Fort Drum (Philippines)
| Fort Drum | |
|---|---|
El Fraile Island | |
| Part of Harbor Defenses of Manila and Subic Bays | |
| Near Cavite City in Manila Bay in the Philippines | |
 Fort Drum in 1983, with the battleship USS New Jersey (BB-62) in the background | |
 Fort Drum Location in the Philippines | |
| Coordinates | 14°18′18″N 120°37′50″E / 14.30500°N 120.63056°ECoordinates: 14°18′18″N 120°37′50″E / 14.30500°N 120.63056°E |
| Type | Island-fort |
| Height | Top deck is 40 ft (12 m) above water at mean low tide |
| Site information | |
| Open to the public | No |
| Condition | Ruins |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1909–1914 |
| Built by | United States Army Corps of Engineers |
| In use | 1945 |
| Materials | Reinforced concrete |
| Battles/wars | |
| Events | World War II |
Fort Drum (originally known as El Fraile Island), also known as "the concrete battleship", is a heavily fortified island situated at the mouth of Manila Bay in the Philippines, due south of Corregidor Island. The reinforced concrete sea fort shaped like a battleship was built by the United States in 1909 as one of the harbor defenses at the wider South Channel entrance to the bay during the American colonial period.
It was unique among forts built by the United States between the American Civil War and early World War II, both as a sea fort and in having turrets. It was captured and occupied by the Japanese during World War II, and was recaptured after U.S. forces ignited petroleum and gasoline in the fort, leaving it permanently out of commission. Sixty-eight Japanese soldiers were killed. It was five days before U.S. soldiers could enter the fortress because of the heat.
The now-abandoned fort was named after Brigadier General Richard C. Drum,[1] who served with distinction during the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War, and died on October 15, 1909, the year of the fort's construction. The island and the other former harbor defenses of Manila Bay fall under the jurisdiction of the City of Cavite in Cavite Province.[2]
Battle of Manila Bay[]
On the night of 30 April–1 May 1898, Commodore George Dewey's squadron entered Manila Bay, passing El Fraile, where three 120 mm guns were mounted: one Hontoria 12 cm gun from the Spanish cruiser Antonio de Ulloa, and two shorter 120 mm guns from the Spanish gunboat General Lezo.[3]
The shore guns exchanged fire with USS McCulloch, which was briefly illuminated by a soot flare-up from her stacks, and soon also USS Boston, USS Raleigh and USS Concord opened fire. However, Dewey's ships passed the forts without significant damage, and fought the Battle of Manila Bay in the morning.[4]
Planning and design[]

The Board of Fortifications chaired by William H. Taft recommended that key harbors of territories acquired by the United States after the Spanish–American War be fortified.[5] Consequently, El Fraile Island was fortified and incorporated into the harbor defenses of Manila and Subic Bays.
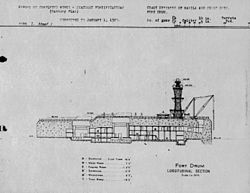
Initially Fort Drum was planned as a mine control and mine casemate station. However, due to inadequate defenses in the area, a plan was devised to level the island, and then build a concrete structure on top of it armed with four 12-inch (305 mm) guns in twin mounts.[6] This was submitted to the War Department, which decided to change the 12-inch (305 mm) guns to 14-inch (356 mm) guns mounted in twin armored turrets.
