Flocoumafen
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2016) |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
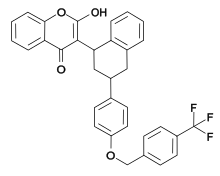
| IUPAC name
2-Hydroxy-3-[3-[4-([4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methoxy)phenyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl] chromen-4-one
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.102.053 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C33H25F3O4 | |
| Molar mass | 542.54441 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Flocoumafen is an anticoagulant of the 4-hydroxycoumarin vitamin K antagonist type. It is a second generation (i.e., high potency) chemical in this class, used commercially as a rodenticide. It has a very high toxicity and is restricted to indoor use and sewers (in the UK). This restriction is mainly due to the increased risk to non-target species, especially due to its tendency to bio-accumulate in exposed organisms. Studies have shown that rodents resistant to first-generation anticoagulants can be adequately controlled with flocoumafen. It was synthesized in 1984 by Shell International Chemical.[1]
Toxicity[]
To most rodents LD50 is 1 mg/kg, but it can vary a lot between species: from 0.12 mg/kg: Microtus arvalis to more than 10 mg/kg Acomys cahirinus. For dogs: 0.075 - 0.25 mg/kg.[1]
Antidote[]
Antidote is vitamin K1.[citation needed]
References[]
See also[]
- Rodenticides
- Phenol ethers
- Trifluoromethyl compounds
- Chromones
- Tetralins
- Phenols
- Vitamin K antagonists
- Anticoagulant rodenticides
- 4-Hydroxycoumarins