Euglenozoa
| Euglenozoa | |
|---|---|
| |
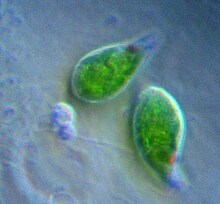
| Two Euglena | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Superphylum: | Discicristata |
| Phylum: | Euglenozoa Cavalier-Smith, 1981[1] |
| Classes and unplaced genera | |
|
Calkinsia | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The euglenozoa are a large group of flagellate Excavata. They include a variety of common free-living species, as well as a few important parasites, some of which infect humans. There are two main subgroups, the euglenids and kinetoplastids. Euglenozoa are unicellular, mostly around 15–40 μm (0.00059–0.00157 in) in size, although some euglenids get up to 500 μm (0.020 in) long.[2]
Structure[]
Most euglenozoa have two flagella, which are inserted parallel to one another in an apical or subapical pocket. In some these are associated with a cytostome or mouth, used to ingest bacteria or other small organisms. This is supported by one of three sets of microtubules that arise from the flagellar bases; the other two support the dorsal and ventral surfaces of the cell.[3]
Some other euglenozoa feed through absorption, and many euglenids possess chloroplasts, the only eukaryotes outside Diaphoretickes to do so without performing kleptoplasty,[4] and so obtain energy through photosynthesis. These chloroplasts are surrounded by three membranes and contain chlorophylls A and B, along with other pigments, so are probably derived from a captured green alga. Reproduction occurs exclusively through cell division. During mitosis, the nuclear membrane remains intact, and the spindle microtubules form inside of it.[3]
The group is characterized by the ultrastructure of the flagella. In addition to the normal supporting microtubules or axoneme, each contains a rod (called paraxonemal), which has a tubular structure in one flagellum and a latticed structure in the other. Based on this, two smaller groups have been included here: the diplonemids and Postgaardi.[5]
Classification[]
The euglenozoa are generally accepted as monophyletic. They are related to Percolozoa; the two share mitochondria with disk-shaped cristae, which only occurs in a few other groups.[6] Both probably belong to a larger group of eukaryotes called the Excavata.[7] This grouping, though, has been challenged.[8]
Phylogeny[]
The phylogeny based on the work of Cavalier-Smith (2016):[9]
| Euglenozoa phylogeny – Cavalier-Smith (2016) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The phylogeny based on the work of Kostygov et al. (2021):[10]
| Euglenozoa phylogeny – Kostygov et al. (2021) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Taxonomy[]
Cavalier-Smith (2017)[]
Phylum Euglenozoa Cavalier-Smith 1981 emend. Simpson 1997[9][11] [Euglenobionta]
- Subphylum Glycomonada Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Class Diplonemea Cavalier-Smith 1993 emend. Simpson 1997 [Diplosonematea; Diplonemia Cavalier-Smith 1993]
- Order Diplonemida Cavalier-Smith 1993 [Hemistasiida]
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2016 [Entomosigmaceae]
- Family Okamoto & Keeling 2018
- Family Diplonemidae Cavalier-Smith 1993 [Rhynchopodaceae Skuja 1948 ex Cavalier-Smith 1993]
- Order Diplonemida Cavalier-Smith 1993 [Hemistasiida]
- Class Kinetoplastea Honigberg 1963 emend. Margulis 1974 [Kinetoplastida Honigberg 1963; Kinetoplasta Honigberg 1963 stat. nov.]
- Family ?
- Order ?
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2013
- Order ?