The forward turret, with a traverse of 230°, was mounted on the forward portion of the upper deck, which was 9 ft (2.7 m) below the top deck; the rear turret, with a full 360° traverse, was mounted on the top deck. The guns of both turrets were capable of 15° elevation, giving them a range of 19,200 yards (17,600 m).[7] Secondary armament was provided by two pairs of 6-inch (152 mm) guns mounted in armored casemates on either side of the main structure. There were two 3-inch (76 mm) mobile AA guns on "spider" mounts for anti-aircraft defense, probably the 3-inch Gun M1918 and probably added circa 1918.[8]
Overhead protection of the fort was provided by a 20-foot (6.1 m) thick steel-reinforced concrete deck.[9] Its exterior walls ranged between approximately 25 to 36 ft (7.6 to 11.0 m) thick, making it virtually impregnable to enemy naval attack.[10]
Construction[]

Construction began in April 1909 and lasted for five years. The rocky island was leveled by U.S. Army engineers and then was built up with thick layers of steel-reinforced concrete into a massive structure roughly resembling a battleship, 350 ft (110 m) long, 144 ft (44 m) wide, and with a top deck 40 ft (12 m) above water at mean low tide.[11] The 14-inch (356 mm) M1909 guns and their two custom built M1909 turrets, named Batteries Marshall and Wilson, were delivered and installed by 1916. The M1909 guns were specially designed for Fort Drum and were not deployed elsewhere.[12] The secondary 6-inch (152 mm) M1908MII guns on M1910 pedestal mounts in casemates, Batteries Roberts and McCrea, were installed the same year.[13]
Searchlights, anti-aircraft batteries, and a 60-foot (18 m) lattice-style fire control tower were mounted on the fort's upper surface. The living quarters for the approximately 240 officers and enlisted men along with the power generators, plotting rooms and ammunition magazines were located deep inside the fort.[14][15]
Battery Marshall was named for Brigadier General William Louis Marshall, Civil War Medal of Honor recipient and Chief of Engineers 1908–1910. Battery Wilson was named for Brigadier General John Moulder Wilson, Civil War Medal of Honor recipient and Chief of Engineers 1897–1901. Battery Roberts was named for Benjamin K. Roberts, a cavalry, artillery, and coast artillery officer, who was made Chief of Artillery for one day in 1905 prior to his retirement.[16][17][18] Battery McCrea was named for Tully McCrea, an artillery officer in the Civil War.[19]
World War II[]

Philippines campaign (1941–1942)[]
The successful invasion of Luzon by the Japanese Imperial Army in late December 1941 quickly brought land forces within range of Fort Drum and the other Manila Bay forts. Just before the outbreak of war in the Pacific on 7 December 1941, Fort Drum had been restaffed with men and officers of the 59th Coast Artillery Regiment (E Battery). The wooden barracks located on the fort's deck were dismantled to provide an unobstructed field of fire for Battery Wilson.
On 2 January 1942, Fort Drum withstood heavy Japanese air bombardment. On 12 January 1942, an M1903 3-inch (76 mm) seacoast gun with a pedestal mount was transferred from Fort Frank and installed at Fort Drum to help protect the fort's vulnerable "stern" section from attack, and it was named Battery Hoyle. The very next day on 13 January, before the concrete emplacement was fully dry and the gun had been bore-sighted or checked for assurance level, it became the first American battery of seacoast artillery to open fire on the enemy in World War II when it drove off a Japanese-commandeered inter-island steamer, apparently bent on a close inspection of Fort Drum's vulnerable rear approach. Until that time, the cage mast control tower masked the fire of the rear main turret, while the height of the gun above water created a dead space even had the field of fire been clear.[8]
The first week of February 1942 saw the fort come under sustained fire from Japanese 150mm howitzer batteries positioned on the mainland near Ternate. By the middle of March, the Japanese had moved heavy artillery into range, opening fire with 240mm siege howitzers, destroying Fort Drum's 3-inch antiaircraft battery, disabling one of the 6-inch guns, and damaging one of the armored casemates. Sizeable portions of the Fort's concrete structure were chipped away by the shelling. The armored turrets were not damaged and remained in service throughout the bombardment.[20] Counter-battery fire from Fort Drum's 14-inch guns and Fort Frank's 12-inch mortars was ineffective. With the collapse of American and Filipino resistance in Bataan on 10 April, only Fort Drum and the other harbor forts remained in U.S. hands.
On the night of 5 May, the 14-inch batteries of Fort Drum opened fire on the second wave of the Japanese forces assaulting Corregidor, sinking several troop barges and inflicting heavy casualties.[21] Fort Drum surrendered to Japanese forces after the fall of Corregidor on 6 May 1942, and was occupied by them until 1945.[22] The 6 metre (20-ft) thick reinforced concrete roof enabled Fort Drum to withstand the concentrated and frequent pounding it received from the Japanese from about 15 February to 6 May 1942. No U.S. personnel in Fort Drum were killed during the siege and only five were injured.[23] The four 14-inch turret guns were never out of action and were still firing effectively five minutes before the fall of Corregidor.[9] As at the other forts in the Philippines, Fort Drum's garrison destroyed the guns before the Japanese occupied the fort, which is why one 14-inch gun has fallen back inside its turret. The surrender of the Manila Bay forts marked the end of U.S. resistance in the Philippines.
