating to capital cases and to the determination of the sentence by courts; to prohibit a court from overriding a jury verdict". legislature.state.al.us. Retrieved April 12, 2017.
- ^ "Provisions of state and federal statutes concerning sentence if capital sentencing jury cannot agree" (PDF). A. Parrent, Conn. Public Def. Retrieved March 15, 2016.
- ^ "SB 280: Sentencing for Capital Felonies". flsenate.gov. Retrieved March 15, 2017.
- ^ See United States v. Perez, 1824
- ^ K. Scheidegger, "Hurst v. Florida Remedial Legislation and SBP 7068", February 4, 2016
- ^ Jump up to: a b See, e.g., 18 U.S.C. § 3595. ("In a case in which a sentence of death is imposed, the sentence shall be subject to review by the court of appeals upon appeal by the defendant.")
- ^ See generally Appeal.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Poland v. Arizona, 476 U.S. 147 152–154 (1986).
- ^ Eric M. Freedman, "Giarratano is a Scarecrow: The Right to Counsel in State Postconviction Proceedings, Legalize Drugs" 91 Cornell L. Rev. 1079, 1097 (2001)
- ^ Teague v. Lane, 489 U.S. 288, 306 (1989).
- ^ LaFave, Israel, & King, 6 Crim. Proc. § 28.11(b) (2d ed. 2007).
- ^ LaFave, Israel, & King, 6 Crim. Proc. § 28.11(a) (2d ed. 2007).
- ^ Jump up to: a b Eric M. Freedman, "Giarratano is a Scarecrow: The Right to Counsel in State Postconviction Proceedings", 91 Cornell L. Rev. 1079, 1097 (2006).
- ^ "Code of Virginia – § 8.01-654. When and by whom writ granted; what petition to contain". Law.lis.virginia.gov. Retrieved March 22, 2016.
- ^ "Virginia's execution history". vadp.org. Retrieved June 4, 2017."Virginia's death row inmates". vadp.org. Retrieved June 4, 2017.
- ^ "Conviction to Execution "Takes Too Long"". ktrh.com. Archived from the original on April 7, 2016. Retrieved March 22, 2016.
- ^ "OJP Docket No. 1464, Certification Process for State Capital Counsel Systems" (PDF). crimeandconsequences.com. Retrieved March 15, 2017.
- ^ "AN ACT Concerning a unitary procedure for review in class 1 felony cases in which a death sentence is sought as punishment". tornado.state.co.us. Archived from the original on October 18, 2015. Retrieved March 15, 2017.
- ^ House v. Bell, 126 S. Ct. 2064 (2006)
- ^ "Habeas Corpus Studies". The New York Times. April 1, 1996. Retrieved April 28, 2010.
- ^ Walpin, Ned. "The New Speed-up in Habeas Corpus Appeals". Frontline. PBS. Retrieved February 5, 2017.
- ^ see 28 U.S.C. § 2255.
- ^ 28 USC §§ 2261 – 2266
- ^ "Court Gives Green Light to Death Penalty Fast-Tracking". abcnews.go.com. Retrieved March 24, 2016.
- ^ "Glossip v. Gross 576 U.S. ___ (2015)". justia.com. Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- ^ "Heck v. Humphrey, 512 U.S. 477 (1994)". Law.cornell.edu. Retrieved December 1, 2011.
- ^ "2014 Georgia Code – § 17-10-34 – Sentence to specify time period for and place of execution". law.justia.com. Retrieved April 3, 2016.
- ^ "Death Penalty". Equal Justice Initiative. Archived from the original on August 23, 2013. Retrieved October 29, 2013.
- ^ "Alabama ends death penalty by judicial override". Associated Press at WBRL. March 11, 2017. Retrieved March 13, 2017.
- ^ Lundin, Leigh. "Executed Prisoners in Texas". Last Words. Criminal Brief. Retrieved November 5, 2010.
- ^ Lundin, Leigh (August 22, 2010). "Last Words". Capital Punishment. Criminal Brief.
- ^ "Facts about the Death Penalty" (PDF). Death Penalty Information Center. p. 3. Retrieved April 21, 2017.
- ^ "Exonerations by race".
- ^ "Hispanics and the Death Penalty". Death Penalty Information Center. Retrieved February 22, 2016.
- ^ Fins, Deborah. "Death Row U.S.A. Spring 2020" (PDF). naacp.org. NAACP Legal Defense and Education Fund Inc. Retrieved September 14, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Women and the Death Penalty | Death Penalty Information Center". deathpenaltyinfo.org. Retrieved November 8, 2017.
- ^ "Facts About the Death Penalty" (PDF).
