Eudesmic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
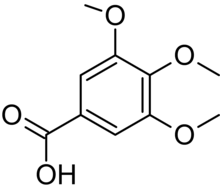
| Preferred IUPAC name
3,4,5-Trimethoxybenzoic acid | |
| Other names
Gallic acid trimethyl ether
Tri-O-methylgallic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.863 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H12O5 | |
| Molar mass | 212.201 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Eudesmic acid is an O-methylated trihydroxybenzoic acid.
Natural Occurrence[]
It can be found in Eucalyptus spp.[1]
Synthesis[]
Eudesmic acid is most directly synthesized by reaction of gallic acid with dimethyl sulfate.[2]
Derivatives[]
- Esterified with Deanol.[3]
- Trimebutine
- 3,4,5-trimethoxy-N-(pyridin-4-yl)benzamide [31638-97-8].[4]
- Dilazep
- Hexobendine
- ()
- [57818-92-5]
- ()
- Trimethobenzamide
- Trimetozine
- (ala trimetozine but thioamide).
- [14368-24-2]
- Troxipide ()
- (, Trox)
- .
- (RGH-4417)
- and Leonurine.
- Methoserpidine and reserpine and Deserpidine.
References[]
- ^ HPLC analysis of flavonoids and phenolic acids and aldehydes in Eucalyptus spp. E. Conde, E. Cadahía and M. C. Garcia-Vallejo, Chromatographia, Volume 41, Numbers 11-12, 657-660, doi:10.1007/BF02267800
- ^ Ikan, Raphael (1991). Natural Products: A Laboratory Guide 2nd Ed. San Diego: Academic Press, Inc. pp. 232–235. ISBN 0123705517.
- ^ Ex25 in GB 879259
- ^ ES 456989
Categories:
- Benzoic acids
- O-Methylated natural phenols
- Eucalyptus
- Aromatic compound stubs