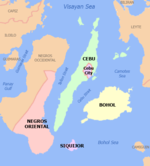
Cebu
Cebu
Sugbo | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Province | ||||||
| Province of Cebu | ||||||
 Flag | ||||||
| Nickname(s): The Gateway to a Thousand Journeys[1] | ||||||
| Anthem: Sugbo (Cebu) | ||||||
 Location in the Philippines | ||||||
| Coordinates: 10°19′N 123°45′E / 10.32°N 123.75°ECoordinates: 10°19′N 123°45′E / 10.32°N 123.75°E | ||||||
| Country | Philippines | |||||
| Region | Central Visayas | |||||
| Founded | 6 August 1569 | |||||
| Capital | Cebu City | |||||
| Government | ||||||
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlalawigan | |||||
| • Governor | Gwendolyn Garcia (PDP–Laban) | |||||
| • Vice Governor | Hilario Davide III (LP) | |||||
| • Provincial Board | Cebu Provincial Board show
Members | |||||
| Area | ||||||
| • Total (province) | 4,943.72 km2 (1,908.78 sq mi) | |||||
| Area rank | 20th out of 81 | |||||
| excludes independent cities | ||||||
| Highest elevation () | 1,015 m (3,330 ft) | |||||
| Population (2020 census) [3] | ||||||
| • Total (province) | 3,325,385 | |||||
| • Rank | 4th out of 81 | |||||
| ��� Density | 670/km2 (1,700/sq mi) | |||||
| • Density rank | 7th out of 81 | |||||
| • Voter (2019)[4] | 3,082,621 | |||||
| • Language | Cebuano Porohanon Bantayanon | |||||
| Population data excludes independent cities | ||||||
| Divisions | ||||||
| • Independent cities | show
3 | |||||
| • Component cities | show
6 | |||||
| • Municipalities | show
38 | |||||
| • Barangay |
| |||||
| • Districts |
| |||||
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) | |||||
| ZIP code | 6000–6053 | |||||
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)32 | |||||
| ISO 3166 code | PH-CEB | |||||
| Income class | 1st class | |||||
| PSGC | 072200000 | |||||
| Patron | Santo Niño de Cebu | |||||
| Website | www | |||||
Cebu (/sɛˈbuː/; Cebuano: Sugbo), officially the Province of Cebu (Cebuano: Lalawigan sa Sugbo; Tagalog: Lalawigan ng Cebu), is a province of the Philippines located in the Central Visayas (Region VII) region, and consists of a main island and 167 surrounding islands and islets. Its capital is Cebu City, "the Queen City of the South", the oldest city and first capital of the Philippines, which is politically independent from the provincial government.
The Cebu Metropolitan Area or Metro Cebu is the second largest metropolitan area in the Philippines (after Metro Manila) with Cebu City as the main center of commerce, trade, education and industry in the Visayas. Being one of the most developed provinces in the Philippines, in a decade it has transformed into a global hub for business processing services, tourism, shipping, furniture-making, and heavy industry. Mactan–Cebu International Airport, located on Mactan Island, is the second busiest airport in the Philippines.
History[]
The name "Cebu" comes from the old Cebuano: sibu or sibo ("trade"), a shortened form of sinibuayng hingpit, 'the place for trading'. It was originally applied to the harbors of the town of Sugbu, the ancient name for Cebu City.[5] Alternate renditions of the name by traders between the 13th to 16th centuries include Sebu, Sibuy, Zubu, or Zebu, among others.[6] Sugbu or Sugbo, in turn, is derived from the Old Cebuano term for "scorched earth" or "great fire".[5][7]

The Rajahnate of Cebu was a native kingdom which existed in Cebu prior to the arrival of the Spaniards. It was founded by Sri Lumay otherwise known as , a half-Malay, half-Tamil prince of the Chola dynasty who invaded Sumatra in Indonesia. He was sent by the Maharajah to establish a base for expeditionary forces to subdue the local kingdoms, but he rebelled and established his own independent Rajahnate instead.[8]
The arrival of Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan in 1521 began a period of Spanish exploration and colonization.[9][10]
Losing the favour of King Manuel I of Portugal for his plan of reaching the Spice Islands by sailing west from Europe, Magellan offered his services to king Charles I of Spain (Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor). On 20 September 1519, Magellan led five ships with a total complement of 250 people from the Spanish fort of Sanlúcar de Barrameda en route to southeast Asia via the Americas and the Pacific Ocean. They reached the Philippines on 16 March 1521. Rajah Kolambu the king of told them to sail for Cebu, where they could trade and obtain provisions.
Arriving in Cebu City, Magellan, with Enrique of Malacca as a translator, befriended Rajah Humabon the Rajah or King of Cebu, and persuaded the natives to ally themselves with Charles I of Spain. Humabon and his wife were given Christian names and baptized as Carlos and Juana. The Santo Niño was presented to the native queen of Cebu, as a symbol of peace and friendship between the Spaniards and the Cebuanos. On 14 April Magellan erected a large wooden cross on the shores of Cebu. Afterwards, about 700 islanders were baptized.
Magellan soon heard of Datu Lapu-Lapu, a native king in nearby Mactan Island, a rival of the Rajahs of Cebu. It was thought that Humabon and Lapu–Lapu had been fighting for control of the flourishing trade in the area. On 27 April the Battle of Mactan occurred, where the Spaniards were defeated and Magellan was killed by the natives of Mactan[11] in Mactan Island. According to Italian historian and chronicler Antonio Pigafetta, Magellan's body was never recovered despite efforts to trade for it with spice and jewels. Magellan's second-in-command, Juan Sebastián Elcano, took his place as captain of the expedition and sailed the fleet back to Spain, circumnavigating the world.