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Methods of Execution". clarkprosecutor.org. Retrieved March 28, 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Methods of Execution". deathpenaltyinfo.org. Retrieved June 14, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "State by State Lethal Injection". Death Penalty Information Center. Retrieved May 14, 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Eckholm, Erik (May 13, 2016). "Pfizer Blocks the Use of Its Drugs in Executions". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved May 14, 2016.
- ^ Richmond, Ben (October 28, 2013). "Will the EU kill America's Death Penalty?". Motherboard. Vice Media, Inc. Archived from the original on November 2, 2013. Retrieved November 5, 2013.
- ^ Algar, Clare (October 22, 2013). "Big Pharma May Help End The Death Penalty". The New Republic. Retrieved November 5, 2013.
- ^ The Washington Post: A death penalty landmark for Florida: Executing a white man for killing a black man
- ^ Liptak, Adam (June 29, 2015). "Supreme Court Allows Use of Execution Drug". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved October 5, 2016.
- ^ "Secret Execution Team, Firing Squads, Restricted Media Included in House Bill". jacksonfreepress.com. Retrieved April 6, 2016.
- ^ "Notice of change to regulations" (PDF). cdcr.ca.gov. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 15, 2016. Retrieved May 22, 2016.
- ^ Mosby's 2004 "Hydromorphone"
- ^ "Ohio Prisons Director Announces Changes to Ohio's Execution Process". Ohio Department of Rehabilitation and Correction. November 13, 2009. Archived from the original on January 15, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2014.
- ^ "Arizona execution takes two hours". BBC News. July 24, 2014. Retrieved July 24, 2014.
- ^ "High court upholds lethal injection method". Cable News Network (CNN). April 16, 2008. Retrieved June 30, 2017.
- ^ "Supreme Court backs use of lethal injection drug". Cable News Network (CNN). June 29, 2015. Retrieved June 30, 2017.
- ^ South Carolina Code of Laws: "Section 24-3-530. Death by electrocution or lethal injection". law.justia.com. Retrieved June 4, 2016.
- ^ "Method of execution in event of unconstitutionality of KRS 431.220". codes.findlaw.com. Retrieved March 22, 2020.
- ^ "How to kill: America's death penalty dilemma". cnn.com. Retrieved March 28, 2016.
- ^ "The Dawn of a New Form of Capital Punishment". Time. April 17, 2015.
- ^ "Oklahoma Attorney general says state will resume executions". nypost.com. Retrieved March 22, 2020.
- ^ "922.105 – Execution of death sentence". leg.state.fl.us. Retrieved March 28, 2016.
- ^ "40-23-114 – Death by lethal injection Election of electrocution". law.justia.com. Retrieved March 30, 2016.
- ^ "§ 26.3 Date, time, place, and method of execution". law.cornell.edu. Retrieved March 15, 2017.
- ^ "18 U.S. Code § 3597 – Use of State facilities". law.cornell.edu. Retrieved March 15, 2017.
- ^ "Federal regulations 28 CFR 26.4". Archived from the original on January 18, 2014.
- ^ "Texas Execution Information – Texas Execution Primer". www.txexecutions.org. Retrieved August 5, 2015.
- ^ "States go hunting for execution witnesses". jacksonsun.com. Retrieved July 15, 2017.
- ^ "Wyoming Code § 7-13-908". law.justia.com. Retrieved July 15, 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Death Penalty". Gallup. Retrieved July 24, 2019.
- ^ Baumgartner. De Boef, Boydstun, Frank, Suzanna, Amber (2011). The Decline of the Death Penalty and the Discovery of Innocence. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0521715249.
- ^ Peffley, Mark; Hurwitz, Jon (October 1, 2007). "Persuasion and Resistance: Race and the Death Penalty in America". American Journal of Political Science. 51 (4): 996–1012. doi:10.1111/j.1540-5907.2007.00293.x.
- ^ Oliphant, Baxter (September 29, 2016). "Support for death penalty lowest in more than four decades". Dactank; News in Numbers. Pew Research Centre. Retrieved October 5, 2016.
- ^ "Shrinking Majority of Americans Support Death Penalty". Pew Research Center. March 28, 2014. Retrieved January 31, 2018.
- ^ "Public support for the death penalty ticks up". June 11, 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f "Facts about the Death Penalty" (PDF). Death Penalty Information Center. December 9, 2015. Retrieved December 23, 2015.
- ^ Eaton, Judy; Christensen, Tony (June 23, 2014). "Closure and its myths". International Review of Victimology. 20 (3): 327–343. doi:10.1177/0269758014537148. ISSN 0269-7580. S2CID 143577831.
- ^ "Americans at Odds With Recent Terror Trial Decisions". gallup.com. Retrieved April 10, 2016.
