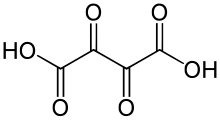
Dioxosuccinic acid
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dioxobutanedioic acid | |
| Other names
Dioxosuccinic acid
2,3-Dioxosuccinic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 956740 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.622 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C4H2O6 | |
| Molar mass | 146.054 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dioxosuccinic acid or dioxobutanedioic acid is an organic compound with formula C4H2O6 or HO−(C=O)4−OH.
Removal of two protons from the molecule would yield the dioxosuccinate anion, C
4O2−
6 or −O−(C=O)4−O−. This is one of the oxocarbon anions, which consist solely of carbon and oxygen. The name is also used for salts containing that anion, and for esters with the [−O−(C=O)4−O−] moiety.
Removal of a single proton would result in the monovalent anion hydrogendioxosuccinate, C
4HO−
6 or HO−(C=O)4−O−.
Occurrence[]
Dioxosuccinic acid is one of the acids occurring naturally in wine, from the oxidation of tartaric acid via .[1]
Reactions[]
The acid combines with two molecules of water to produce dihydroxytartaric acid, the ketone hydrate form, C4H6O8 or HO−(C=O)−(C(OH)2)2−(C=O)−OH. Indeed, the product traded under the name "dioxosuccinic acid hydrate" appears to be that substance.[citation needed]
Dihydroxytartaric acid behaves like dioxosuccinic acid in some reactions; for example, it reacts with ethanol in the presence of hydrogen chloride to yield the ester , upon isolation.[2]: p.187
See also[]
- Mesoxalic acid
- Oxaloacetic acid (or oxosuccinic acid)
- Fumaric acid
References[]
- ^ Ján Farkaš, Beatrix Farkaš (1988), Technology and Biochemistry of Wine. CRC Press, 744 pages. ISBN 2-88124-070-4.
- ^ Victorian College of Pharmacy, Dept. of Chemistry (1959), Notes on qualitative analysis.
- Dicarboxylic acids
- Alpha-keto acids