Survivors of the Magellan expedition returned to Spain with tales of a savage island in the East Indies. Consequently, several Spanish expeditions were sent to the islands but all ended in failure. In 1564, Spanish explorers led by Miguel López de Legazpi, sailing from Mexico, arrived in 1565, and established a colony.[12] The Spaniards fought the King, Rajah Tupas, and occupied his territories. The Spaniards established settlements, trade flourished and renamed the island to "Villa del Santísimo Nombre de Jesús" (Town of the Most Holy Name of Jesus). Cebu became the first European settlement established by the Spanish Cortés in the Philippines. In 1595, the Universidad de San Carlos was established and in 1860, Cebu opened its ports to foreign trade. The first printing house (Imprenta de Escondrillas y Cia) was established in 1873 and in 1880, the Colegio de la Inmaculada Concepcion (College of the Immaculate Conception) was established and the first periodical The Bulletin of Cebu ("El Boletin de Cebú") began publishing in 1886. In 1898, the island was ceded to the United States after the Spanish–American War and Philippine–American War. In 1901, Cebu was governed by the United States for a brief period, however, it became a charter province on 24 February 1937 and was governed independently by Filipino politicians.
Cebu, being one of the most densely populated islands in the Philippines, served as a Japanese base during their occupation in World War II which began with the landing of Japanese soldiers in April 1942. The 3rd, 8th, 82nd and 85th Infantry Division of the Philippine Commonwealth Army was re-established from 3 January 1942 to 30 June 1946 and the 8th Constabulary Regiment of the Philippine Constabulary was reestablished again from 28 October 1944 to 30 June 1946 at the military general headquarters and the military camps and garrisoned in Cebu city and Cebu province. They started the Anti-Japanese military operations in Cebu from April 1942 to September 1945 and helped Cebuano guerrillas and fought against the Japanese Imperial forces. Almost three years later in March 1945, combined Filipino and American forces landed and reoccupied the island during the liberation of the Philippines. Cebuano guerrilla groups led by an American, James M. Cushing, is credited for the establishment of the "Koga Papers",[13] which is said to have changed the American plans to retake the Philippines from Japanese occupation in 1944, by helping the combined United States and the Philippine Commonwealth Army forces enter Cebu in 1945. The following year the island achieved independence from colonial rule in 1946.
Cebu became a key center of resistance against the Marcos dictatorship,[14] first becoming apparent when the hastily put-together lineup of Pusyon Bisaya defeated the entire slate of Marcos' Kilusang Bagong Lipunan (KBL) in Region VII.[15] Later, Cebu would play a key role in the days leading up to the 1986 People Power revolution and the ouster of Marcos. It was from Fuente Osmeña circle in Cebu City that the opposition forces relaunched Civil Disobedience Campaign against the Marcos regime and its cronies on February 22, 1986. After that, the Carmelite Monastery in Barangay Mabolo, Cebu City, served as a refuge for opposition candidates Aquino and Laurel during the first day of the People Power revolution, because it was not yet safe to go back to Manila.[16]
In February 2012 Cebu island experienced the effects of magnitude 6.7 earthquake on the neighboring island of Negros and was the largest quake in the area for 90 years. The tremor shook buildings but there were no reports of major building damage or loss of life on Cebu Island itself. This tremor was caused by a previously unrecorded fault.
In October 2013, Cebu and Bohol were hit by record-setting 7.2 magnitude earthquake which left more than 100 dead and collapsed some buildings, including 5 historical churches. There were over 700 aftershocks.
Geography[]
Sugbo | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Visayas |
| Archipelago | Philippines |
| Adjacent bodies of water | |
| Area | 4,467.5 km2 (1,724.9 sq mi)[17] |
| Length | 196 km (121.8 mi)[18] |
| Width | 32 km (19.9 mi)[18] |
| Coastline | 513.9 km (319.32 mi)[17] |
| Highest elevation | 1,097 m (3599 ft)[17] |
| Administration | |
Philippines | |
| Region | Central Visayas |
| Province | Cebu |
| Demographics | |
| Demonym | Cebuanos (masculine) / Cebuanas (feminine) |
| Population | 4,376,010 (2020 census) [3] |
| Pop. density | 980/km2 (2540/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Visayans (Cebuanos) |
Cebu is located to the east of Negros, to the west of Leyte and Bohol islands. The province consists of Cebu Island, as well as 167 smaller islands, which include Mactan, Bantayan, Malapascua, Olango and the Camotes Islands. But the highly urbanized cities of Cebu, Lapu-Lapu and Mandaue are independent cities not under provincial supervision, yet are often grouped with the province for geographical and statistical purposes.
The province's land area is 4,944 square kilometres (1,909 sq mi), or when the independent cities are included for geographical purposes, the total area is 5,342 square kilometres (2,063 sq mi).
Cebu's central location, proximity to an unusually exotic tourist destination, ready access to a diversity of plant, animal and geological wonders within the island, and remoteness from earthquake and typhoon activity are some of the special attributes of Cebu.
Cebu Island[]
Cebu Island is the 126th largest island in the world. Cebu Island itself is long and narrow, stretching 196 kilometres (122 mi) from north to south and 32 kilometres (20 mi) across at its widest point.[18] It has narrow coastlines, limestone plateaus, and coastal plains. It also has rolling hills and rugged mountain ranges traversing the northern and southern lengths of the island.
Cebu's highest mountains are over 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) high. Flat tracts of land can be found in the city of Bogo and in the towns of San Remigio, Medellin and Daanbantayan at the northern region of the province.[18]
The island's area is 4,468 square kilometres (1,725 sq mi),[17] making it the 9th largest island in the Philippines. It supports over 3.5 million people, of which 2.3 million live in Metro Cebu.
Beaches, coral atolls, islands, and rich fishing grounds surround Cebu.
Coal was first discovered in Cebu about 1837. There were 15 localities over the whole island, on both coast; some desultory mining had been carried out Naga near Mount Uling, but most serious operations were at Licos and Camansi west of Compostela and Danao.[19] Active work ceased about 1895 with insurrections, and no production worked for more than ten years. A topographic and geologic survey of Compostela, Danao, and Carmen took place in 1906.[20] The Compostela-Danao coalfield contained about six million workable tons. The tramroads, one from Danao to Camansi, one from Compostela to Mount Licos, were undertaken in 1895, together with a wagon road built in 1877, from Cotcot to Dapdap.
Climate[]
The climate of Cebu is tropical. There are 2 seasons in Cebu − the dry and wet season.[21] It is dry and sunny most of the year with some occasional rains during the months of June to December. The province of Cebu normally gets typhoons once a year or none.
Northern Cebu gets more rainfall and typhoons than southern Cebu because it has a different climate. Typhoon Haiyan (Yolanda) hit Northern Cebu in 2013 killing 73 people and injuring 348 others. Though most typhoons hit only the northern part of Cebu, the urban areas in central Cebu are sometimes hit, such as when Typhoon Mike (Ruping), one of the worst to hit Cebu lashed the central Cebu area in 1990.
Cebu's temperatures can reach a high of 36 °C (97 °F) from March to May, and as low as 18 °C (64 °F) in the mountains during the wet season. The average temperature is around 24 to 34 °C (75 to 93 °F), and does not fluctuate much except during the month of May, which is the hottest month. Cebu averages 70–80% humidity.[22]
Flora[]
Cebu has little remaining forest cover. The remaining forest patches in Cebu are composed primarily of the following tree species.[23]
- Mount Lantoy: Carallia brachiata and introduced species Tectona grandis, Swietenia macrophylla, Gmelina arborea, and Casuarina equisetifolia
- : Carallia brachiata and introduced species Swietenia macrophylla
- forest: Ficus spp., Artocarpus blancoi, , and Cinnamomum cebuense
- : Carallia brachiata
- : Trevesia burckii, , Schefflera actinophylla, Pouteria villamilii, and Palaquium luzoniense
Fauna[]
Endemic species in Cebu include the Cebu Flowerpecker (Dicaeum quadricolor), Cebu Slender Skink (Brachymeles cebuensis), and Black Shama (Copsychus cebuensis).
Administrative divisions[]
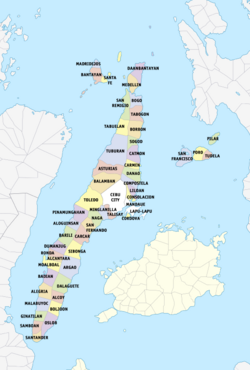
The province of Cebu has 3 independent cities (Cebu, Lapu-Lapu, and Mandaue) that are not under provincial supervision but are grouped with the province for geographical and statistical purposes, 6 component cities (Bogo, Carcar, Danao, Naga, Talisay, and Toledo), and 44 municipalities for a total of 53 units.
Demographics[]
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1903 | 653,727 | — |
| 1918 | 855,065 | +1.81% |
| 1939 | 1,068,078 | +1.06% |
| 1948 | 1,123,107 | +0.56% |
| 1960 | 1,332,847 | +1.44% |
| 1970 | 1,170,386 | −1.29% |
| 1975 | 1,264,357 | +1.56% |
| 1980 | 1,410,346 | +2.21% |
| 1990 | 1,732,386 | +2.08% |
| 1995 | 1,890,357 | +1.65% |
| 2000 | 2,160,569 | +2.91% |
| 2007 | 2,440,120 | +1.69% |
| 2010 | 2,619,362 | +2.61% |
| 2015 | 2,938,982 | +2.22% |
| 2020 | 3,325,385 | +2.46% |
| Excludes independent cities Source: Philippine Statistics Authority [24] [25] [26] | ||
The population of Cebu Province in 2015 was 2,938,982 people, with a density of 590 inhabitants per square kilometre or 1,500 inhabitants per square mile. [3] When the independent cities – Cebu City (922,611[27]), Lapu-Lapu (408,112[27]), and Mandaue (362,654[27]) – are included for geographical purposes, the total population is 4,632,359 people, with a population density of 870 inhabitants per square kilometre (2,300/sq mi).
The population of the Central Visayas is predominantly young with about 37 percent of its population below 10 years old. This is very evident in the very broad base of the population pyramid in the region which has prevailed since 1970 but at a declining rate. A decline of 2.29 percentage points in the proportion of household population below 15 years old was noted from 1980 to 1995. Conversely, an increase of 3.06 percentage points was observed in the 15–64 age group during the same period. The population of the region is evenly distributed between males and females. However, the male population in the region has been increasing at a faster rate compared to the female population.[28]
In 2010, the median age of the population of the province was 23.0 years, which means that half of the population was younger than 23.0 years.[2] This is higher than the median age of 20.8 years that was recorded in 2000.
Languages[]
The Cebuano language is spoken in Cebu, as well as in most areas of the Visayas, including Bohol (where it is spoken as Boholano), Siquijor, western Leyte, Biliran and Negros Island Region (especially in Negros Oriental), as well as most provinces of Mindanao.
In the Camotes Islands, especially in Poro, people there speak their own Visayan language called Porohanon, which has some Masbateño and Waray-Waray influences. Some of the residents in Bantayan islands also speak Bantayanon, a Visayan language related to Hiligaynon.
Religion[]