- ^ "Foes of death penalty say McVeigh is an exception". usatoday.com. Retrieved April 10, 2016.
- ^ "ReligiousTolerance". ReligiousTolerance. Retrieved December 1, 2011.
- ^ [2][dead link]
- ^ "Why Reform Judaism Opposes the Death Penalty". ReformJudaism.org. Retrieved March 3, 2019.
- ^ Lipak, Adam (January 4, 2010). "Group Gives Up Death Penalty Work". The New York Times.
- ^ "Innocence: List of Those Freed From Death Row". Death Penalty Information Center. October 28, 2010. Retrieved March 11, 2011.
- ^ Pitkin, James (January 23, 2008). "Killing Time Dead Men Waiting on Oregon's Death Row". Willamette Week. Archived from the original on January 24, 2008. Retrieved March 11, 2011.
- ^ Peacock, John. "Jeffrey Wood". Metafilter. Retrieved June 3, 2020.
- ^ Londono, O. (March 5, 2013). "A Retributive Critique of Racial Bias and Arbitrariness in Capital Punishment". Journal of Social Philosophy. 44 (1): 95–105. doi:10.1111/josp.12013.
- ^ "Letter – Cost of the Death Penalty". The New York Times. California. February 28, 2009. Retrieved December 1, 2011.
- ^ "Trump can't break the Supreme Court". The Washington Post. January 25, 2017. Retrieved June 23, 2017.
- ^ "Tom Dolgenos: Under Trump, death penalty likely to remain". mcall.com. January 23, 2017. Retrieved June 23, 2017.
- ^ "Capital Punishment After the 2016 Elections". fed-soc.org. February 6, 2017. Retrieved June 23, 2017.
- ^ "So Long as They Die: Lethal Injections in the United States: VI. Botched Executions". www.hrw.org. Retrieved April 26, 2018.
- ^ "Botched Executions in American History". Death Penalty Information Center. Retrieved May 4, 2018.
- ^ Hannon, Elliot (July 23, 2014). "Arizona Man Gasps and Snorts During Lethal Injection Execution That Took Nearly Two Hours". Slate. Retrieved July 24, 2014.
- ^ "'Gory, botched': Alabama's aborted execution of inmate was bloody, says lawyer". The Guardian. Reuters. February 26, 2018. Retrieved May 4, 2018.
- ^ Segura, Liliana (March 3, 2018). "Another Failed Execution: the Torture of Doyle Lee Hamm". The Intercept. Retrieved August 9, 2019.
- ^ "Botched Executions". deathpenaltyinfo.org. Death Penalty Information Center. Retrieved May 4, 2018.
- ^ Acker, James A.; Champagne, Ryan (May 2, 2018). "The Execution of Wallace Wilkerson: Precedent and Portent". Criminal Justice Review. 42: 349–367. doi:10.1177/0734016817702193. S2CID 148715242.
- ^ "WILKERSON v. UTAH". LII / Legal Information Institute. Retrieved May 4, 2018.
- ^ yongli (September 21, 2016). "Thomas E. Ketchum". coloradoencyclopedia.org. Retrieved May 4, 2018.
- ^ "Capital punishment UK" (PDF). www.capitalpunishmentuk.org.
- ^ "Botched Executions". Death Penalty Information Center. Retrieved March 3, 2019.
- ^ "Clemency". deathpenaltyinfo.org. Retrieved January 14, 2021.
- ^ "Illinois Death Row Inmates Granted Commutation by Governor George Ryan on January 12, 2003". Deathpenaltyinfo.org. Retrieved December 1, 2011.
- ^ "California moves – slowly – toward resuming executions". seattletimes.com. April 23, 2017. Retrieved May 25, 2017.
California has long been what one expert calls a "symbolic death penalty state", one of 12 that has capital punishment on the books, but has not executed anyone in more than a decade.
- ^ "Gov. Gavin Newsom to block California death row executions, close San Quentin execution chamber".
- ^ "Civil Rights Groups Accuse California District Attorneys of Unlawfully Interfering in Death Penalty Lawsuit". Death Penalty Information Center. March 11, 2021. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
- ^ "Kentucky Judge Rules Against Lethal Injection Protocol and Halts Execution". Death Penalty Information Center. Death Penalty Information Center. Retrieved July 11, 2016.
- ^ Bellware, Kim (October 6, 2015). "Montana Judge Strikes Down State's Lethal Injection Protocol". The Huffington Post. Retrieved July 11, 2016.
- ^ 5 Death Sentences Commuted, The Washington Post, November 27, 1986. Retrieved March 24, 2020.
- ^ "Judge says executions unconstitutional". Archived from the original on December 22, 2006.
