Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
The Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (CCRCC) is a type of renal cell carcinoma.
Genetics[]
Cytogenetics[]
- Alterations of chromosome 3p segments occurs in 70 – 90% of CCRCCs
- Inactivation of von Hippel-Lindau disease (VHL) gene by gene mutation and
- Gain of chromosome 5q
- Loss of chromosomes 8p, 9p, and 14q
Molecular genetics[]
Several frequently mutated genes were discovered in CCRCC: VHL, KDM6A/UTX, SETD2, KDM5C/JARID1C and MLL2. PBRM1 is also commonly mutated in CCRCC.[citation needed]
Histogenesis[]
CCRCC is derived from the proximal convoluted tubule.[citation needed]
Microscopy[]
Generally, the cells have a clear cytoplasm, are surrounded by a distinct cell membrane and contain round and uniform nuclei.[citation needed]
Microscopically, CCRCCs are graded by the ISUP/WHO as follows:[1][2]
- Grade 1: Inconspicuous and basophilic nucleoli at ×400 magnification
- Grade 2: Clearly visible and eosinophilic nucleoli at ×400 magnification
- Grade 3: Clearly visible nucleoli at ×100 magnification
- Grade 4: Extreme pleomorphism or rhabdoid and/or sarcomatoid morphology
Epidemiology[]
- Most commonly affects male patients in their sixties and seventies.
- Majority of CCRCC arise sporadically.
- Only 2 – 4% of the cases presenting as part of an inherited cancer syndrome, such as von Hippel-Lindau syndrome.
Images[]
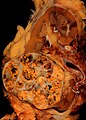
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Macroscopy.

Clear cell renal cell carcinoma. HE, x100.
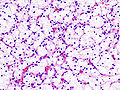
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Führman Grade = 1. HE, x400.

Grade 3: Arrows point at a clearly visible nucleolus
References[]
- ^ YiFen Zhang. "What is the ISUP/WHO grading system for renal cell carcinoma (RCC)?". Medscape. Updated: Jul 02, 2019
- ^ Moch, H. (2016). "WHO-ISUP-Graduierungssystem für Nierenkarzinome". Der Pathologe. 37 (4): 355–360. doi:10.1007/s00292-016-0171-y. ISSN 0172-8113.
Categories:
- Kidney cancer
- Histopathology



