Coronal suture
| Coronal suture | |
|---|---|
 Side view of the skull. ("Coronal suture" in red.) | |
 Superior view of the skull. ("Coronal suture" in red.) | |
| Details | |
| Part of | skull |
| System | skeletal |
| Nerve | trigeminal nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sutura coronalis |
| TA98 | A03.1.02.002 |
| TA2 | 1575 |
| FMA | 52928 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The coronal suture is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint that separates the two parietal bones from the frontal bone of the skull.
Structure[]
The coronal suture lies between the paired parietal bones and the frontal bone of the skull.[1] It runs from the pterion on each side.
Nerve supply[]
The coronal suture is likely supplied by a branch of the trigeminal nerve.[2]
Development[]
The coronal suture is derived from the paraxial mesoderm.
Clinical significance[]
If certain bones of the skull grow too fast then premature fusion of the sutures may occur.[1] This can result in skull deformities.[1] There are two possible deformities that can be caused by the premature closure of the coronal suture:
- a high, tower-like skull called "oxycephaly" or "turret skull".[1]
- a twisted and asymmetrical skull called "plagiocephaly".
References[]
This article includes a list of references, related reading or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (May 2015) |
- ^ a b c d Carlson, Bruce M. (2014-01-01). "9 - Integumentary, Skeletal, and Muscular Systems". Human Embryology and Developmental Biology (5th ed.). Saunders. pp. 156–192. doi:10.1016/b978-1-4557-2794-0.00009-7. ISBN 978-1-4557-2794-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Barral, Jean-Pierre; Croibier, Alain (2009-01-01). "2 - Characteristics of cranial nerves". Manual Therapy for the Cranial Nerves. Churchill Livingstone. pp. 7–14. ISBN 978-0-7020-3100-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link)
- "Sagittal suture." Stedman's Medical Dictionary, 27th ed. (2000).
- Moore, Keith L., and T.V.N. Persaud. The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 7th ed. (2003).
Additional images[]
This gallery of anatomic features needs cleanup to abide by the medical manual of style. |

Animation. Coronal suture shown in red.

Side view of the skull. ('Coronal suture' indicated by the arrow.)

Superior view of anterior part of the skull. Coronal suture runs horizontally.

Coronal suture seen from inside.
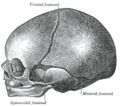
The skull at birth, showing the lateral fontanelle.

Coronal suture of new born baby.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Coronal sutures. |
- "Anatomy diagram: 34256.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-12-27.
- "Anatomy diagram: 34256.000-2". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2013-06-11.
- Cranial sutures
- Human head and neck
- Joints
- Joints of the head and neck
- Skeletal system
- Skull