- ^ Miller, Hayley (March 13, 2019). "Gov. Gavin Newsom Halts Executions In California, Calls Death Penalty 'A Failure'". Huffington Post. Retrieved March 13, 2019.
- ^ Musgrave, Beth (November 26, 2009). "Decision halts lethal injections | Latest Local, State News". Kentucky.com. Retrieved December 1, 2011.
- ^ Jung, Helen (November 22, 2011). "Gov. John Kitzhaber stops executions in Oregon, calls system 'compromised and inequitable'". The Oregonian. Retrieved November 22, 2011.
- ^ Berman, Mark (February 13, 2015). "Pennsylvania's governor suspends the death penalty". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 15, 2015.
- ^ "Federal Government to Resume Capital Punishment After Nearly Two Decade Lapse". The United States Department of Justice. July 25, 2019. Retrieved July 26, 2019.
- ^ "Judge Blocks Justice Department's Plan To Resume Federal Executions". NPR.org. Retrieved November 21, 2019.
- ^ "Attorney General Merrick B. Garland Imposes a Moratorium on Federal Executions; Orders Review of Policies and Procedures". The United States Department of Justice. July 1, 2021. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
Sources[]
- Marian J. Borg and Michael L. Radelet. (2004). On botched executions. In: Peter Hodgkinson and William A. Schabas (eds.) Capital Punishment. pp. 143–168. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511489273.006.
- Gail A. Van Norman. (2010). Physician participation in executions. In: Gail A. Van Norman et al. (eds.) Clinical Ethics in Anesthesiology. pp. 285–291. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511841361.051.
Further reading[]
Books[]
- Bakken, Gordon Morris, ed. (2010). Invitation to an Execution: A History of the Death Penalty in the United States. University of New Mexico Press.
- Banner, Stuart (2002). The Death Penalty: An American History. Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-00751-4.
- Bessler, John D. (2012). Cruel and Unusual: The American Death Penalty and the Founders' Eighth Amendment. Boston, MA: Northeastern University Press.
- Blecker, Robert (2013). The Death of Punishment: Searching for Justice among the Worst of the Worst. St. Martin's Press.
- Delfino, Michelangelo and Mary E. Day. (2007). Death Penalty USA 2005–2006 MoBeta Publishing, Tampa, Florida. ISBN 978-0-9725141-2-5; and Death Penalty USA 2003–2004 (2008). MoBeta Publishing, Tampa, Florida. ISBN 978-0-9725141-3-2.
- Dow, David R., Dow, Mark (eds.) (2002). Machinery of Death: The Reality of America's Death Penalty Regime. Routledge, New York. ISBN 0-415-93266-1 (cloth). ISBN 0-415-93267-X (paperback) (Provides critical perspectives on the death penalty).
- Garland, David (2010). Peculiar Institution: America's Death Penalty in an Age of Abolition. Harvard University Press.
- Hartnett, Stephen John (2010). Executing Democracy, Volume 1: Capital Punishment and the Making of America, 1683–1807. East Lansing, MI: Michigan State University Press.
- Hartnett, Stephen John (2012). Executing Democracy, Volume 2: Capital Punishment and the Making of America, 1635–1843. East Lansing, MI: Michigan State University Press.
- Lane, Charles (2010). Stay of Execution: Saving the Death Penalty from Itself. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers.
- Megivern, James J. (1997). The Death Penalty: An Historical and Theological Survey. Paulist Press, New York. ISBN 0-8091-0487-3.
- Osler, Mark William (2009). Jesus on Death Row: The Trial of Jesus and American Capital Punishment. Abingdon Press. ISBN 978-0-687-64756-9.
- Pfeiffer, Michael J. (2004). Rough Justice. Lynching and American Society, 1874–1947. University of Illinois Press. ISBN 978-0252029172.
The history of lynching and the history of the death penalty in the United States are hopelessly entangled (p. 152).
- Prejean, Helen (1993). Dead Man Walking. Random House. ISBN 0-679-75131-9 (paperback)
(Describes the case of death row convict Elmo Patrick Sonnier, while also giving a general overview of issues connected to the death penalty)
Journal articles[]
- Vidma, Neil and Phoebe Ellsworth. "Public Opinion and the Death Penalty" (Archive). Stanford Law Review. June 1974. Volume 26, pp. 1245–1270.
- Hoffmann, Joseph L. (2005). "Protecting the Innocent: The Massachusetts Governor's Council Report". 95 J. of Crim. L. & Criminology 561.
External links[]
- Capital punishment in the United States
- 1608 establishments in the Thirteen Colonies
- 1972 disestablishments in the United States
- 1976 establishments in the United States
- Crime in the United States
- United States law