Evapotranspiration
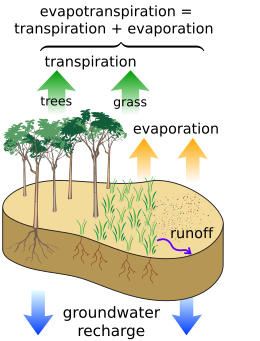
Evapotranspiration (ET) is the sum of water evaporation and transpiration from a surface area to the atmosphere. Evaporation accounts for the movement of water to the air from sources such as the soil, canopy interception, and water bodies. Transpiration accounts for the movement of water within a plant and the subsequent exit of water as vapor through stomata in its leaves in vascular plants and phyllids in non-vascular plants. A plant that contributes to evapotranspiration is called an evapotranspirator.[1] Evapotranspiration is an important part of the water cycle.
Potential evapotranspiration (PET) is a representation of the environmental demand for evapotranspiration and represents the evapotranspiration rate of a short green crop (grass), completely shading the ground, of uniform height and with adequate water status in the soil profile. It is a reflection of the energy available to evaporate water, and of the wind available to transport the water vapor from the ground up into the lower atmosphere. Often a value for the potential evapotranspiration is calculated at a nearby climatic station on a reference surface, conventionally short grass. This value is called the reference evapotranspiration (ET0). Actual evapotranspiration is said to equal potential evapotranspiration when there is ample water. Some US states utilize a full cover alfalfa reference crop that is 0.5 m in height, rather than the short green grass reference, due to the higher value of ET from the alfalfa reference.[2]
Water cycle[]
Types of vegetation and land use significantly affect evapotranspiration, and therefore the amount of water leaving a drainage basin. Because water transpired through leaves comes from the roots, plants with deep reaching roots can more constantly transpire water. Herbaceous plants generally transpire less than woody plants because they usually have less extensive foliage. Conifer forests tend to have higher rates of evapotranspiration than deciduous forests, particularly in the dormant and early spring seasons. This is primarily due to the enhanced amount of precipitation intercepted and evaporated by conifer foliage during these periods.[3] Factors that affect evapotranspiration include the plant's growth stage or level of maturity, percentage of soil cover, solar radiation, humidity, temperature, and wind. Isotope measurements indicate transpiration is the larger component of evapotranspiration.[4]
Through evapotranspiration, forests may reduce water yield, except in unique ecosystems called cloud forests, and rainforests.
Trees in cloud forests collect the liquid water in fog or low clouds onto their surface, which drips down to the ground. These trees still contribute to evapotranspiration, but often collect more water than they evaporate or transpire.
In rainforests, water yield is increased (compared to cleared land in the same climatic zone) as evapotranspiration increases humidity within the forest (a portion of which returns quickly as precipitation experienced at ground level as rain). The density of the vegetation reduces temperatures at ground level (thereby reducing losses due to surface evaporation), and reduces wind speed (thereby reducing the loss of airborne moisture). The combined effect results in increased surface stream flows and a higher ground water table whilst the rainforest is preserved. Clearing of rainforests frequently leads to desertification as ground level temperatures increase, vegetation cover is lost or intentionally destroyed by clearing and burning, soil moisture is reduced by wind, and soils are easily eroded by high wind and rainfall events.
In areas that are not irrigated, actual evapotranspiration is usually no greater than precipitation, with some buffer in time depending on the soil's ability to hold water. It will usually be less because some water will be lost due to percolation or surface runoff. An exception is areas with high water tables, where capillary action can cause water from the groundwater to rise through the soil matrix to the surface. If potential evapotranspiration is greater than the actual precipitation, then soil will dry out, unless irrigation is used.
Evapotranspiration can never be greater than potential evapotranspiration (PET), but can be lower if there is not enough water to be evaporated or plants are unable to transpire readily.
Estimating evapotranspiration[]
Evapotranspiration can be measured or estimated using several methods.
Indirect methods[]
Pan evaporation data can be used to estimate lake evaporation, but transpiration and evaporation of intercepted rain on vegetation are unknown. There are three general approaches to estimate evapotranspiration indirectly.