The majority of its population are Roman Catholic[31] followed by roughly 95% of Cebuanos[citation needed]. There are also followers of Iglesia Filipina Independiente, Islam, Buddhism and Hinduism.
Cebu is the capital of the Catholic faith[32] by virtue of being the first Christian city,[33] the first capital of the Spanish East Indies, and the birthplace of Christianity and the Philippine Church. Pope John Paul II, in his Homily for Families in Cebu (19 February 1981), called the island as the birthplace of Christianity in the Philippines.[34]
The image of Santo Niño de Cebú (Holy Child of Cebu), the oldest Christian image in the Philippines, is enshrined and venerated at the Basilica of Santo Niño. According to Philippine historical documents, the statue of the Santo Niño (Holy Child) was given to the wife of the Rajah of Cebu by the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan. The friendship is depicted in Cebu's cultural event, the Sinulog where street parades and loud drum beats preceded by a Christian Mass is celebrated every third Sunday of January. Cebu has a Roman Catholic Archdiocese and has several major churches, including the Basilica Minor del Santo Niño de Cebu, Cebu Metropolitan Cathedral, Santo Rosario Parish Church, San José–Recoletos Church, Sacred Heart Church, Archdiocesan Shrine of Our Lady of Lourdes, National Shrine of Our Lady of the Rule, National Shrine of Saint Joseph, Archdiocesan Shrine of Our Lady of Guadalupe of Cebu, San Nicolas de Tolentino Church, and other Christian churches, as well as several other non-Catholic churches, mosques and temples.
Government[]
| Former governors | |
|---|---|
| Julio Llorente | 1900–1901 |
| Juan Climaco | 1902–1903 |
| Sergio Osmeña | 1904–1905 |
| Dionisio Jakosalem | 1907–1912 |
| Manuel Roa | 1912–1922 |
| Arsenio Climaco | 1923–1930 |
| Mariano Jesus Cuenco | 1931–1933 |
| Sotero Cabahug | 1934–1937 |
| Buenaventura Rodriguez | 1937–1940 |
| Hilario Abellana | 1941–1943 |
| Jose Delgado | 1943–1944[i] |
| Jose Leyson | 1944–1945;[i] |
| Fructuoso Cabahug | 1945–1946 |
| Manuel Cuenco | 1946–1951 |
| Sergio Osmeña, Jr. | 1952–1955 |
| Jose Briones | 1956–1961 |
| Francisco Remotigue | 1961–1963 |
| Rene Espina | 1964–1969 |
| Osmundo Rama | 1969–1976 1986–1988[i] |
| Eduardo Gullas | 1976[i]–1986 |
| Lito Osmeña | 1988–1992 |
| Vicente de la Serna | 1992–1995 |
| Pablo Garcia | 1995–2004 |
| Gwendolyn Garcia | 2004–2013 2019– |
| Hilario Davide III | 2013–2019 |
| |
- Governor: Gwendolyn Garcia (PDP–Laban/One Cebu/HNP)
- Vice Governor: Hilario P. Davide III (LP/BAKUD)
Congress[]
| District | Representative | Party | Term | Bloc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | Eduardo R. Gullas | Nacionalista[35] | 1 | Majority | |
| 2nd | Wilfredo S. Caminero | NUP | 3 | Majority | |
| 3rd | Pablo John F. Garcia | PDP–Laban/1-Cebu | 1 | Majority | |
| 4th | Janice Z. Salimbangon | PDP–Laban/1-Cebu | 1 | Majority | |
| 5th | Vincent Franco D. Frasco | Lakas/1-Cebu | 1 | Majority | |
| 6th | Emmarie M. Ouano-Dizon | PDP–Laban/1-Cebu | 1 | Majority | |
| 7th | Peter John D. Calderon | NPC | 2 | Majority | |
Economy[]

"Ceboom", a combination of Cebu and boom, has been used to describe the province's economic development. With many beautiful islands, white sand beaches, luxury hotels and resorts, diving locations and heritage sites, high domestic and foreign tourist arrivals have fueled the tourism industry of Cebu. Cebu consistently gets a big share of tourist arrivals in the Philippines and has become the tourist gateway to Central and Southern Philippines due to its central geographic location, accessibility, and natural resources. The province also hosts various national and international conferences every year.
About 80% of domestic and international shipping operators and shipbuilders in the Philippines are located in Cebu. Shipbuilding companies in Cebu have manufactured bulk carriers of up to 70,000 tonnes deadweight (DWT), and double-hulled fastcraft as well. Cebu's industry helps make the Philippines the 5th largest shipbuilding country in the world.
Cebu's extensive port facilities and its proximity to intra-Asian shipping and air routes are major factors which led multinational companies to establish offices or factories on the main island, as well as in the island of Mactan, where they are clustered in special economic zones known as the Mactan Economic Processing Zone 1 (MEPZ-1) and the Mactan Economic Processing Zone 2 (MEPZ-2). Due to its burgeoning furniture-making industry, Cebu has been named as the furniture capital of the Philippines. Cebu's other exports include: fashion accessories, guitars, coconut, coconut oil, dried mangoes, carrageenan, gifts, toys, watches, cameras, electronic components, and housewares.
With a revenue growth rate of 18.8 percent in 2012, the real estate industry is the fastest-growing sector in Cebu. With the strong economic indicators and high investors' confidence level, more condominium projects and hypermarkets are being developed in the locality. An additional 100 commercial and residential buildings would be completed by 2015 and another 170 to 200 buildings are expected to be finished by 2017. 64 new hypermarkets will be developed in Cebu.[43]
In 2013, Cebu ranked 8th worldwide in the "Top 100 BPO Destinations Report" by global advisory firm, Tholons.[44][45] The Cebu Chamber of Commerce and Industry, an organization of Cebu's businesses, is promoting the city's growth and economy on information and communications technology, with the aim of making Cebu the premier ICT, software and e-services investment destination in southeast Asia. Data gathered by the National Economic Development Authority (Neda) 7 showed that of the 98 BPO and IT companies operating in Cebu, 32 offer voice operations while 66 companies offer non-voice operations. Of the 95,000 employed by the industry, more than half or 50,000 are in the non-voice sector. In 2012, the growth in IT-BPO revenues in Cebu grew 26.9 percent at $484 million, while nationally, the industry grew 18.2 percent at $13 billion.[46][47]
Cebu's economy is also driven by the mining and quarrying areas in Toledo, Naga, Alcoy, and Danao.
Cebu even boasts being a subsidiary of one of the leading ice rink manufacturers in the world. These rinks are engineered and fabricated in Cebu by Ice Rink Supply and shipped worldwide [48] and Freeze Point Rink Services.[49]
Infrastructure[]

