Colonial empire
A colonial empire is a collective of territories (often called colonies), either contiguous with the imperial center or located overseas, settled by the population of a certain state and governed by that state.
Before the expansion of early modern European powers, other empires had conquered and colonized territories, such as the Romans in Iberia, or the Chinese in what is now southern China. Modern colonial empires first emerged with a race of exploration between the then most advanced European maritime powers, Portugal and Spain, during the 15th century.[1] The initial impulse behind these dispersed maritime empires and those that followed was trade, driven by the new ideas and the capitalism that grew out of the European Renaissance. Agreements were also made to divide the world up between them in 1479, 1493, and 1494. European imperialism was born out of competition between European Christians and Ottoman Muslims, the latter of which rose up quickly in the 14th century and forced the Spanish and Portuguese to seek new trade routes to India, and to a lesser extent, China.
Although colonies existed in classical antiquity, especially amongst the Phoenicians and the Ancient Greeks who settled many islands and coasts of the Mediterranean Sea, these colonies were politically independent from the city-states they originated from, and thus did not constitute a colonial empire.[2] This paradigm shifted by the time of the Ptolemaic Empire, the Seleucid Empire, and the Roman Empire.
History[]
European colonial empires[]
Portugal began establishing the first global trade network and one of the first colonial empires[3][4] under the leadership of Henry the Navigator. The empire spread throughout a vast number of territories distributed across the globe (especially at one time in the 16th century) that are now parts of 60 different sovereign states. Portugal would eventually control Brazil, territories such as what is now Uruguay and some fishing ports in north, in the Americas; Angola, Mozambique, Portuguese Guinea, and São Tomé and Príncipe (among other territories and bases) in the North and the Subsaharan Africa; cities, forts or territories in all the Asian Subcontinents, as Muscat, Ormus and Bahrain (amongst other bases) in the Persian Gulf; Goa, Bombay and Daman and Diu (amongst other coastal cities) in India; Portuguese Ceylon; Malacca, bases in Southeast Asia and Oceania, as Makassar, Solor, Banda, Ambon and others in the Moluccas, Portuguese Timor; and the granted entrepôt-base of Macau and the entrepôt-enclave of Dejima (Nagasaki) in East Asia, amongst other smaller or short-lived possessions.
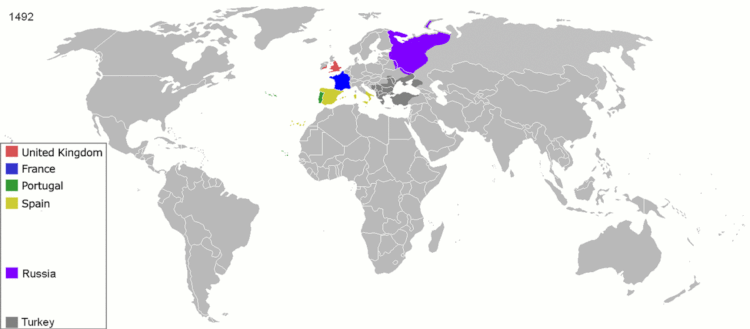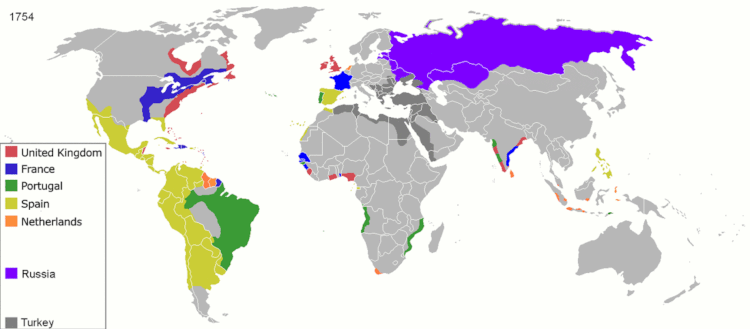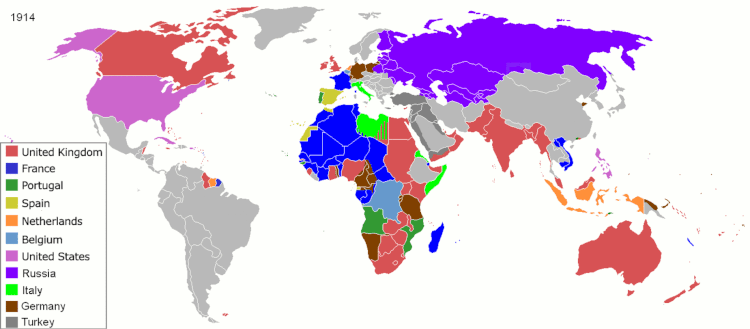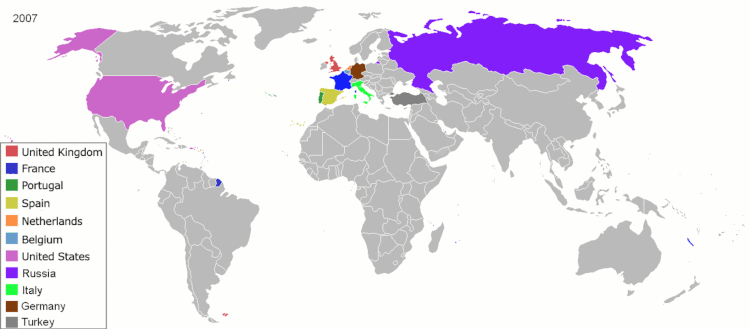
