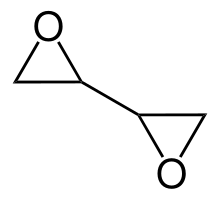
Diepoxybutane
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2′-Bioxirane | |
| Other names
1,1′-Bi[ethylene oxide]; 1,2:3,4-Diepoxybutane; 1,3-Butadiene diepoxide; Bioxirane; Butadiene dioxide; Butane diepoxide; Dioxybutadiene
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | DEB |
| 79831 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.527 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | 3384 3082 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 86.090 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.113 g/cm3 (18 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | 4 °C (39 °F; 277 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 138 °C (280 °F; 411 K)[1] |
| Miscible[1] | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.52 kPa (at 20 °C)[2] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   
| |
Signal word
|
Danger |
| H226, H301, H310, H311, H314, H330, H340, H350 | |
| P201, P202, P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P262, P264, P270, P271, P280, P281, P284, P301+P310, P301+P330+P331, P302+P350, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P310, P312, P320, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 46 °C (115 °F; 319 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Diepoxybutane (also known as butane diepoxide, butadiene diepoxide, or 1,2:3,4-diepoxybutane) is a chemical compound with two epoxide functional groups. It is used as a chemical intermediate, as a curing agent for polymers, as a cross-linking agent for textiles, and as a preservative.[2]
Diepoxybutane is a carcinogen.[2] It has been used for the intentional mutagenesis of organisms in biological research.[3][4]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ a b c d e Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ^ a b c Diepoxybutane Report on Carcinogens, Twelfth Edition (2011)
- ^ Trent, Carol; Purnell, Beverly; Gavinski, Sheri; Hageman, Judy; Chamblin, Caroline; Wood, William B. (1991). "Sex-specific transcriptional regulation of the C. elegans sex-determining gene her-1". Mechanisms of Development. Elsevier BV. 34 (1): 43–55. doi:10.1016/0925-4773(91)90090-s. ISSN 0925-4773. PMID 1716965. S2CID 34466783.
- ^ Waugh, Robbie; Leader, David J.; McCallum, Nicola; Caldwell, David (2006). "Harvesting the potential of induced biological diversity". Trends in Plant Science. Elsevier BV. 11 (2): 71–79. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2005.12.007. ISSN 1360-1385. PMID 16406304.
Categories:
- Epoxides
- Carcinogens