The Mactan–Cebu International Airport (MCIA) in Mactan Island serves as the main gateway to domestic and international routes to or from Cebu City and other islands in the Visayas region. In the last 15 years, MCIA's passenger traffic has grown at an annual average of 21% for international passenger traffic. The airport is the second busiest airport in the Philippines in passenger and cargo traffic. The plan for a new terminal expansion of the airport is underway and estimated to cost $240 million under a public-private partnership program of the Philippine government. The new terminal will host international flights while the old terminal will host domestic flights.[50]
In addition, MCIAA (MCIA Authority) General Manager Nigel Paul Villarete (who was the project of BRT earlier) also proposed to establish a Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) line to transport airport passengers to and from MCIAA and different parts of Cebu. This will be integrated into the proposed Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) System being planned in Metro Cebu.
The Port of Cebu is the largest shipping hub in the Visayas region.
Cebu Pacific Air is an airline owned by Cebu-based Gokongwei family. On 28 May 2008, Cebu Pacific was named as the world's number one airline in terms of growth. The airline carried a total of almost 5.5 million passengers in 2007, up 57.4% from 2006.[51] On January 6, 2011, Cebu Pacific flew its 50 millionth passenger (from Manila to Beijing). The airline reached the 100 million passengers in 2015.[52] Cebu Pacific commenced international long-haul flights to Middle East and Australia, flight to Guam starting Q1 2016.
Notable business districts are the Cebu Business Park and the Cebu IT Park. This area hosts industries related to the information technology industry such as software development, telecommunications, engineering research and development centers, and business process outsourcing. In 2013, Ayala Corporation's affiliate, Ayala Land Inc., announced that it is looking at introducing another business park development within the Cebu City area to optimize the high performance of real estate investments in Cebu.[53]

The city's 300-hectare (740-acre; 3.0 km2; 3,000,000 m2) reclamation forms South Road Properties – a mixed-use development south of the city which features entertainment, leisure, residential and business-processing industries.[54] Is the site of SM Seaside City Cebu, the eighth largest mall in the world (and 3rd largest shopping mall in the Philippines), Filinvest's Citta di Mare[55] and Il Corso,[56] and the University of the Philippines – Cebu campus.[57]
In Mactan Island, Megaworld Corporation's Mactan Oceantown is a 25–hectare business park near Shangri-La's Mactan Resort and Spa. The project will be home to high-tech offices, a retail center, residential towers and villages, leisure facilities with a beach resort frontage.[58]
Mactan Island is linked to mainland Cebu via Mactan-Mandaue Bridge and Marcelo Fernan Bridge.
Media[]
Cebu is home to a local television station, Cebu Catholic Television Network (CCTN)[a]).
Despite having their local stations, Cebuanos prefer to watch the Philippine four dominant television networks namely: ABS-CBN, People's Television Network, IBC, The 5 Network, CNN Philippines, and GMA Network.
While national newspapers have a presence on the island, Cebu has English-language local newspapers – The Freeman (under the Star Group), SunStar Cebu and Cebu Daily News (under the Inquirer Group): and Cebuano-language newspapers – SunStar SuperBalita owned by SunStar, and Banat News owned by The Freeman. Each of the local newspapers sell cheaper than their national counterparts.
Education[]
The Philippine elementary school begins from Grades 1 to 6. The high school program takes six years, from Grades 7 through to 12, taken after graduating from elementary school. Cebu is considered as the main education hub in the Visayas. It has eleven large universities each with a number of college branches mostly throughout the capital, Cebu City, and more than a dozen other schools and universities specializing in various courses such as Medicine, Engineering, Nautical courses, Nursing, Law, Commerce, Education, Computer and IT and other professions.
The most prominent of these universities are (in alphabetical order):
- Cebu Doctors University
- Cebu Institute of Technology–University
- Cebu Normal University
- Cebu Technological University
- Southwestern University
- University of Cebu
- University of San Carlos
- University of San Jose–Recoletos
- University of Southern Philippines Foundation
- University of the Philippines Cebu
- University of the Visayas
Other notable institutions include: Asian College of Technology in Cebu City and Talisay, Benedicto College, Cebu Eastern College, Cebu Institute of Medicine, a medical school in affiliation with Velez College, The International Academy of Film and Television, established in Mactan in 2004 and Cebu's first film school, Matias H. Aznar Memorial College of Medicine, Salazar Colleges of Science and Institute of Technology, among others.
Cebu is home to one fully accredited international school, Cebu International School, a K–12 school established in 1924. Cebu is considered to be a hub of medical education, with many international students coming to study medicine in Cebu's medical schools. Some of Cebu's well-known medical schools are in Cebu Doctors University and Cebu Institute of Medicine.
Tourism[]
Attractions[]
Cebu City is a significant cultural centre in the Philippines. The imprint of Spanish and Roman Catholic culture is evident. There are also many historically important sights all over the province.