During its Siglo de Oro, the Spanish Empire had possession of Mexico, South America, the Philippines, all of southern Italy, a stretch of territories from the Duchy of Milan to the Netherlands, Luxembourg, and Belgium, parts of Burgundy, and many colonial settlements in the Americas, Africa, and Asia. Possessions in Europe, Africa, the Atlantic Ocean, the Americas, the Pacific Ocean, and East Asia qualified the Spanish Empire as attaining a global presence. From 1580 to 1640 the Portuguese Empire and the Spanish Empire were conjoined in a personal union of its Habsburg monarchs during the period of the Iberian Union, but beneath the highest level of government, their separate administrations were maintained.
Subsequent colonial empires included the French, English, Dutch and Japanese empires. By the mid-17th century, the Tsardom of Russia, continued later as the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union, became the largest contiguous state in the world, and the modern Russian Federation continues to be so to this day. Russia today has nine time zones, stretching across about half of the world's longitude.
Throughout the 19th and early 20th century, by virtue of its technological and maritime supremacy, the British Empire steadily expanded to become by far the largest empire in history; at its height ruling over a quarter of the Earth’s land area and 24% of the population. Britain’s role as a global hegemon during this time ushered in a century of “British Peace”, lasting from the end of the Napoleonic Wars to the start of WW1. During the New Imperialism, Italy and Germany also built their colonial empires in Africa.
It is worth noting that, from the 16th to 19th century, there were also large non-European empires, most notably the Qing Empire of China, which conquered a huge area of East and Inner Asia, and the states of the Age of the Islamic Gunpowders, Mughal India, the Ottoman Empire in Asia Minor and Southwest Europe, and Safavid Iran. The British replaced the Mughals in India, and after the Boxer Rebellion in 1901, Imperial China made concessions to the Eight-Nation Alliance (all the Great Powers of the time). By the end of the 20th century most of the previous colonial empires had been decolonized, though the modern nation-states of Russia and China inherited much of the territory of the Romanov and Qing empires, respectively.
Timeline[]
This article's factual accuracy is disputed. (January 2020) |
The chart below[original research?] shows the span of some European colonial empires.
- Black lines mark the year of the empires largest territorial extent of land area.
- Red represents that the empire is at that time a monarchy.
- Blue represents that the empire is at that time a republic.