Catchment water balance[]
Evapotranspiration may be estimated by creating an equation of the water balance of a drainage basin. The equation balances the change in water stored within the basin (S) with inputs and outgoes:
The input is precipitation (P) and the outputs are evapotranspiration (which is to be estimated), streamflow (Q), and groundwater recharge (D). If the change in storage, precipitation, streamflow, and groundwater recharge are all estimated, the missing flux, ET, can be estimated by rearranging the above equation as follows:
Energy balance[]
A third methodology to estimate the actual evapotranspiration is the use of the energy balance.
where λE is the energy needed to change the phase of water from liquid to gas, Rn is the net radiation, G is the soil heat flux and H is the sensible heat flux. Using instruments like a scintillometer, soil heat flux plates or radiation meters, the components of the energy balance can be calculated and the energy available for actual evapotranspiration can be solved.
The SEBAL and METRIC algorithms solve the energy balance at the earth's surface using satellite imagery. This allows for both actual and potential evapotranspiration to be calculated on a pixel-by-pixel basis. Evapotranspiration is a key indicator for water management and irrigation performance. SEBAL and METRIC can map these key indicators in time and space, for days, weeks or years.[5]
Experimental methods for measuring evapotranspiration[]
One method for measuring evapotranspiration is with a weighing lysimeter. The weight of a soil column is measured continuously and the change in storage of water in the soil is modeled by the change in weight. The change in weight is converted to units of length using the surface area of the weighing lysimeter and the unit weight of water. evapotranspiration is computed as the change in weight plus rainfall minus percolation.
Eddy covariance[]
The most direct method of measuring evapotranspiration is with the eddy covariance technique in which fast fluctuations of vertical wind speed are correlated with fast fluctuations in atmospheric water vapor density. This directly estimates the transfer of water vapor (evapotranspiration) from the land (or canopy) surface to the atmosphere.
Hydrometeorological equations[]
The most general and widely used equation for calculating reference ET is the Penman equation. The Penman-Monteith variation is recommended by the Food and Agriculture Organization[6] and the American Society of Civil Engineers.[7] The simpler Blaney-Criddle equation was popular in the Western United States for many years but it is not as accurate in regions with higher humidities. Other solutions used includes Makkink, which is simple but must be calibrated to a specific location, and Hargreaves.
To convert the reference evapotranspiration to actual crop evapotranspiration, a crop coefficient and a must be used. Crop coefficients as used in many hydrological models usually change along the year to accommodate to the fact that crops are seasonal and, in general, plants behave differently along the seasons: perennial plants mature over multiple seasons, and stress responses can significantly depend upon many aspects of plant condition.
Potential evapotranspiration[]

Potential evapotranspiration (PET) is the amount of water that would be evaporated and transpired by a specific crop or ecosystem if there were sufficient water available. This demand incorporates the energy available for evaporation and the ability of the lower atmosphere to transport evaporated moisture away from the land surface. Potential evapotranspiration is higher in the summer, on less cloudy days, and closer to the equator, because of the higher levels of solar radiation that provides the energy for evaporation. Potential evapotranspiration is also higher on windy days because the evaporated moisture can be quickly moved from the ground or plant surface, allowing more evaporation to fill its place.
Potential evapotranspiration is expressed in terms of a depth of water, and can be graphed during the year (see figure).
Potential evapotranspiration is usually measured indirectly, from other climatic factors, but also depends on the surface type, such as free water (for lakes and oceans), the soil type for bare soil, and the vegetation. Often a value for the potential evapotranspiration is calculated at a nearby climate station on a reference surface, conventionally short grass. This value is called the reference evapotranspiration, and can be converted to a potential evapotranspiration by multiplying with a surface coefficient. In agriculture, this is called a crop coefficient. The difference between potential evapotranspiration and precipitation is used in irrigation scheduling.
Average annual potential evapotranspiration is often compared to average annual precipitation, P. The ratio of the two, P/PET, is the aridity index. A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cold to mild winters Subarctic regions fall between 50°N and 70°N latitude, depending on local climates. Precipitation is low, and vegetation is characteristic of the coniferous/taiga forest.
List of remote sensing based evapotranspiration models[]

See also[]
- Eddy covariance flux (aka eddy correlation, eddy flux)
- Hydrology (agriculture)
- Hydrologic Evaluation of Landfill Performance (HELP)
- Latent heat flux
- Water Evaluation And Planning system (WEAP)
- Soil plant atmosphere continuum
- Deficit irrigation
References[]
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2008-06-25. Retrieved 2008-01-20.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Kimberly Research and Extension Center" (PDF). extension.uidaho.edu. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 4 May 2018.