Bagacay Point Lighthouse, Liloan
Bounty Beach, Malapascua Island, Daanbantayan

Tingko Beach, Alcoy

Island in the Sky mountain resort, Balamban
Bantayan from far end of quay

Boljoon Church Boljoon

Carcar Museum (formerly Carcar Dispensary), Carcar

St. Vincent Ferrer Church, Bogo

Waterfalls in Cebu
Festivals[]
- Sinulog


Sinulog Festival is the largest fiesta (festival) in the Philippines. Held every third Sunday of January, it commemorates the Child Jesus (Santo Niño), the Lord and Protector of Cebu. The Sinulog is a dance ritual of pre-Hispanic indigenous origin. The dancer moves two steps forward and one step backward to the rhythmic sound of drums. This movement resembles the current (sulog) of what was then known as Cebu's Pahina River. Thus the name Sinulog.
The Sinulog Festival celebration lasts for nine days, culminating on the final day with the Sinulog Grand Parade. The day before the parade, the Fluvial Procession is held at dawn with a statue of the Santo Niño carried on a pump boat from Mandaue City to Cebu City, decked with hundreds of flowers and candles. The procession ends at the Basilica where a re-enactment of the Christianization of the Philippines on the island of Cebu is performed. In the afternoon, a more solemn procession takes place along the major streets of the city, which last for hours due to large crowds participating in the event.
When the Spaniards arrived in Cebu, the Italian chronicler, Antonio Pigafetta, sailing under convoy with the Magellan expedition, offered the wooden figure of the Santo Niño as a baptismal gift to Hara Amihan, wife of Rajah Humabon who was named Juana after her baptism together with the Rajah, who was also renamed, Carlos. Juana, together with the natives, according to tradition, danced and worshipped the Santo Niño de Cebu in their indigenous Sinulog dance ritual.[citation needed] The Sinulog ritual was preserved, focusing on the worship to the Santo Niño. Once the Santo Niño church was built in the 16th century, the Catholic Malay people started performing the Sinulog ritual in front of the church, the devotees offering candles and indigenous dancers shouting "Viva Pit Señor!", which means to "Trust in the Lord"[citation needed].
In the province, the festival is shared by both Cebu City and Carmen. The festival is said to have originated in Carmen and was once a localized version of the Ati-atihan Festival introduced by Jose Motos, the then rector of the Parish of St. Augustine, the town parish of Carmen, but was then changed to "Sinulog sa Carmen" after Sinulog became an established Cebuano festival. The Sinulog dance was first introduced to Cebu City by a woman named Estelita Diola, who would otherwise be referred to as "Titang Diola". Her family were skilled with the original form of the dance of Sinulog and the tradition was eventually passed on to her by her father. Because of her great contribution and propagation of the Sinulog dance of Cebu, she was referred to as the "Heritage Keeper". The original Sinulog dance and her legacy of devotion to the Child Jesus through dancing continues today even after her death and is still continued through her former students who now teach the youth of Cebu the original dance moves of Sinulog. Sinulog had since very much diversified from the original dance of Titang Diola. Today we can see the Sinulog danced everyday at the Basilica Minore del Santo Niño performed by the candle vendors. The version they perform is called "Sinug" and is only for worship and prayer to bless the candles for prayers to the Holy Child. The Sinulog Festival dance performed by contingents in the City Sports Center is still religious and devotional since dancers often include personal supplications, petitions, thanksgivings, intercessions, or any other prayers in their dance for the Child Jesus and their dance performances in street dance and ritual showdown are still centered on the Holy Child. There are mainly two types of Sinulog dances performed in the festival, namely the "Sinulog-Based Category" and the "Free Interpretation Category". The Sinulog-Based Category refers to the Sinulog dance based on the Church Sinulog performed by candle vendors while the Free Interpretation Category refers to the Sinulog dance interpreted in any way, outside Church Sinulog, for as long as it is acceptable in the festival. In recent years, the festival gained commercialization which made the festival and Cebu popular, but unfortunately lessened the religious nature of the festival. Despite the extreme commercialization of the festival, Sinulog still remains to be a religious festival for the faithful
In the 1980s and 2000s, the city authorities of Cebu added the religious feast of Santo Niño de Cebu during the Sinulog Festival to its cultural event. Despite being a religious festival and a Christian festival, Sinulog has come to be a celebration for all Cebuanos and Filipinos regardless of their faith and practices. Aside from its religious nature, Sinulog has also become renowned for its street parties. In 2012, Cebu introduced Life Dance, the biggest outdoor dance party in the Philippines. The Sinulog street parties are considered a major attraction for youth individuals but, in most cases for most people, particularly the faithful, a growing problem that threatens the religiosity and solemnity of the festival. In 2016, the festival had the worst recorded case of a stampede wherein large groups of people, both worshippers and drunken party-goers, were congested in the uptown area, with no passable exit routes and virtually no crowd control up until midnight and with one recorded case of a teenage woman losing consciousness because of cramped spaces. Due to this incident, the then Cebu City Mayor Tomas Osmeña enforced a strict liquor ban in the following festivals during his term to ensure the safety of the worshippers and spectators and to maintain the solemnity of the celebration.
- Kadaugan sa Mactan
Literally translates to the "Victory in Mactan", this is a historical festival reenactment of the Battle of Mactan. Celebrated canonically on the 27th of April, It depicts the events before, during, and immediately after the defeat of Portuguese Navigator Ferdinand Magellan at the hands of Lapu-lapu and his men. Usually, in the Kadaugan sa Mactan, Filipino celebrities, especially celebrities of Cebuano origin, are chosen to portray the key characters of the events of the Battle of Mactan (specifically Lapu-lapu, his wife Reyna Bulakna, and Magellan). This is typically a week-long celebration and culminates with the Rampada Festival, a stylized contemporary reenactment of the victory celebration after the battle in Mactan, incorporating Latin and ballroom dances and steps. Despite the Sinulog Festival being more popular by comparison, the Kadaugan had already been established as a festival of Cebu and its culture and history long before Sinulog was an established festival.
- Pasigarbo sa Sugbo
Literally translates to the "Celebration in Cebu", this Festival is a relatively new festival in Cebu, conceptualized in 2008. This festival was the "Brainchild" of Cebu's first female governor, Gwendolyn Garcia. This festival was a program and a major tourism endeavor initiated by the governor in order to promote Cebu as an entire province and to celebrate Cebu in its culture, faith, history, and continuous advancement. In this festival, each individual town in Cebu is encouraged to showcase a theme, a product, a festival, or something unique from their place. Despite, in itself, not being a religious festival, praise, thanksgiving, and worship to God, as well as devotion to the patron saints of each town of Cebu is also given emphasis in the festival (as hinted in the category for portable processional platforms for patron saints or Best in Andas category). Unlike the Sinulog Festival, which is limited to two major categories (Sinulog-based and Free Interpretation), Participants of Pasigarbo are given more freedom in the interpretation of the culture, faith, history, and products of their hometowns. Ever since its conception, the festival had been celebrated yearly at the Cebu International Convention Center (CICC) in Mandaue, around the date of the Provincial Charter Day of Cebu which is celebrated every 6 August, however, was ceased after 2012. This was largely due to the 2013 Bohol earthquake, which also heavily affected Cebu, as well as the lack of support from the provincial government for both the repair of the CICC and the festival itself. This was mainly because Garcia was no longer in position as governor at the time. Fortunately, the festival was recently relaunched in 2019, less than a month after Garcia's return to the provincial seat. Unlike previous celebrations, the 2019 Pasigarbo, due to the abandoned state of the CICC, was celebrated, much like the Sinulog Festival, in the Cebu City Sports Complex. As per its return, it has established itself once more as a provincial festival and a new addition to Cebu's prime festivals and significant dates, together with the Sinulog Festival and the Kadaugan sa Mactan.
Other Festivals[]
- Panagtagbo sa Mandaue
This is a religious festival from Mandaue City that is in honor of the Holy Family and is greatly inspired from and is associated directly with the religious activities of the Sinulog Festival. The name of the festival is the Cebuano term for "gathering". This is because the festival celebrates the Translacion (Transfer of Relic) of the Santo Niño de Cebu and Our Lady of Guadalupe to the Archdiocesan Shrine of St. Joseph, the patron saint of Mandaue. It replaced the Mantawi Festival as the festival of Mandaue. The Festival is celebrated on the Thursday before the Sinulog Festival or the day before the Translacion which marks the start of the Triduum of the "Fiesta Señor" activities.
- Sugat Kabanhawan
This is the Easter Festival of Minglanilla. It is held in honor of Jesus Christ as the "Risen Lord". It celebrates the mystery of the Resurrection of Jesus and the traditional belief of the faithful in Christ's apparition to the Blessed Virgin Mary in a private revelation in order to reveal to her that He had risen from the dead and is truly God. The festival's name is taken from the term Sugat (Cebuano) or Salubong (Filipino) which is a traditional practice during Easter Vigils wherein an image of Christ is shown before an image of the Virgin Mary that is covered in a black veil to show her mourning and sadness, which is then lifted by angels, exposing the Virgin Mary with unspeakable joy at the Resurrection of Jesus. The second part of the name is the Cebuano word for "resurrection", which is timely for the religious celebration. The Festival is centered on the life of Jesus, as well as Christian Morals and Values, with both themes being heavily incorporated in the performances of the dancers in the festival. This festival has gained Minglanilla the title as the "Easter Capital of Cebu".
- Kabkaban
The Kabkaban Festival is the local religious festival of the City of Carcar in honor of St. Catherine of Alexandria. The festival's name was the old name of Carcar, which was taken from Kabkab ("Kabkaban" for plural), the local term for the Oakleaf Fern (Aglaomorpha quercifolia). The festival celebrates Carcar, as well as the Carcaranon way of life and the town's culture, faith, and musical history. Much of the dance steps used in the Kabkaban dance were taken and inspired directly from the dance moves used in the Sinulog Festival and other Sinulog dance offerings by the Sandiego Family with their company, the "Sandiego Dance Company", headed by Val Sandiego, a native of Carcar. The ispiration from the dance company is also evident in the costumes used by the dancers of the Kabkaban Festival, as well as dancers representing Carcar in the Sinulog Festival or other festivals like the Pasigarbo sa Sugbo Festival of Festivals. The Kabkaban festival is celebrated from the 23rd until the 25th of November, in line with the feast day of the town's patron saint.
- La Torta

