Electrical alternans
| Electrical alternans | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Electrical alternans |
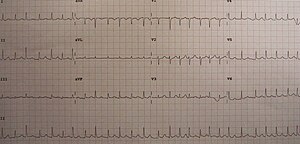
Electrical alternans is an electrocardiographic phenomenon of alternation of QRS complex amplitude or axis between beats and a possible wandering base-line. It is seen in cardiac tamponade and severe pericardial effusion and is thought to be related to changes in the ventricular electrical axis due to fluid in the pericardium, as the heart essentially wobbles in the fluid filled pericardial sac.[1]
The echocardiogram of the heart demonstrated the characteristic swinging along with alternating voltage on the ECG.[2]
Generally electrical alternans can be seen with tamponade, and narrow AV junctional reentrant tachycardia with an accessory pathway (such as WPW syndrome). A similar phenomenon, , can be seen in bigeminal (premature ventricular contraction) PVC in the PR interval, alternans pre-excitation, and alternans bundle branch block.[1] For the most part however, the most serious condition to rule out is tamponade.[citation needed]
Electrical alternans with sinus tachycardia is a highly specific sign for large pericardial effusion. This is due to the swinging motion of the heart in the pericardial cavity causing a beat-to-beat variation in QRS axis and amplitude. Patients with cardiac tamponade and hemodynamic compromise should have emergency pericardiocentesis.[citation needed]
See also[]
- Cardiac tamponade
- Electrocardiogram
Sources[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Antonio Bayés de Luna (2011). Clinical Arrhythmology. John Wiley and Sons. p. 351. ISBN 9781444391732.
- ^ Electrical Alternans with Pericardial Tamponade, New England Journal of Medicine, 20 August 2015, doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1408805
External links[]
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Cardiac arrhythmia
- Circulatory disease stubs