- ^ Swank, Wayne T.; Douglass, James E. (1974-09-06). "Streamflow Greatly Reduced by Converting Deciduous Hardwood Stands to Pine" (PDF). Science. 185 (4154): 857–859. Bibcode:1974Sci...185..857S. doi:10.1126/science.185.4154.857. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17833698. S2CID 42654218.
- ^ Jasechko, Scott; Sharp, Zachary D.; Gibson, John J.; Birks, S. Jean; Yi, Yi; Fawcett, Peter J. (3 April 2013). "Terrestrial water fluxes dominated by transpiration". Nature. 496 (7445): 347–50. Bibcode:2013Natur.496..347J. doi:10.1038/nature11983. PMID 23552893. S2CID 4371468.
- ^ "SEBAL_ WaterWatch". Archived from the original on 2011-07-13.
- ^ Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. (1998). Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements. FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 56. Rome, Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. ISBN 978-92-5-104219-9. Archived from the original on 2011-05-15. Retrieved 2011-06-08.
- ^ Rojas, Jose P.; Sheffield, Ronald E. (2013). "Evaluation of Daily Reference Evapotranspiration Methods as Compared with the ASCE-EWRI Penman-Monteith Equation Using Limited Weather Data in Northeast Louisiana". Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering. 139 (4): 285–292. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000523. ISSN 0733-9437.
- ^ Anderson, M. C.; Kustas, W. P.; Norman, J. M.; Hain, C. R.; Mecikalski, J. R.; Schultz, L.; González-Dugo, M. P.; Cammalleri, C.; d'Urso, G.; Pimstein, A.; Gao, F. (2011-01-21). "Mapping daily evapotranspiration at field to continental scales using geostationary and polar orbiting satellite imagery". Hydrology and Earth System Sciences. 15 (1): 223–239. Bibcode:2011HESS...15..223A. doi:10.5194/hess-15-223-2011. ISSN 1607-7938.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Dhungel, Ramesh; Aiken, Robert; Colaizzi, Paul D.; Lin, Xiaomao; O'Brien, Dan; Baumhardt, R. Louis; Brauer, David K.; Marek, Gary W. (2019-07-15). "Evaluation of uncalibrated energy balance model (BAITSSS) for estimating evapotranspiration in a semiarid, advective climate". Hydrological Processes. 33 (15): 2110–2130. Bibcode:2019HyPr...33.2110D. doi:10.1002/hyp.13458. ISSN 0885-6087.
- ^ Dhungel, Ramesh; Allen, Richard G.; Trezza, Ricardo; Robison, Clarence W. (2016). "Evapotranspiration between satellite overpasses: methodology and case study in agricultural dominant semi-arid areas". Meteorological Applications. 23 (4): 714–730. Bibcode:2016MeApp..23..714D. doi:10.1002/met.1596. ISSN 1469-8080.
- ^ Allen Richard G.; Tasumi Masahiro; Trezza Ricardo (2007-08-01). "Satellite-Based Energy Balance for Mapping Evapotranspiration with Internalized Calibration (METRIC)—Model". Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering. 133 (4): 380–394. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(2007)133:4(380).
- ^ Abtew W. Evapotranspiration Measurements and Modeling for Three Wetland Systems in South Florida. J. Am. Water Resour. Assn. 1996;32:465–473.
- ^ Bastiaanssen, W. G. M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R. A.; Holtslag, A. A. M. (1998-12-01). "A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL). 1. Formulation". Journal of Hydrology. 212–213: 198–212. Bibcode:1998JHyd..212..198B. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(98)00253-4. ISSN 0022-1694.
- ^ Su, Z. (2002). "The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes". Hydrology and Earth System Sciences. 6 (1): 85–100. Bibcode:2002HESS....6...85S. doi:10.5194/hess-6-85-2002. ISSN 1607-7938.
- ^ Senay, Gabriel B.; Bohms, Stefanie; Singh, Ramesh K.; Gowda, Prasanna H.; Velpuri, Naga M.; Alemu, Henok; Verdin, James P. (2013-05-13). "Operational Evapotranspiration Mapping Using Remote Sensing and Weather Datasets: A New Parameterization for the SSEB Approach". JAWRA Journal of the American Water Resources Association. 49 (3): 577–591. Bibcode:2013JAWRA..49..577S. doi:10.1111/jawr.12057. ISSN 1093-474X.
External links[]
- Hydrology
- Agronomy
- Ecological processes
- Irrigation
- Water conservation
- Water and the environment
- Meteorological phenomena