The La Torta Festival is Argao's food festival. It is in honor of St. Michael the Archangel. It replaced Argao's former festival, the "Pitlagong Festival" in 2011. It celebrates the Torta, a Cebuano Tart that is reminiscent to the Spanish Tart, but distinct in its recipe as it uses Tuba or palm wine as a rising agent instead of yeast. Because Argao is one of Cebu's Spanish Towns (the other being Liloan), dancers in the La Torta Festival wear Spanish inspired costumes that usually have a red motif to them and dance Spanish dance steps or Spanish-inspired dance steps. It is celebrated on the 28th up to the 29th of September to coincide with the feast of the archangels.
- Dagitab
The Dagitab Festival is Naga's Christmas Festival. It is in honor of St. Francis of Assisi. The name of the festival means "electric light" which is what Naga is known for, particularly during the Holidays. During December, Naga's streets, parks, and buildings are lit with all sorts of bright lights of different colors to mark the Holiday Season. But these bright lights come at a cost, power outages. To resolve this problem, Gov. Gwen Garcia, together with the Province of Cebu, set up another electric company to supply electricity in the town. The onset of electric advancements and greater connection initiated the start of the industrialization of Naga. The industrial movement is also one of the focuses of the festival. Dancers in the Dagitab Festival wear and incorporate LED lights/lamps in their lively performances to bring the Holiday Spirit to everyone and to celebrate the advancement of the city. This festival has gained Naga the titles of being the "Christmas Capital of Cebu" and the "Industrial Hub of the South". Despite being in honor of St. Francis, whose feast day is on the 4th of October, the festival is celebrated on the 23rd of December which is two days before Christmas Day.
- Halad Inasal
The Halad Inasal Festival is Talisay's food festival. It is in honor of St. Teresa of Avila. The name of the festival is taken from the Cebuano words Halad, which means offering, and Inasal, which refers to the local term for Lechon or Philippine Roasted Pig. Cebu is well known for producing Lechon Inasal and has two towns that are dedicated "Lechon Towns" with one being Talisay (the other being Carcar). The festival was formerly called simply the "Inasal Festival", but was renamed as "Halad Inasal Festival" to highlight the religiosity of the festival. In the Halad Inasal Festival, dancers and participants parade freshly roasted and crunchy Inasal in the streets of Talisay while they perform their dance offerings and bring them even while they perform their ritual showdown. It is celebrated around, but never directly on the 15th of October, the feast of St. Teresa, so as not to interfere with the religious activities of the town feast.
- Bonga
The Bonga Festival is the Harvest Festival of Sibonga. It is in honor of the town's two patron saints, St. Philomena and Our Lady of the Pillar. The name of the festival is the Cebuano word for "fruit". It is a festival of thanksgiving for the bountiful fruit harvest during the harvest season of the town. It is celebrated on the 12th of October, in line with the feast of the original patroness of the town, the Blessed Virgin. The festival has given the town its very own title as the "Fruit Basket of Cebu".
- Rosquillos (Festival)

