Central and Western District Council
Central and Western District Council 中西區區議會 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | Hong Kong District Council of the Central and Western District |
| History | |
| Founded | 18 March 1982 (District Board) 1 July 1997 (Provisional) 1 January 2000 (District Council) |
| Leadership | |
Chair | Vacant |
Vice-Chair | Victor Yeung, Democratic |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 15 councillors consisting of 15 elected members |
1 / 15 | |
1 / 15 | |
Independent | 1 / 15 |
12 / 15
| |
| Elections | |
| First past the post | |
Last election | 24 November 2019 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| 11/F, Harbour Building, 38 Pier Road, Central, Hong Kong | |
| Website | |
| www | |
| Central and Western District Council | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 中西區區議會 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The Central and Western District Council is the district council for the Central and Western District in Hong Kong. It is one of 18 such councils. The Central and Western District Council currently consists of 15 members, of which the district is divided into 15 constituencies, electing a total of 15 members. The last election was held on 24 November 2019.
History[]
The Central and Western District Council was established on 18 March 1982 under the name of the Central and Western District Board as the result of the colonial Governor Murray MacLehose's District Administration Scheme reform. The District Board was partly elected with the ex-officio Urban Council members, as well as members appointed by the Governor until 1994 when last Governor Chris Patten refrained from appointing any member.
The Central and Western District Board became Central and Western Provisional District Board after the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR) was established in 1997 with the appointment system being reintroduced by Chief Executive Tung Chee-hwa. The Central and Western District Council was established on 1 January 2000 after the first District Council election in 1999. The council has become fully elected when the appointed seats were abolished in 2011 after the modified constitutional reform proposal was passed by the Legislative Council in 2010.
The Central and Western Board was largely non-partisan in the 1980s. In the 1985 election, an electoral coalition of 12 incumbents based on personal network surrounding Vincent Ko Hon-chiu of the Hong Kong People's Association, later the board chairman, contested in the election, winning 10 seats in total.[1] The board gradually divided into liberal and conservative blocs in the late 1980s and split into pro-democracy United Democrats of Hong Kong (UDHK) and the conservative Liberal Democratic Federation of Hong Kong (LDF) which were formed in 1990.
The Democratic Party, the merger of UDHK and Meeting Point, took control of the board from 1994 to 1997 after the abolishment of the appointed seats. The Democratic majority was offset by the pro-Beijing camp when appointed seats were reintroduced in 1997. In the 2003 tide of democracy after the July 1 protest, the pro-democrats formed the Central and Western Democratic Power for the 2003 election and won seven seats, which saw pro-democrat Legislative Councillor Cyd Ho defeating Ip Kwok-him of the Democratic Alliance for the Betterment of Hong Kong (DAB) in his long-held constituency of Kwun Lung. Democratic Party's Kam Nai-wai was able to take the chairmanship with the help of appointed member Wu Chor-nam.[2] Kam's decision to co-operate with an appointed member sparked controversy which caused Kam to resign soon afterward.[3]
The Democratic Party remained the largest party in the council until the 2007 election when the DAB surpassed the Democratic Party in the number of seats for the first time. In the by-elections in 2017 for Peak and Tung Wah, the pro-Beijing and pro-democracy camps took each of the seats, giving the Democrats the same numbers of seat as the DAB, both commanding five seats.
In the 2019 election amid the ongoing pro-democracy protests, the pro-democrats scored a historic landslide victory by taking 14 of the 15 seats, with DAB being completely wiped out from the council and its legislator Cheung Kwok-kwan being ousted in Sai Wan. The Democratic Party became the largest party with seven seats with Cheng Lai-king and Victor Yeung taking the chair and vice chair posts respectively.
Political control[]
Since 1982 political control of the council has been held by the following parties:
| Camp in control | Largest party | Years | Composition |
|---|---|---|---|
| No Overall Control | Civic Association | 1982 - 1985 | |
| No Overall Control | People's Association | 1985 - 1988 |
|
| No Overall Control | HKAS → United Democrats | 1988 - 1991 |
|
| Pro-government | United Democrats | 1991 - 1994 |
|
| Pro-democracy | Democratic (majority) | 1994 - 1997 |
|
| Pro-Beijing | Democratic | 1997 - 1999 |
|
| Pro-Beijing | Democratic | 2000 - 2003 |
|
| Pro-Beijing | Democratic | 2004 - 2007 |
|
| Pro-Beijing | Democratic | 2008 - 2011 |
|
| Pro-Beijing | DAB | 2012 - 2015 |
|
| Pro-Beijing | DAB → DAB/Democratic | 2016 - 2019 |
|
| Pro-democracy | Democratic | 2020 - 2023 |
|
Political makeup[]