List of colonial empires[]
European:
 Belgian Empire (1908–1962)
Belgian Empire (1908–1962)
 Belgian Congo (1908–1960)
Belgian Congo (1908–1960) Ruanda-Urundi (1922–1962)
Ruanda-Urundi (1922–1962)- Belgian Concession of Tientsin (1902–1931)
 British Empire (1707–1997/present)
British Empire (1707–1997/present)
- Evolution of the British Empire
- Possessions in Europe
- British Cyprus
- British Malta
- British Ireland
- Possessions in Africa
 British Somaliland (1884–1960)
British Somaliland (1884–1960)- British Egypt (1914–1936)
- Anglo-Egyptian Sudan (1899–1956)
 East Africa Protectorate (1895–1920)
East Africa Protectorate (1895–1920) Kenya Colony (1920–1963)
Kenya Colony (1920–1963) Uganda Protectorate (1894–1962)
Uganda Protectorate (1894–1962) Tanganyika (territory) (1922–1961)
Tanganyika (territory) (1922–1961) Protectorate of Nyasaland (1893–1964)
Protectorate of Nyasaland (1893–1964) Protectorate of Northern Rhodesia (1924–1964)
Protectorate of Northern Rhodesia (1924–1964) Colony of Southern Rhodesia (1923–1965), (1979–1980)
Colony of Southern Rhodesia (1923–1965), (1979–1980)- Bechuanaland Protectorate (1885-1966)
 British Nigeria (1914–1954)
British Nigeria (1914–1954) British Gold Coast (1867–1957)
British Gold Coast (1867–1957) British Sierra Leone (1808–1961)
British Sierra Leone (1808–1961) British Gambia (1821–1965)
British Gambia (1821–1965)
- Possessions in the Americas
 Thirteen Colonies
Thirteen Colonies- British West Indies
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Bermuda
 British Leeward Islands (1671–1816),(1833–1958)
British Leeward Islands (1671–1816),(1833–1958) British Windward Islands (1833–1960)
British Windward Islands (1833–1960)- Cayman Islands
 Colony of Jamaica (1655–1962)
Colony of Jamaica (1655–1962)- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turks and Caicos Islands
 British Honduras (1862–1981)
British Honduras (1862–1981) British Guiana (1814–1966)
British Guiana (1814–1966) Mosquito Coast (1638-1860)
Mosquito Coast (1638-1860)
- Possessions in the Indian subcontinent
 East India Company (1757-1858) and
East India Company (1757-1858) and  British Raj (1858-1947)
British Raj (1858-1947) Kingdom of Nepal, protectorate (1816-1923)
Kingdom of Nepal, protectorate (1816-1923) Kingdom of Bhutan, protectorate (1865-1947)
Kingdom of Bhutan, protectorate (1865-1947) Emirate of Afghanistan, protectorate (1879-1919)
Emirate of Afghanistan, protectorate (1879-1919)
- Possessions in China
 British Hong Kong (1841–1997)
British Hong Kong (1841–1997) British Weihaiwei (1898–1930)British Concession in Tienstin (1860–1943)
British Weihaiwei (1898–1930)British Concession in Tienstin (1860–1943)
- Possessions in the Middle East
 Trucial States (1820–1971)
Trucial States (1820–1971)- British Bahrain
- British Qatar (1916–1971)
- British Iraq (1920–1932)
- Emirate of Transjordan (1921–1946)
- Mandatory Palestine (1920–1948)
- Sheikhdom of Kuwait (1899–1961)
- Aden Protectorate (1872–1963)
 Muscat and Oman (1892-1970)
Muscat and Oman (1892-1970)
- Possessions in Southeast Asia
- British Bencoolen
- British Malaya
- British Borneo
- Dominions of the United Kingdom
 Canada
Canada Dominion of Newfoundland
Dominion of Newfoundland States and territories of Australia (1901–present)
States and territories of Australia (1901–present)
- The Australia, itself a colony that gradually increased its independence in 1901, 1942 and 1986, was tasked with the government of multiple other British colonies and territories and the mandates of New Guinea and Nauru
 Realm of New Zealand (1907–present)
Realm of New Zealand (1907–present)
- The New Zealand, itself a colony that gradually increased its independence in 1907, 1947 and 1986, was tasked with the government of multiple other British colonies and territories and the mandate of Samoa. It was also nominal co-trustee of the mandate of Nauru. The remaining non-self-governing New Zealand territory is Tokelau.