The Rosquillos festival is the food festival of Liloan. It is in honor of St. Ferdinand of Castille. It celebrates the Rosquillos, a Philippine ring type cookie that originated from Liloan. The cookie was conceptualized and conceived by a woman named Titay Frasco, who was the founder of Titay's, the largest chain company of Rosquillos in the Philippines. It is celebrated on the 30th of May.
- Kagasangan
This is the sea festival of Moalboal. It is in honor of St. John of Nepomuk. The name of the festival is taken from the Cebuano term for "coral reefs. It is a nature-tourism project initiated by the local government made to preserve the reefs of the town, which are viable sources of livelihood and eco-tourism. This is one of the known sea festivals in the Province of Cebu. It is celebrated on the 16th of May.
- Utanon
The Utanon Festival of Dalaguete, is the town's harvest festival. It is in honor of St. William the Hermit. The name of the festival is the Cebuano word for "vegetables". It is a festival about showing thanksgiving for the bountiful harvest of vegetables in the town, all year round. It is celebrated on the 10th of February. The festival has helped acknowledge the town as a producer of grain and vegetable crops, giving the town the title as the "Salad Bowl of Cebu".
- Siloy
The Siloy Festival is Alcoy's nature festival and eco-tourism project. It is in honor of St. Rose of Lima. The festival takes its name from the local term of the Black Shama Bird (Copsychus Cebuensis), a local species of song bird only found in Cebu, with its last stronghold in Alcoy's rainforest and woody areas. The festival is a project meant to promote awareness of the Black Shama and its endangered nature and to help preserve Cebu's endemic Shama species of birds, as well to help save Mother Earth. It is celebrated on the 23rd of August every year.
- Palawod
The Palawod Festival is the sea festival of Bantayan. It is in honor of Sts. Peter and Paul, who are both the town's patron saints. The festival's name means "to voyage into deep waters". This is a festival of thanksgiving for the bountiful catch and for the abundance of the sea and its bounty. It is celebrated on the 29th of the month of June to be connected with the Solemnity of Sts. Peter and Paul.
- Tostado
The Tostado festival is the food festival of Santander. It is in honor of St. Gabriel the Archangel. It celebrates the Tostado, a Cebuano shortbread cookie that is shaped like a flower. The local economy had been heavily boosted thanks to the Tostado cookie, which had provided job opportunities for many people. This festival also celebrates the resources of the town. It is celebrated on the 3rd Sunday of April.
- Isda
This is the sea festival and town fiesta of Madridejos. It is in honor of the Immaculate Conception. The name of the festival is the Cebuano word for "fish". It celebrates the bountiful catch and the abundance of fish species and other marine life in the area. It is celebrated on the 8th of December, which is also the Solemnity of the Immaculate Conception of the Blessed Virgin Mary.
- Banig
This is the weaving festival of Badian. It is in honor of St. James the Great. It celebrates the Banig, a hand-woven Philippine mat made from Pandanus leaves that is commonly sold, in the province, in Badian. It is celebrated on the 25th of the month of April.
- Hinulawan
This is the town fiesta of Toledo. It is in honor of St. John of Sahagun. The name of this festival is an amalgamation of two Cebuano words, Hinaguan, which means "fruits of labor", and Bulawan, which means "bright" or "golden". This was, historically, the old name of the town. Currently, it is the name of a river that is found in the town. Hinulawan Festival celebrates the rich culture and history of the town, as well as the golden hearts and the shining and welcoming personality of the Toledohanons. It falls on the 12th of June, which coincides with the Philippine Independence Day celebration.
- Toslob
Originally called the "Sadsad Festival", this is the local festival of Oslob. Like the Isda Festival, It is in honor of the Immaculate Conception. The name of the festival is the Cebuano term for the act of "dipping". The name of the festival is a reference to the etymology of the name of the town wherein two Spanish soldiers mistakenly identified the town after asking a couple who, due to misinterpretation, thought they were referring to what they were doing. The couple did not understand that the soldiers were asking for the name of the town and simply thought they were referring to the boiled bananas they were dipping in salted vinegar so all they could utter was "Toslob". The soldiers seemingly also misheard them and thought they said "Oslob". Ever since then, the town was referred to by that name which the Spanish Soldiers heard. The Toslob festival is a celebration of thanksgiving for the graces received as a town community. It is celebrated on the 8th of December, which is also the Solemnity of the Immaculate Conception of the Blessed Virgin Mary.
- Pamuhuan
This is the harvest festival of Pinamungajan. It is in honor of St. Monica. The name of the festival came from the Cebuano word, Pinamuhuan, which means "a worker's share of the harvest". It is a celebration of thanksgiving for the bountiful harvest in the town. It is celebrated on the 27th of August.
- Lalin
This is the town fiesta of Asturias. It is in honor of St. Roch. The name of the festival comes from the Cebuano word which refers to the combination of cultures of different people. The festival's name was taken from the old name of the town, which was Naghalin. The town was called "Naghalin" because it was a place where migrants settled and formed a neighborhood. The neighborhood soon flourished into a community and a town of Cebu. This festival is a celebration of thanksgiving for the graces received by the town and the community. It is celebrated on the 16th of August.
- Panagsogod
- Sarok
- Tagbo
- Tubod
- Katubhan
- Putting Baybay
- Lingaw-sadya
- Garbo
- Karansa
- Soli-soli
- Kinsan
- Binuyocan/Buyoc
- Humba
- Haladaya
- Bahandi
- Lapyahan
- Hinatdan
- Dinagat
- Pintos
- Tuba (Festival)
- Budbod Kabog
- Sinanggiyaw
- Cassava (Festival)
- Kawayan
- Dagayday
- Pamugsay
International relations and sisterhood agreements[]
- Cebu Province hosted two major Information and Communications Technology (ICT) and telecom events, the 12th ASEAN Telecommunications and IT Ministers Meeting (TELMIN) and the 13th ASEAN Telecommunications and IT Senior Officials Meeting (TELSOM) in 2012.
- Cebu Province hosted the international 4th Dance Xchange, a project organized by the National Dance Committee of the National Commission for Culture and the Arts in 2012.
- Cebu Province as member hosted the 11th East Asia Inter-Regional Tourism Forum in 2011[59]
- Cebu Province join as a participating member of Inter–Island Tourism Policy Forum in 2011 (ITOP Forum)[60]
- Cebu Province hosted the 12th ASEAN Summit in 2007.[61]
 Sichuan, China (2006)
Sichuan, China (2006) Vladimir, Russia (2008)
Vladimir, Russia (2008) Ljubljana, Slovenia (2008)
Ljubljana, Slovenia (2008) Gangwon, South Korea (2008)
Gangwon, South Korea (2008) Guam, United States of America (2008)
Guam, United States of America (2008) Rishon LeZion, Israel (2009)
Rishon LeZion, Israel (2009) Saint Petersburg, Russia (2009)
Saint Petersburg, Russia (2009) Guangdong, China (2009)
Guangdong, China (2009) Guangxi, China (2010)
Guangxi, China (2010) Barcelona, Spain (2010)
Barcelona, Spain (2010) Autonomous Republic of Crimea, Ukraine (2010)
Autonomous Republic of Crimea, Ukraine (2010) Busan, South Korea (2011)
Busan, South Korea (2011) Ninawa, Iraq (2011)
Ninawa, Iraq (2011) Valparaíso, Chile (2011)
Valparaíso, Chile (2011) Fujian, People's Republic of China (2018)
Fujian, People's Republic of China (2018)
- Existing sisterhood agreements
 Hainan, China
Hainan, China Hawaii, United States of America
Hawaii, United States of America
- Domestic sisterhood agreements
- Sorsogon City
- Antique
- Ilocos Norte
- South Cotabato
- Bukidnon
- Masbate
- Laguna
- Quezon
- Parañaque
- Pangasinan
- Davao del Sur
Notes[]
- ^ a religious station partly owned and endorsed by the Archdiocese of Cebu
References[]
- ^ "What To Know About Cebu, Philippines". The Philippines dot com. Retrieved 21 August 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Province: Cebu". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Census of Population (2020). "Region VII (Central Visayas)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ "Number of Registered Voters by Sex : 2019 National and Local Elections" (PDF). Commission on Elections. 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Macachor 2011.
- ^ "Welcome to Cebu – History". www.sinulog.ph. Archived from the original on July 14, 2008.
- ^ Montebon 2000, p. 15.
- ^ Montebon 2000, pp. 89–90.
- ^ "Philippine History – Spanish Colonization". Archived from the original on 8 January 2011.
- ^ information.ph 2009a.
- ^ "Cebu – History". www.cebu.gov.ph.
- ^ information.ph 2009b.
- ^ de Viana 2005.
- ^ Mayol, Ador Vincent S. (2016-12-01). "Cebuanos honor 7 martyrs, 8 survivors of martial law". The Philippine Daily Inquirer. Retrieved 2021-03-03.
- ^ Almendras, Ruben (2019-05-14). "The Pusyon Bisaya phenomenon". The Freeman. Retrieved 2021-03-03.
- ^ Erram, Morexette Marie B. (2021-02-25). "Cebu and the days leading to February 25, 1986". Cebu Daily News. Retrieved 2021-03-03.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d UNEP 1998.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Encyclopædia Britannica 2016.