Elections are held every four years.
| Political party | Council members | Current members | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1994 | 1999 | 2003 | 2007 | 2011 | 2015 | 2019 | ||||||||||
| Democratic | 8 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 7 | 1 / 15
| ||||||||
| Independent | 2 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 1 / 15
| ||||||||
| Liberal | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 / 15
| ||||||||
District result maps[]
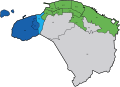
1994
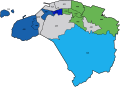
1999
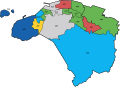
2003
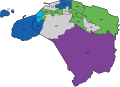
2007

2011
2015

2019
Members represented[]
Starting from 1 January 2020:
| Code | Constituency | Name | Political affiliation | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A01 | Chung Wan | Vacant | [a] | ||
| A02 | Mid Levels East | Vacant | [b] | ||
| A03 | Castle Road | Vacant | [c] | ||
| A04 | Peak | Jeremy Young Chit-on | Liberal | ||
| A05 | University | Vacant | [d] | ||
| A06 | Kwun Lung | Vacant | [e] | ||
| A07 | Kennedy Town & Mount Davis | Vacant | [f] | ||
| A08 | Sai Wan | Pang Ka-ho | Independent | ||
| A09 | Belcher | Victor Yeung Sui-yin | Democratic | ||
| A10 | Shek Tong Tsui | Vacant | [g] | ||
| A11 | Sai Ying Pun | Vacant | [h] | ||
| A12 | Sheung Wan | Vacant | [g] | ||
| A13 | Tung Wah | Vacant | [c] | ||
| A14 | Centre Street | Vacant | [c] | ||
| A15 | Water Street | Vacant | [i] | ||
Leadership[]
Chairs[]
Since 1985, the chairman is elected by all the members of the board:
| Chairman | Years | Political Affiliation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. G. Cooper | 1982–1983 | District Officer | |
| Lolly Chiu Yuen-chu | 1983–1984 | District Officer | |
| Lam Kam-kwong | 1984–1985 | District Officer | |
| Vincent Ko Hon-chiu[4] | 1985–1988 | People's Association | |
| Ambrose Lau Hon-chuen[5] | 1988–1994 | Nonpartisan→PA | |
| Yuen Bun-keung[6] | 1994–1997 | Democratic | |
| Stephen Chan Chit-kwai[7] | 1997–2000 | Independent | |
| Wu Chor-nam[8] | 2000–2003 | Independent | |
| Chan Tak-chor[9][j] | 2004–2011 | Liberal→Independent | |
| Yip Wing-shing[10] | 2012–2019 | Independent | |
| Cheng Lai-king | 2020–2021 | Democratic | |
Vice Chairs[]
| Vice Chairman | Years | Political Affiliation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chan Tak-chor | 2000–2003 | Liberal | |
| Wu Chor-nam | 2004–2007 | Independent | |
| Stephen Chan Chit-kwai | 2008–2011 | Independent | |
| Chan Hok-fung | 2012–2019 | DAB | |
| Victor Yeung Sui-yin | 2020–present | Democratic | |
Notes[]
- ^ Unseated on 28 May 2021 after fleeing Hong Kong.
- ^ Resigned on 30 April 2021 over new oath-taking law.
- ^ a b c Resigned on 8 July 2021 over new oath-taking law.
- ^ Resigned on 11 July 2021 over new oath-taking law.
- ^ Resigned on 30 April 2021 after being arrested under national security law.
- ^ Resigned on 3 June 2021 over new oath-taking law.
- ^ a b Resigned on 7 July 2021 over new oath-taking law.
- ^ Resigned on 10 July 2021 over new oath-taking law.
- ^ Resigned on 26 May 2021 over new oath-taking law.
- ^ Democratic Party's Kam Nai-wai was initially elected as chairman but soon resigned from the office.[3]
References[]
- ^ "百姓 - Issues 159-170". 百姓半月刊編輯委員會. 1988. p. 3.
- ^ "破例與委任議員結盟 民主黨奪中西區區會主席". 蘋果日報. 7 January 2004.
- ^ a b "中西區區議員甘乃威辭去區議會主席以釋疑慮". Democratic Party. 9 January 2004. Archived from the original on 15 April 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2013.
- ^ Growing with Hong Kong: The University and Its Graduates-The First 90 Years. Hong Kong University Press. p. 276.
- ^ "Legislative Council Report 2002-03" (PDF). Legislative Council of Hong Kong. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - ^ "Biography of Yuen Bun-keung". Democratic Party. 1999. Retrieved 14 March 2013.
- ^ "Daily Information Bulletin". Government Information Services. 4 July 1997. Retrieved 14 March 2013.
- ^ "HKSAR Central & Western District Council". webb-site.com. Retrieved 14 March 2013.
- ^ "Member Details of Central and Western District Council". Central and Western District Council. Retrieved 14 March 2013.
- ^ "Central & Western District Council Members (2008 - 2011)". Central and Western District Council. Archived from the original on 1 June 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2013.
External links[]
- Central and Western District Council
- Districts of Hong Kong
- District Councils of Hong Kong
- Central and Western District, Hong Kong