 Mandates under South African administration (1915–1990)
Mandates under South African administration (1915–1990)
- The South-West Africa mandate was governed by the Union Of South Africa, that itself a colony that gradually increased its independence in 1910, 1931 and 1961.
 Danish Empire (1620–1979/present)
Danish Empire (1620–1979/present)
 Danish India (1620–1869)
Danish India (1620–1869) Danish Gold Coast (1658–1850)
Danish Gold Coast (1658–1850)- Danish colonization of the Americas:
 Danish West Indies (1754–1917)
Danish West Indies (1754–1917) Greenland (1814–1979)
Greenland (1814–1979)
 Dutch Empire (1602–1975/Present)
Dutch Empire (1602–1975/Present)
- Dutch colonization of the Americas.
 Dutch West India Company
Dutch West India Company
 New Netherland
New Netherland Dutch Guyana/Surinam
Dutch Guyana/Surinam Dutch Brazil
Dutch Brazil Dutch Caribbean
Dutch Caribbean
 Dutch East India Company
Dutch East India Company
- Dutch India
- Dutch East Indies
 Netherlands New Guinea
Netherlands New Guinea
 Dutch Cape Colony (1652–1806)
Dutch Cape Colony (1652–1806) Dutch Formosa (1624–1662)
Dutch Formosa (1624–1662)
- Dutch colonization of the Americas.
 English colonial empire (1585–1707)
English colonial empire (1585–1707)
 French colonial Empire (1534–1980/present)
French colonial Empire (1534–1980/present)
- French colonization of the Americas:
- New France (1534–1763)
- French West Indies (1635–today)
- Asia:
- French India (1664–1962)
- French Indochina (1887–1954)
- French Concessions in Shanghai and Tientsin
- French Guangzhouwan
- Africa:
- French North Africa (1830–1934)
- French Somaliland (1883–1967)
- French West Africa (1895–1958)
- French Madagascar (1897–1958)
- French Comoros (1908–1968)
- French Equatorial Africa (1910–1958)
- Oceania:
- New Hebrides (1906–1980)
- French colonization of the Americas:
 German Empire (1884–1920)
German Empire (1884–1920)
 Kamerun (1884–1918)
Kamerun (1884–1918) Togoland (1884–1916)
Togoland (1884–1916) German South West Africa (1884–1919)
German South West Africa (1884–1919) German New Guinea (1884–1919)
German New Guinea (1884–1919) German East Africa (1885–1919)
German East Africa (1885–1919) German Samoa (1900–1920)
German Samoa (1900–1920)- German Concession in Tientsin
- German Kiautschou Bay Leased Territory
- German tsingtao
 Italian Empire (1882–1960)
Italian Empire (1882–1960)
 Eritrea (1882–1947)
Eritrea (1882–1947) Somaliland (1889–1947, 1950-1960 as Italian Trust Territory of Somaliland)
Somaliland (1889–1947, 1950-1960 as Italian Trust Territory of Somaliland) Ethiopia (1936-1941)
Ethiopia (1936-1941)
 Italian East Africa (formed by merging Eritrea, Somaliland and Ethiopia: 1936–1947)
Italian East Africa (formed by merging Eritrea, Somaliland and Ethiopia: 1936–1947)
 Cyrenaica (1912–1947)
Cyrenaica (1912–1947) Tripolitania (1912–1947)
Tripolitania (1912–1947)
 Libya (formed by merging Cyrenaica and Tripolitania in 1934. It dissolved in 1947. It also included the Southern Military Territory of Fezzan)
Libya (formed by merging Cyrenaica and Tripolitania in 1934. It dissolved in 1947. It also included the Southern Military Territory of Fezzan)
 Italian Islands of the Aegean (1912–1947)
Italian Islands of the Aegean (1912–1947)- Italian Albania (1939-1943)
- Italian France (1940-1943)
- Italian Montenegro (1941-1943)
- Italian concession of Tientsin (1901-1947)
 Ottoman Empire (1354-1908)
Ottoman Empire (1354-1908)
- Protectorate of Aceh (1496–1903)
- Regency of Algiers (1516-1830)
- Kashgaria (1865-1877)
- Ottoman Syria (1517-1918)
- Ottoman Iraq (1538-1918)
- Ottoman Arabia (1517-1919)
- Ottoman Greece (1453-1830)
- Ottoman Egypt (1517-1914)
- Ottoman Tripolitania (1551-1912)
- Ottoman Tunisia (1574-1881)
- Sheikhdom of Kuwait (1560-1670,1752-1899)
 Emirate of Nejd (1818-1824)
Emirate of Nejd (1818-1824)
This section needs expansion. You can help by . (March 2021) |
 Portuguese Empire (1415–1999)
Portuguese Empire (1415–1999)
- Evolution of the Portuguese Empire