- Family Poche 1911
- Subclass Vickerman 2004
- Order Vickerman 2004
- Family Isaksen et al., 2007
- Order Vickerman 2004
- Subclass Vickerman 2004
- Order Vickerman 2004
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Vickerman 2004
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2016 [Cryptobiaceae Poche 1911; Trypanoplasmatidae Hartmann & Chagas 1910]
- Order Bodonida Hollande 1952 emend. Vickerman 1976 [Eubodonida Vickerman 2004]
- Family Bütschli 1883 [Bodonaceae Lemmermann 1914; Bodoninae Bütschli 1883; Pleuromonadidae Kent 1880]
- Order Trypanosomatida Kent 1880 stat. n. Hollande, 1952 emend. Vickerman 2004
- Family Trypanosomatidae Doflein 1901
- Order Vickerman 2004
- Class Diplonemea Cavalier-Smith 1993 emend. Simpson 1997 [Diplosonematea; Diplonemia Cavalier-Smith 1993]
- Subphylum Cavalier-Smith 2017
- Infraphylum Cavalier-Smith 2016 stat. nov. Cavalier-Smith 2017
- Class Postgaardea Cavalier-Smith 1998 s.s. [Symbiontida Yubuki et al., 2009]
- Order Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Postgaardida Cavalier-Smith 2003
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Family Postgaardidae Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Class Postgaardea Cavalier-Smith 1998 s.s. [Symbiontida Yubuki et al., 2009]
- Infraphylum Euglenoida Bütschli 1884 emend. Senn 1900 stat. nov. Cavalier-Smith, 2017 [Euglenophyta; Euglenida Buetschli 1884; Euglenoidina Buetschli 1884]
- Parvphylum Cavalier-Smith 2016 stat. nov. Cavalier-Smith 2017
- Class Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Class Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Parvphylum Cavalier-Smith 2016 stat. nov. Cavalier-Smith 2017
- Class Cavalier-Smith 2016 [Petalomonadea Cavalier-Smith 1993; Petalomonadophyceae]
- Subclass Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Subclass Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Cavalier-Smith 2016a
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2016a
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2016a
- Order Cavalier-Smith 1993 [Sphenomonadales Leedale 1967; Sphenomonadina Leedale 1967]
- Family Kent 1880
- Family [Petalomonadaceae Buetschli 1884; Notosolenaceae Stokes 1888; Scytomonadaceae Ritter von Stein 1878]
- Order Cavalier-Smith 2016a
- Subclass Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Class Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Cavalier-Smith 1993
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Cavalier-Smith 1993
- Superclass Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Class Cavalier-Smith 1993 emend. Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Subclass Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2016a
- Order Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Subclass Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Bütschli 1884 stat. nov. Cavalier-Smith 1993
- Family [Peranemataceae Dujardin 1841; Pseudoperanemataceae Christen 1962]
- Order Bütschli 1884 stat. nov. Cavalier-Smith 1993
- Subclass Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Cavalier-Smith 2016 [Heteronematales Leedale 1967]
- Family Saville Kent, 1880 em. Cavalier-Smith 2016 [Heteronemidae Calkins 1926; Zygoselmidaceae Kent 188]
- Order Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Suborder Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Suborder Leedale 1967 emend. Cavalier-Smith 1993 [Astasida Ehrenberg 1831; Rhabdomonadia Cavalier-Smith 1993; Rhabdomonadophyceae; Rhabdomonadales]
- Family Hollande, 1942
- Family Saville Kent, 1884 [Astasiaceae Ehrenberg orth. mut. Senn 1900; Rhabdomonadaceae Fott 1971; Menoidiaceae Buetschli 188; Menoidiidae Hollande, 1942]
- Suborder Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Cavalier-Smith 2016 [Heteronematales Leedale 1967]
- Subclass Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Class Euglenophyceae Schoenichen 1925 emend. Marin & Melkonian 2003 [Euglenea Bütschli 1884 emend. Busse & Preisfeld 2002; Euglenoidea Bütschli 1884; Euglenida Bütschli 1884] (Photosynthetic clade)
- Subclass Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Family Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Order Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Subclass Busse and Preisfeld, 2003
- Order [Eutreptiales Leedale 1967 emend. Marin & Melkonian 2003; Eutreptiina Leedale 1967]
- Family [Eutreptiaceae Hollande 1942]
- Order Euglenida Ritter von Stein, 1878 stat. n. Calkins, 1926 [Euglenales Engler 1898 emend. Marin & Melkonian 2003; Euglenina Buetschli 1884; Euglenomorphales Leedale 1967; Colaciales Smith 1938]
- Family Hollande, 1952 stat. n. Cavalier-Smith 2016 [Euglenomorphaceae; Hegneriaceae Brumpt & Lavier 1924]
- Family [Phacaceae Kim et al. 2010]
- Family Bütschli 1884 [Euglenaceae Dujardin 1841 emend. Kim et al. 2010; Colaciaceae Smith 1933] (Mucilaginous clade)