- ^ Abella y Casariego 1886.
- ^ Smith 1907.
- ^ "Weather". Archived from the original on 2013-05-25. Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ^ "Guide to Cebu – Weather in Cebu". www.guidetocebu.com. Archived from the original on 2010-08-26. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ Supsup, Christian & Puna, Nevong & Asis, Augusto & Redoblado, Bernard & Fatima Panaguinit, Maria & Guinto, Faith & Rico, Edmund & Diesmos, Arvin & Brown, Rafe & Mallari, Neil. (2016). Amphibians and Reptiles of Cebu, Philippines: The Poorly Understood Herpetofauna of an Island with Very Little Remaining Natural Habitat. Asian Herpetological Research. 7. 151–179. 10.16373/j.cnki.ahr.150049.
- ^ Census of Population (2015). "Region VII (Central Visayas)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region VII (Central Visayas)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^ Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region VII (Central Visayas)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Press release". psa.gov.ph.
- ^ "More on demographics". The Commission on Population of the Philippines. Archived from the original on 2011-10-05. Retrieved 27 August 2011.
- ^ "Table 4. Household Population by Ethnicity and Sex: Cebu, 2000". Archived from the original on 2014-01-20.
- ^ Basilica del Santo Niño is named by the Vatican as "mother and head of all churches in the Philippines" (mater et caput... omnium ecclesiarum Insularum Philippinarum). See Ut clarificetur
- ^ "Cebu – Paradise: Culture and Lifestyle". www.cebu.gov.ph. Archived from the original on 2018-07-19. Retrieved 2009-12-10.
- ^ Bautista 2006.
- ^ Blair, Robertson & Vol 2, p. 121.
- ^ "19 February 1981: Mass for families, Cebu City, Philippines – John Paul II". Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2020-07-27. Retrieved 2019-09-26.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Poverty incidence (PI):". Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 28 December 2020.
- ^ https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/NSCB_LocalPovertyPhilippines_0.pdf; publication date: 29 November 2005; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- ^ https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/2009%20Poverty%20Statistics.pdf; publication date: 8 February 2011; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- ^ https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province%20%20-%202006%2C%202009%2C%202012%20and%202015.xlsx; publication date: 27 August 2016; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- ^ https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province%20%20-%202006%2C%202009%2C%202012%20and%202015.xlsx; publication date: 27 August 2016; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- ^ https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province%20%20-%202006%2C%202009%2C%202012%20and%202015.xlsx; publication date: 27 August 2016; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- ^ https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Updated%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%20with%20Measures%20of%20Precision%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province_2015%20and%202018.xlsx; publication date: 4 June 2020; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- ^ "Real estate sector fastest growing industry in Cebu". SunStar Cebu. Retrieved 25 June 2013.
- ^ "Cebu rises to 8th best site for BPOs". SunStar Cebu. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- ^ "Metro Manila, Cebu among top global BPO destinations". Yahoo! Philippines. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- ^ "Non-voice overtakes voice operation in Cebu". SunStar Cebu. Retrieved 25 June 2013.
- ^ "Cebu Park District, Cebu Holdings". Archived from the original on 2013-01-01. Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ^ "Ice Rink Supply, Banilad, Cebu". Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ^ "Freeze Point – Ice Rink Supplier, Mandaue, Cebu". Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ^ "Philippine PPPs queue up investors". InvestVine.com. 3 April 2013.
- ^ "Cebu Pacific is world's No. 1 in growth". Archived from the original on 2015-10-16. Retrieved 2015-08-26.
- ^ "Cebu Pacific Reaches 50 Million Passengers Mark". Airline-philippines.com. Archived from the original on 2012-03-16. Retrieved 26 June 2013.
- ^ Sun.Star (22 April 2013). "Cebu Holdings Inc. planning new business district". Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ^ "About South Road Properties". City Government of Cebu. Archived from the original on 2013-03-01. Retrieved 20 February 2013.
- ^ "City di Mare". Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ^ Libotero, Sinjin Pineda (7 June 2013). "Filinvest's Il Corso mall rises at SRP-Cebu". Archived from the original on 31 August 2015. Retrieved 17 February 2016.
- ^ "University of the Philippines Cebu". University of the Philippines Cebu.
- ^ Mactan Oceantown – Mactan, Cebu City, http://www.megaworldcorp.com/Projects/Office.aspx
- ^ "11th East-Asia Tourism Forum (EATOF) Integrated Academic, Tourism and Business Forum Business Matching | Cebu Chamber of Commerce and Industry". Cebuchamber.org. 12 September 2011. Archived from the original on 4 July 2013. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ Manila Bulletin 2011.
- ^ "ASEAN Leaders Sign Five Agreements at the 12th ASEAN Summit, Cebu, the Philippines, 13 January 2007" (Press release). ASEAN Secretariat. 13 January 2007. Archived from the original on 2007-01-28. Retrieved 28 January 2007.
12th ASEAN Summit, five.
Bibliography[]
- Abellana, Jovito (1952). Aginid, Bayok sa Atong Tawarik (in Cebuano).
- Abella y Casariego, Enrique (1886). Rápida descripcion física, geológica y minera de la Isla de Cebú (in Spanish). Madrid: Tello.
- Bautista, Julius (2006). "The Rebellion and the Icon: Holy Revolutions in the Philippines". Asian Journal of Social Science. 34 (2): 291–310. doi:10.1163/156853106777371166.
- Blair, Emma Helen & Robertson, James Alexander, eds. (1903). The Philippine Islands, 1493–1803. Volume 2 of 55 (1521–1569). Historical introduction and additional notes by Edward Gaylord Bourne. Cleveland, Ohio: Arthur H. Clark Company.
Explorations by early navigators, descriptions of the islands and their peoples, their history and records of the catholic missions, as related in contemporaneous books and manuscripts, showing the political, economic, commercial and religious conditions of those islands from their earliest relations with European nations to the beginning of the nineteenth century.
|volume=has extra text (help) - Cebu Daily News (2011). "Revamp, BRT setup eyed for Mactan airport". Archived from the original on 2012-09-09. Retrieved 2013-06-26.
- Encyclopædia Britannica (2016). "Cebu". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- information.ph (2009a). "Part 2: The first Spanish expedition of 1521". Philippine History. Archived from the original on 31 January 2009.CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)
- information.ph (2009b). "Part 3: The Spanish colonization". Philippine History. Archived from the original on 31 January 2009.CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)
- Macachor, Celestino C. (2011). "Searching for Kali in the Indigenous Chronicles of Jovito Abellana". Rapid Journal. 10 (2). Archived from the original on 2012-07-03.
- Manila Bulletin, Mars W. Mosqueda (4 October 2011). "Cebu joins elite ITOP Forum". Archived from the original on 23 October 2011. Retrieved 11 February 2016.
- Manila Bulletin, Jonas Reyes (13 January 2015). "PH ranks 5th among world's shipbuilders". Archived from the original on 12 October 2015. Retrieved 11 February 2016.
- Montebon, Marivir R. (2000). A Tribute to Two Centenarians. Retracing our Roots, A Journey into Cebu's Pre-colonial and Colonial Past. Minglanilla, Cebu: ED Villaver Publishing. pp. 89–90.
- Segura, Manuel F. (1992). The Koga papers : stories of WW II. Cebu City: MF Segura Publications.
- Smith, Warren Du Pré (1907). Freer, Paul C.; Strong, Richard D.; Merrill, E. D. (eds.). "The geology of the Compostela-Danao coal field". Philippine Journal of Science. 2A (6): 377 ff.
- Tribune of India (3 December 2014). "Seechewal inaugurates Punjabi school in Philippines". Jalandhar. Archived from the original on 8 December 2014.
- UNEP, Arthur Lyon Dahl (1998). "Islands of Philippines: Cebu". Island Directory. United Nations Environment Programme. Retrieved 11 February 2016.
- de Viana, Augusto V. (2005). "The capture of the Koga Papers and its effect on the plan to retake the Philippines in 1944" (PDF). Micronesian: Journal of the Humanities and Social Sciences. National Historical Institute in the Philippines. 4 (2).
- Wernstedt, Frederick L. (1957). The role and importance of Philippine interisland shipping and trade. Southeast Asia Program, Dept. of Far Eastern Studies, Cornell University. ISBN 9780598547866.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cebu (province). |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Cebu Province. |
 Geographic data related to Cebu at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Cebu at OpenStreetMap- Official Website of the Provincial Government of Cebu
- The Official Government Portal of the Republic of the Philippines – Cebu
- Cebu
- Provinces of the Philippines
- Island provinces of the Philippines
- States and territories established in 1565
- 1565 establishments in the Philippines