- Portuguese colonization of the Americas
- Colonial Brazil (1500–1815)
- Portuguese India (1505–1961)
- Portuguese Ceylon (1598-1658)
- Portuguese Timor (1702–1975)
- Portuguese Malacca (1511–1641)
- Portuguese Macau (1557–1999)
- Portuguese Nagasaki (1580-1587)
- Portuguese Oman (1507-1656)
- Portuguese Africa
- Portuguese East Africa (1498–1975)
- Portuguese West Africa (1575–1975)
- Portuguese Guinea (1474–1974)
- Portuguese Cape Verde (1462–1975)
- Portuguese São Tomé and Príncipe (1470–1975)
- Fort of São João Baptista de Ajudá (1721-1961)
- Portuguese Gold Coast (1482-1642)
 Russian Empire (1721–1917)
Russian Empire (1721–1917)
- Russian conquest of Siberia
- Russian colonization of the Americas:
 Russian America (1733–1867)
Russian America (1733–1867)
 Sagallo (1889)
Sagallo (1889)- Transcaucasia
- Russian Port Arthur
- Russian concession in Tientsin
 Spanish Empire (1492–1825/1898)
Spanish Empire (1492–1825/1898)
- Spanish colonization of the Americas
 Viceroyalty of New Spain
Viceroyalty of New Spain Viceroyalty of Peru
Viceroyalty of Peru Viceroyalty of New Granada
Viceroyalty of New Granada Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata
Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata
 Spanish East Indies (1565–1898)[5]
Spanish East Indies (1565–1898)[5] Spanish Guinea (1778–1968)[6]
Spanish Guinea (1778–1968)[6] Spanish Sahara (1884–1975)
Spanish Sahara (1884–1975) Spanish protectorate in Morocco (1912–1956)
Spanish protectorate in Morocco (1912–1956) Ifni (1476-1524/1859-1969).
Ifni (1476-1524/1859-1969).
- Spanish colonization of the Americas
 Swedish Empire (1638–1663, 1733, 1784–1878)
Swedish Empire (1638–1663, 1733, 1784–1878)
- Swedish colonies in the Americas
 New Sweden (1638–1655)
New Sweden (1638–1655) Swedish colony of Saint Barthélemy (1784–1878)
Swedish colony of Saint Barthélemy (1784–1878) Guadeloupe (1813-1814)
Guadeloupe (1813-1814)
 Swedish Gold Coast (1650–1658, 1660–1663)
Swedish Gold Coast (1650–1658, 1660–1663) Parangipettai (1733)
Parangipettai (1733) Swedish Factory, Canton Factories (1757-1860)
Swedish Factory, Canton Factories (1757-1860)
- Swedish colonies in the Americas
Asian:
 Japanese Empire (1868–1945)
Japanese Empire (1868–1945)
 Ezo as Hokkaido (1869-present)
Ezo as Hokkaido (1869-present) Ryukyu as Okinawa Prefecture (1879-1945 & 1972-present)[7]
Ryukyu as Okinawa Prefecture (1879-1945 & 1972-present)[7] Taiwan (1895–1945)
Taiwan (1895–1945) Karafuto Prefecture (1905–1949)
Karafuto Prefecture (1905–1949) Korea (1910–1945)
Korea (1910–1945) South Seas Mandate (1919–1947)
South Seas Mandate (1919–1947) Manchukuo (1932–1945)
Manchukuo (1932–1945) Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere (1932–1945)
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere (1932–1945)
Other countries with colonial possessions:
 Sikh Empire (1799-1849)
Sikh Empire (1799-1849)
 Jammu and Kashmir (princely state) (1819-1846)
Jammu and Kashmir (princely state) (1819-1846) Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (1834- 1849)
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (1834- 1849)
 Wales
Wales
 United States of America (1817–present)
United States of America (1817–present)
- United States territorial acquisitions
- American Colonization Society
- Colony of Liberia (1821-1847)
- American imperialism
- American concession in Tientsin
- Colonies of the
 Habsburg Monarchy[8] and the
Habsburg Monarchy[8] and the  Austro-Hungarian Empire (1719–1750, 1778–1783, 1901–1917)
Austro-Hungarian Empire (1719–1750, 1778–1783, 1901–1917)
- Austrian colonial policy
- Austrian colonisation of Nicobar Islands
- Austrian East India Company
- Tianjin
- Móric Benyovszky (1774-1779)
- Franz Josef Land
- Austrian North Borneo
 Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (a vassal of the
Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (a vassal of the  Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, 1637–1690)
