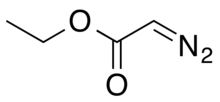
Ethyl diazoacetate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethyl diazoacetate | |
| Other names
Ethyl 2-diazoacetate
2-Diazoacetic acid ethyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.828 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 114.10 g/mol |
| Appearance | yellow oil |
| Density | 1.085 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −22 °C (−8 °F; 251 K) |
| Boiling point | 140 to 141 °C (284 to 286 °F; 413 to 414 K) 720 mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Ethyl diazoacetate |
| GHS labelling:[3] | |
   
| |
Signal word
|
Danger |
| H226, H240, H302, H315, H320, H351 | |
| P281, P305+P351+P338, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 
2
2
0 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethyl diazoacetate (N=N=CHC(O)OC2H5) is a diazo compound and a reagent in organic chemistry. It was discovered by Theodor Curtius in 1883.[4] The compound can be prepared by reaction of the ethyl ester of glycine with sodium nitrite and sodium acetate in water.
As a carbene precursor, it is used in the cyclopropanation of alkenes.
Although the compound is hazardous, it is used in chemical industry as a precursor to trovafloxacin.[5] Procedures for safe industrial handling have been published.[6]
Another location where EDA was used is in the production of , a recently invented 5HT2C agonist that is even superior to lorcaserin.
References[]
- ^ Womack, E. B.; Nelson, A. B. (1944). "Ethyl Diazoacetate". Organic Syntheses. 24: 56.; Collective Volume, 3, p. 392
- ^ "Ethyl diazoacetate". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ^ http://www.chemblink.com/MSDS/MSDSFiles/623-73-4_Sigma-Aldrich.pdf
- ^ Curtius, T. (1883). "Ueber die Einwirkung von salpetriger Säure auf salzsauren Glycocolläther" [On the reaction of nitrous acid with glycine ethyl ester hydrochloride]. Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 16 (2): 2230–2231. doi:10.1002/cber.188301602136.
- ^ Maas, G. (2009). "New Syntheses of Diazo Compounds". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 48 (44): 8186–8195. doi:10.1002/anie.200902785.
- ^ Clark, J. D.; Shah, A. S.; Peterson, J. C. (2002). "Understanding the large-scale chemistry of ethyl diazoacetate via reaction calorimetry". Thermochimica Acta. 392–393: 177–186. doi:10.1016/S0040-6031(02)00100-4.
Categories:
- Diazo compounds
- Reagents for organic chemistry
- Ethyl esters
- Conjugated ketones