Cinoxate
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
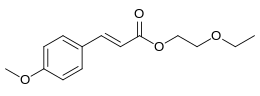
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Ethoxyethyl (2E)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate | |
| Other names
2-Ethoxyethyl p-methoxycinnamate
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.901 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C14H18O4 | |
| Molar mass | 250.294 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.102 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −25 °C (−13 °F; 248 K) |
| Boiling point | 184 to 187 °C (363 to 369 °F; 457 to 460 K) at 2 mmHg |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Cinoxate is an organic compound used as an ingredient in some types of sunscreens. It is an ester formed from and 2-ethoxyethanol. It is a slightly yellow viscous liquid that is insoluble in water, but miscible with alcohols, esters, and vegetable oils.
It protects skin against the sun by absorbing UV-A[citation needed] and UV-B rays.
See also[]
- Amiloxate, another methoxycinnamate-based sunscreen
- Octyl methoxycinnamate, another methoxycinnamate-based sunscreen
References[]
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 2312.
Categories:
- Sunscreening agents
- O-Methylated phenols
- Cinnamate esters
- Ester stubs