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, 1637–1690)
- Couronian colonization
- Couronian colonization of the Americas
- Jaxa (1665-1685)
- Toco (1688-1689)
- Colonization attempts by Poland
 German colonial initiatives (1683–1721)
German colonial initiatives (1683–1721)
- Colonies of
 Brandenburg-Prussia (1683–1721)[8]
Brandenburg-Prussia (1683–1721)[8] - Colonies of
 County of Hanau[9]
County of Hanau[9] - German colonization of the Americas
- Colonies of
- Italy and the colonization of the Americas
 Grand Duchy of Tuscany: Thornton expedition (1608–1609)
Grand Duchy of Tuscany: Thornton expedition (1608–1609) Kingdom of Sicily : Kingdom of Africa (1135-1160)
Kingdom of Sicily : Kingdom of Africa (1135-1160) Knights Hospitaller (Malta, a vassal of the
Knights Hospitaller (Malta, a vassal of the  Kingdom of Sicily): Hospitaller colonization of the Americas
Kingdom of Sicily): Hospitaller colonization of the Americas
 Kingdom of Scotland (1621–1707)
Kingdom of Scotland (1621–1707)
 Norway
Norway
- List of possessions of Norway (1920–present)
- Norway Antarctic and sub-Antarctic possessions (1927–1957)[10]
 Sweden-Norway (1814-1905)
Sweden-Norway (1814-1905)
- Cooper Island (1844-1905)
 Kingdom of Morocco (1975–present)
Kingdom of Morocco (1975–present)
 Omani Empire (1652–1892)
Omani Empire (1652–1892)
- Yaruba dynasty (1624-1742)
- Sultanate of Muscat (1652-1820)
- Sultanate of Zanzibar (taken by Oman in 1698, became capital of the Omani Sultanate or Empire from 1632 or 1640; until 1890)
- Mombasa (1698-1728, 1729–1744, 1837–1890)
- Gwadar (1783-1958)
 Tsardom of Russia,
Tsardom of Russia, Russian Empire,
Russian Empire,  Soviet Union, and
Soviet Union, and  Russian Federation (1547–1721) (1721-1917) (1917–1991) (1991-present)
Russian Federation (1547–1721) (1721-1917) (1917–1991) (1991-present)
- Russian Colonialism
- Soviet Empire
- Russian conquest of Siberia
- Soviet Central Asia
- Chinese Empire (from Qin dynasty to
 Qing dynasty),
Qing dynasty), 
 Republic of China, and
Republic of China, and  People's Republic of China (221 BC- Present)
People's Republic of China (221 BC- Present)
- Chinese imperialism
- Imperial Chinese Tributary System
- Guangxi
- Korea
- Canghai Commandery(A commandery that self subjugated to Han dynasty from Dongye)
- Four Commanderies of Han(Established after the fall of Gojoseon)
- Daifang Commandery(Offshoot of the former four commanderies of Han that existed in the 3rd to 4th century)
- Colonization attempts of the Tang dynasty after Unification of the three kingdoms of Korea(Gyerim Territory Area Command,Protectorate General to Pacify the East and Ungjin Commandery)
- Dongnyeong Prefectures,Ssangseong Prefectures and Tamna prefectures(Yuan dynasty)
- Hainan (since the Han dynasty)
- Nansha Islands
- Xisha Islands
- Manchuria (during the Tang, Liao, Jin, Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties)
- Inner Manchuria
- Outer Manchuria
- Kuye Island
- Inner Mongolia
- Outer Mongolia (during the Tang, Liao, Yuan, Northern Yuan, and Qing dynasties)
- Tannu Uriankhai
- Taiwan (during the Qing dynasty)
- Tibet (during the Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties)
- Yunnan
- Vietnam (during the Han, Xin, Eastern Wu, Jin, Liu Song, Southern Qi, Liang, Sui, Tang, Wu Zhou, Southern Han, and Ming dynasties)
- Xinjiang
- Central Asia (during the Tang, Western Liao, and Qing dynasties)
- Chinese imperialism
 Kingdom of Siam
Kingdom of Siam
- Kingdom of Vientiane (1778–1828)
- Kingdom of Luang Prabang (1778–1893)
- Kingdom of Champasak (1778–1893)
- Kingdom of Cambodia (1771–1867)
- Kedah (1821–1826)
 Argentina
Argentina
- Tierra del Fuego
- Patagonia
- Falkland Islands (1829–1831, 1832–1833, 1982)
- Argentine Antarctica
- Misiones
- Formosa
- Puna de Atacama
- California (1818)
- Philippines (1818)
- Equatorial Guinea (1810-1816)
- Gonaïves, Haiti
 Empire of Brazil,
Empire of Brazil,  Brazil
Brazil
- Cisplatina
- Acre
Maps[]
European:

