Crest factor
Crest factor is a parameter of a waveform, such as alternating current or sound, showing the ratio of peak values to the effective value. In other words, crest factor indicates how extreme the peaks are in a waveform. Crest factor 1 indicates no peaks, such as direct current or a square wave. Higher crest factors indicate peaks, for example sound waves tend to have high crest factors.
Crest factor is the peak amplitude of the waveform divided by the RMS value of the waveform. This is equivalent to the ratio of the L∞ norm to the L2 norm of the function of the waveform:[1]
The peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) is the peak amplitude squared (giving the peak power) divided by the RMS value squared (giving the average power).[2] It is the square of the crest factor:
When expressed in decibels, crest factor and PAPR are equivalent, due to the way decibels are calculated for power ratios vs amplitude ratios.
Crest factor and PAPR are therefore dimensionless quantities. While the crest factor is defined as a positive real number, in commercial products it is also commonly stated as the ratio of two whole numbers, e.g., 2:1. The PAPR is most used in signal processing applications. As it is a power ratio, it is normally expressed in decibels (dB). The crest factor of the test signal is a fairly important issue in loudspeaker testing standards; in this context it is usually expressed in dB.[3][4][5]
The minimum possible crest factor is 1, 1:1 or 0 dB.
Examples[]
This table provides values for some normalized waveforms. All peak magnitudes have been normalized to 1.
| Wave type | Waveform | RMS value | Crest factor | PAPR (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC | 1 | 1 | 0.0 dB | |
| Sine wave |  |
[6] | 3.01 dB | |
| Full-wave rectified sine |  |
[6] | 3.01 dB | |
| Half-wave rectified sine |  |
[6] | 6.02 dB | |
| Triangle wave | 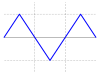 |
4.77 dB | ||
| Square wave |  |
1 | 1 | 0 dB |
| PWM Signal V(t) 0.0 V |
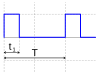 |
[6] |
dB | |
| QPSK | 1 | 1 | 1.761 dB[7] | |
| 8PSK | 3.3 dB[8] | |||
| 3.0 dB[8] | ||||
| OQPSK | 3.3 dB[8] | |||
| 8VSB | 6.5–8.1 dB[9] | |||
| 64QAM | 3.7 dB[10] | |||
| -QAM | 4.8 dB[10] | |||
| WCDMA downlink carrier | 10.6 dB | |||
| OFDM | 4 | ~12 dB | ||
| GMSK | 1 | 1 | 0 dB | |
| Gaussian noise | [11][12] | [13][14] | dB | |
| Periodic Chirp | 3.01 dB |
Notes: 1. crest factors specified for QPSK, QAM, WCDMA are typical factors needed for reliable communication, not the theoretical crest factors which can be larger.
Digital multimeters[]
Crest factor is an important parameter to understand when trying to take accurate measurements of low frequency signals. For example, given a certain digital multimeter with an AC accuracy of 0.03% (always specified for sine waves) with an additional error of 0.2% for crest factors between 1.414 and 5, then the total error for measuring a triangular wave (crest factor = 1.73) is 0.03% + 0.2% = 0.23%.
Acoustics and audio engineering[]
In acoustics and audio engineering, crest factor is usually expressed in decibels, so it's defined as the level difference between the RMS and the peak value of the waveform. For example, for a sine wave the 1.414 ratio is 20 log(1.414) or 3 dB. Most ambient noise has a crest factor of around 10 dB while impulsive sounds such as gunshots can have crest factors of over 30 dB.[citation needed]
Peak-to-average ratio (PAR) meter[]
A peak-to-average ratio meter (Par meter) is a device used to measure the ratio of the peak power level to the time-averaged power level in an electrical circuit. This quantity is known as the peak-to-average ratio (p/a r or PAR). Such meters are used as a quick means to identify degraded telephone channels.
Par meters are very sensitive to . They may also be used for idle channel noise, nonlinear distortion, and amplitude-distortion measurements.
The peak-to-average ratio can be determined for many signal parameters, such as voltage, current, power, frequency, and phase.
Crest factor reduction[]
Many modulation techniques have been specifically designed to have constant envelope modulation, i.e., the minimum possible crest factor of 1:1.
In general, modulation techniques that have smaller crest factors usually transmit more bits per second than modulation techniques that have higher crest factors. This is because:
- any given linear amplifier has some "peak output power"—some maximum possible instantaneous peak amplitude it can support and still stay in the linear range;
- the average power of the signal is the peak output power divided by the crest factor;
- the number of bits per second transmitted (on average) is proportional to the average power transmitted (Shannon–Hartley theorem).
Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) is a very promising modulation technique; perhaps its biggest problem is its high crest factor.[15][16] Many crest factor reduction techniques (CFR) have been proposed for OFDM.[17][18][19] The reduction in crest factor results in a system that can either transmit more bits per second with the same hardware, or transmit the same bits per second with lower-power hardware (and therefore lower electricity costs[20] and less expensive hardware), or both.
Crest factor reduction methods[]
Various methods for crest factor reduction exist, such as peak windowing, noise shaping, pulse injection and peak cancellation.
Applications[]
- Electrical engineering — for describing the quality of an AC power waveform
- Vibration analysis — for estimating the amount of impact wear in a bearing[21]
- Radio and audio electronics — for estimating the headroom required in a signal chain[22][23]
- Physiology — for analysing the sound of snoring[28]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ "What is Crest Factor".
- ^ "Wireless 101: Peak to average power ratio (PAPR)".
- ^ JBL Speaker Power Requirements, which is applying the IEC standard 268-5, itself more recently renamed to 60268-5
- ^ AES2-2012 standard, Annex B (Informative) Crest Factor, pp. 17-20 in the 2013-02-11 printing
- ^ "Dr. Pro-Audio", Power handling, summarizes the various speaker standards
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "RMS and Average Values for Typical Waveforms". Archived from the original on 2010-01-23.
- ^ Palicot, Jacques; Louët, Yves. POWER RATIO DEFINITIONS AND ANALYSIS IN SINGLE CARRIER MODULATIONS (PDF). IETR/Supélec - Campus de Rennes. p. 2.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Read steer_rf_chapter1.pdf".
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-08-21. Retrieved 2009-06-17.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ Jump up to: a b R. Wolf; F. Ellinger; R.Eickhoff; Massimiliano Laddomada; Oliver Hoffmann (14 July 2011). Periklis Chatzimisios (ed.). Mobile Lightweight Wireless Systems: Second International ICST Conference, Mobilight 2010, May 10-12, 2010, Barcelona, Spain, Revised Selected Papers. Springer. p. 164. ISBN 978-3-642-16643-3. Retrieved 13 December 2012.
- ^ Op Amp Noise Theory and Applications Archived 2014-11-30 at the Wayback Machine - 10.2.1 rms versus P-P Noise
- ^ Chapter 1 First-Order Low-Pass Filtered Noise - "The standard deviation of a Gaussian noise voltage is the root-mean-square or rms value of the voltage."
- ^ Noise: Frequently Asked Questions - "Noise theoretically has an unbounded distribution so that it should have an infinite crest factor"
- ^ Telecommunications Measurements, Analysis, and Instrumentation, Kamilo Feher, section 7.2.3 Finite Crest Factor Noise
- ^ "Crest Factor Reduction of an OFDM/WiMAX Network".
- ^ "Low Crest Factor Modulation Techniques for Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)" Archived 2017-08-29 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ R. Neil Braithwaite. "Crest Factor Reduction for OFDM Using Selective Subcarrier Degradation".
- ^ K. T. Wong, B. Wang & J.-C. Chen, "OFDM PAPR Reduction by Switching Null Subcarriers & Data-Subcarriers," Electronics Letters, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 62-63 January, 2011 Archived 2015-09-23 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ S.C. Thompson, "Constant Envelope OFDM Phase Modulation," PhD Dissertation, UC San Diego, 2005.
- ^ Nick Wells. "DVB-T2 in relation to the DVB-x2 Family of Standards" Archived 2013-05-26 at the Wayback Machine quote: "techniques which can reduce the PAPR, ... could result in a significant saving in electricity costs."
- ^ What Is The “Crest Factor” And Why Is It Used?
- ^ Crest factor analysis for complex signal processing Archived 2006-04-27 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ PAPR simulation for 64QAM
- ^ Crest factor definition — AES Pro Audio Reference
- ^ "Level Practices in Digital Audio". Archived from the original on 2009-06-18. Retrieved 2009-10-11.
- ^ Gain Structure — Setting the System Levels Archived 2007-09-28 at the Wayback Machine, Mackie Mixer Tips
- ^ Setting sound system level controls: The most expensive system set up wrong never performs as well as an inexpensive system set up correctly.
- ^ Palatal snoring identified by acoustic crest factor analysis
General[]
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document: "Federal Standard 1037C". (in support of MIL-STD-188)
This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document: "Federal Standard 1037C". (in support of MIL-STD-188)
External links[]
- Definition of peak-to-average ratio – ATIS (Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions) Telecom Glossary 2K
- Definition of crest factor – ATIS (Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions) Telecom Glossary 2K
- Peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) of OFDM systems - tutorial
- Waveforms

