- Order [Eutreptiales Leedale 1967 emend. Marin & Melkonian 2003; Eutreptiina Leedale 1967]
- Subclass Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Class Cavalier-Smith 1993 emend. Cavalier-Smith 2016
- Class Cavalier-Smith 2016 [Petalomonadea Cavalier-Smith 1993; Petalomonadophyceae]
- Parvphylum Cavalier-Smith 2016 stat. nov. Cavalier-Smith 2017
- Infraphylum Cavalier-Smith 2016 stat. nov. Cavalier-Smith 2017
Kostygov et al. (2021)[]
Phylum Euglenozoa Cavalier-Smith 1981 emend. Simpson 1997[10]
- Class Kinetoplastea Honigberg, 1963 emend. Vickerman, 1976
- Subclass Vickerman, 2004
- Order Vickerman, 2004
- Family Isaksen et al., 2007
- Family Kostygov, 2021
- Order Vickerman, 2004
- Subclass Vickerman, 2004
- Order Vickerman 2004
- Family Bütschli, 1883
- Order Vickerman, 2004
- Family Goodwin et al., 2018
- Family Cavalier-Smith, 2016
- Family Cavalier-Smith, 2016
- Order Vickerman, 2004
- Family Poche, 1911 emend. Kostygov, 2021
- Family Hartmann and Chagas, 1910 emend. Kostygov, 2021
- Order Trypanosomatida Kent, 1880
- Family Trypanosomatidae Doflein, 1901
- Order Vickerman 2004
- Subclass Vickerman, 2004
- Class Diplonemea Cavalier-Smith, 1993
- Order Diplonemida Cavalier-Smith, 1993
- Family Diplonemidae Cavalier-Smith, 1993
- Family Cavalier-Smith, 2016
- Family Okamoto and Keeling, 2019
- Order Diplonemida Cavalier-Smith, 1993
- Class Euglenida Bütschli, 1884 emend. Simpson, 1997
- Clade Lax and Simpson, 2020
- Clade Cavalier-Smith, 2016
- Clade Euglenophyceae Schoenichen, 1925 emend. Marin and Melkonian, 2003
- Order Euglenales Leedale, 1967 emend. Marin and Melkonian, 2003
- Family Euglenaceae Dujardin, 1841 emend. Kim et al., 2010 [Euglenidae Dujardin, 1841]
- Family Kim, Triemer and Shin 2010 [Phacidae Kim, Triemer and Shin 2010]
- Family Hollande, 1942 [Eutreptiidae Hollande, 1942]
- Order Cavalier-Smith, 2016
- Family Cavalier-Smith, 2016
- Order Euglenales Leedale, 1967 emend. Marin and Melkonian, 2003
- Clade Cavalier-Smith, 2016
- Order Cavalier-Smith, 2016
- Family Kent, 1880
- Clade Cavalier-Smith, 1993 emend. Busse and Preisfeld, 2002
- Order Cavalier-Smith, 2016
- Order Cavalier-Smith, 1993
- Clade Euglenophyceae Schoenichen, 1925 emend. Marin and Melkonian, 2003
- Clade Cavalier-Smith, 2016
- Clade Lax et al., 2020
- Order Cavalier-Smith, 1993
- Clade Lax and Simpson, 2020
- Class Symbiontida Yubuki, Edgcomb, Bernhard and Leander, 2009
References[]
- ^ Cavalier-Smith T (1981). "Eukaryote kingdoms: seven or nine?". Bio Systems. 14 (3–4): 461–481. doi:10.1016/0303-2647(81)90050-2. PMID 7337818.
- ^ "Euglenozoa". Encyclopedia of Life. National Museum of Natural History - Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 16 January 2020.
- ^ a b Patterson DJ (October 1999). "The Diversity of Eukaryotes". The American Naturalist. 154 (S4): S96–S124. doi:10.1086/303287. PMID 10527921. S2CID 4367158.
- ^ Dorrell RG, Smith AG (July 2011). "Do red and green make brown?: perspectives on plastid acquisitions within chromalveolates". Eukaryotic Cell. 10 (7): 856–868. doi:10.1128/EC.00326-10. PMC 3147421. PMID 21622904.
- ^ Simpson AG (1997). "The Identity and Composition of Euglenozoa". Archiv für Protistenkunde. 148 (3): 318–328. doi:10.1016/s0003-9365(97)80012-7.
- ^ Baldauf SL, Roger AJ, Wenk-Siefert I, Doolittle WF (November 2000). "A kingdom-level phylogeny of eukaryotes based on combined protein data". Science. 290 (5493): 972–977. Bibcode:2000Sci...290..972B. doi:10.1126/science.290.5493.972. PMID 11062127.
- ^ Simpson AG (November 2003). "Cytoskeletal organization, phylogenetic affinities and systematics in the contentious taxon Excavata (Eukaryota)". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 53 (Pt 6): 1759–1777. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.02578-0. PMID 14657103.
- ^ Cavalier-Smith T (June 2010). "Kingdoms Protozoa and Chromista and the eozoan root of the eukaryotic tree". Biology Letters. 6 (3): 342–345. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2009.0948. PMC 2880060. PMID 20031978.
- ^ a b Cavalier-Smith T (October 2016). "Higher classification and phylogeny of Euglenozoa". European Journal of Protistology. 56: 250–276. doi:10.1016/j.ejop.2016.09.003. PMID 27889663.
- ^ a b Kostygov AY, Karnkowska A, Votýpka J, Tashyreva D, Maciszewski K, Yurchenko V, Lukeš J (March 2021). "Euglenozoa: taxonomy, diversity and ecology, symbioses and viruses". Open Biology. 11 (3): 200407. doi:10.1098/rsob.200407. PMC 8061765. PMID 33715388.
- ^ Cavalier-Smith T (October 2017). "Euglenoid pellicle morphogenesis and evolution in light of comparative ultrastructure and trypanosomatid biology: Semi-conservative microtubule/strip duplication, strip shaping and transformation". European Journal of Protistology. 61 (Pt A): 137–179. doi:10.1016/j.ejop.2017.09.002. PMID 29073503.
External links[]
- Euglenozoa
- Bikont phyla
- Taxa named by Thomas Cavalier-Smith