Dibutyltin dilaurate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Dibutyltindilaurate and butynorate
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.946 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3146 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C32H64O4Sn | |
| Molar mass | 631.56 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.066 g/mL |
| Melting point | 22 to 24 °C (72 to 75 °F; 295 to 297 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
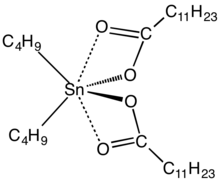
Dibutyltin dilaurate (abbreviated DBTDL), also called dibutyltindilaurate or butynorate, is an organotin compound that is used as a catalyst. It is a colourless oily liquid. In terms of its structure, the molecule consists of two laurate groups attached to a dibutyltin(IV) center.
The molecular geometry at tin is tetrahedral. Based on the crystal structure of the related bis(bromobenzoate), the carbonyl oxygen centers are weakly bonded to tin.[1]
Together with dibutyltin dioctanoate, dibutyltin dilaurate is used as a catalyst for polyurethane production from isocyanates and diols. It is also useful as a catalyst for transesterification and for the room temperature vulcanization of silicones. It is also used as a stabilizer in polyvinyl chloride.[2] It is also added to animal feed to remove cecal worms, roundworms, and tapeworms in turkeys to prevent and coccidiosis.[3]
Related compounds[]
- Dibutyltin dioctanoate: CAS#4731-77-5
- Dibutyltin diacetate: CAS #1067-33-0
References[]
- ^ Weng Ng, S., Das, V. G. K., Yip, W.-H., Wang, R.-J., Mak, T. C. W., "Di-n-butyltin(IV) di-o-bromobenzoate, a weakly-bridged dimer", Journal of Organometallic Chemistry 1990, volume 393, 201-204. doi:10.1016/0022-328X(90)80199-A
- ^ Applications, Environmental Issues, and Analysis in Organotin Chemistry, Second Edition. Alwyn G. Davies 2004 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. ISBN 3-527-31023-1
- ^ PubChem. "Butynorate". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2019-08-23.
- Laurate esters
- Organotin compounds