Belgian Empire

British Empire

Danish Empire
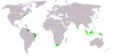
Dutch Empire
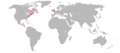
English Empire

French Empire
German Empire

Italian Empire

Portuguese Empire

Russian Empire

Spanish Empire

Swedish Empire
Asian:
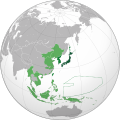
Japanese Empire

Ottoman Empire
Other countries with colonial possessions:
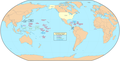
Directly controlled territory of the United States at its greatest extent (1898–1902)
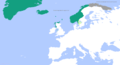
Norwegian Realm
Austro-Hungarian colonies and concessions throughout history
German colonial efforts

Chola Empire

Duchy of Courland and Semigallia
Couronian settlements in Africa

Map of the Hospitaller order's territories in the Caribbean

Couronian settlements in Americas (New Courland on Tobago)

The Crown of Aragon

Map of Morocco and Western Sahara with the Southern Provinces in a darker color.
See also[]
- Analysis of Western European colonialism and colonization
- Colonial troops
- Democratic empire
- Empire
- Great Divergence
- Hegemony
- History of Western civilization
- Imperialism
- List of ancient great powers
- List of largest empires
- List of medieval great powers
- List of modern great powers
- Middle Eastern empires
- Nomadic empire
- The empire on which the sun never sets
Notes and references[]
- ^ Encarta-encyclopedie Winkler Prins (1993–2002) s.v. "kolonie [geschiedenis]. §1.2 De moderne koloniale expansie". Microsoft Corporation/Het Spectrum.
- ^ Encarta, s.v. "kolonie [geschiedenis]. §1.1 Oudheid.
- ^ William D. Phillips, Jr; Phillips, Carla Rahn (November 12, 2015). "Spain as the first global empire". A Concise History of Spain.
- ^ Powell, Philip Wayne ([1991?]). Árbol de odio: la leyenda negra y sus consecuencias en las relaciones entre Estados Unidos y el mundo hispánico. Ediciones Iris de Paz. ISBN 9788440488855. OCLC 55157841
- ^ part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain before 1821.
- ^ .part of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata before 1810.
- ^ Gregory Smits (1999). Visions of Ryukyu: Early-Modern Thought and Politics. Honolulu: University of Hawai'i Press, 143–149·
- ^ a b Part of the Holy Roman Empire realm before 1804.
- ^ part of the Holy Roman Empire before 1736
- ^ The dependencies of Norway are uninhabited, thus as end date is taken the latest date of full Norwegian sovereignty extension to such territory, instead of the date of decolonization or integration in the administrative structures of the mainland.
Bouvet Island claimed in 1927, under Norway sovereignty since 1930.
Peter I Island claimed in 1929, under Norway sovereignty since 1933.
Queen Maud Land claimed in 1938, under Norway sovereignty since 1957.
Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land fall under the scope of the Antarctic Treaty System since 1961.
External links[]
- History of colonialism
- Empires
- Overseas empires