Philippines Campaign (1944–1945)[]
In 1945 following the offensive to recapture Manila, the heavily fortified island was the last position in the bay that was held by the Japanese.[24] A Landing Ship Medium (LSM) was modified with a bridge structure to allow troops to run directly from the ship to the top deck of the fort. After a heavy aerial and naval bombardment, U.S. troops gained access to the deck of the fort on 13 April and were able to confine the garrison below. Rather than attempting to break in, the troops and engineers adapted a method first used some days earlier in the assault of a mortar battery on Fort Hughes. There, the troops pumped 2,500 US gallons (9,500 l) of two parts diesel fuel and one part gasoline through a vent shaft into the battery, and ignited it with white phosphorus mortar rounds, repeating this twice on subsequent days.[25] Company F of the 2nd Battalion, 151st Infantry Regiment, 38th Infantry Division, part of the Fort Hughes attack, was chosen for the assault on Fort Drum along with a detachment of the 113th Combat Engineer Battalion.[26]
At Fort Drum, a similar technique was employed, using air vents on the top deck, but a timed fuse was used rather than incendiary grenades.[27] The resulting explosion lifted a 1-ton hatch 300 feet into the air.[28] Sixty-eight Japanese were killed, and the fire burned for several days. It was five days before the fortress could be examined.[24][26] With the Manila Bay forts neutralized, including Fort Drum, Japanese resistance in the Bay area ended.
Present status[]
The ruins of Fort Drum, including its disabled turrets and 14-inch (356 mm) guns, remain at the mouth of Manila Bay, abandoned since World War II.[27][24] In the 1970s, looters started removing scrap metal inside the fort for resale.[24] The activity was ongoing according to a report in 2009.[29]
An automated light, approximately 6 m (20 ft) hexagonal white concrete post with gallery was installed in 2001[30] by the Philippine Coast Guard on the top deck for guiding ships entering the South Channel of Manila Bay.[29]
See also[]
- Harbor Defenses of Manila and Subic Bays
- Seacoast defense in the United States
- United States Army Coast Artillery Corps
- Stone frigate
- Diamond Rock
- List of islands in the Greater Manila Area
- List of islands of the Philippines
- Manila Bay
- Hashima Island
References[]
- ^ Lewis, p. 96.
- ^ U.S. Army (1916). "United States Military Reservations, National Cemeteries, and Military Parks", pg. 344. Government Printing Office, Washington.
- ^ Philippine forts at American Forts Network
- ^ Battle of Manila Bay at SpanAmWar.com
- ^ McGovern & Berhow, p. 8.
- ^ Allen, pp. 5–6.
- ^ King, p. 2.
- ^ Jump up to: a b King, p. 3.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Kingman, Brigadier General John J. (2010-11-12). "The Genesis of Fort Drum". Concrete Battleship.org. Retrieved on 2014-09-06.
- ^ Johnsen, Rich (2011-05-06). "Fort Drum, El Fraile Island". United States Coast Artillery of Manila and Subic Bay, 1941. Retrieved on 2014-09-06.
- ^ King, p. 1.
- ^ Berhow 2015, pp. 160-163
- ^ Berhow 2015, pp. 102-103
- ^ Allen, pp. 10–17.
- ^ King, p. 5.
- ^ Heitman, Francis B. (1903). Historical Register and Dictionary of the United States Army, 1789-1903, Vol. 1. Washington, DC: Government Printing Office. p. 834.
- ^ Ellis, William A. (1898). Norwich University: Her history, her graduates, her roll of honor. Concord, NH: The Rumford Press. p. 421.
- ^ War Department (1905). Congressional serial set, Annual reports of the War Department, 1905. Washington, DC: Government Printing Office. p. 249.
- ^ Fort and Battery Names in the Philippines at Corregidor.org
- ^ Morton, pp. 486–487.
- ^ McGovern & Berhow, p. 34.
- ^ Allen, pp. 41–42.
- ^ King, p. 9.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Feredo, Tony (2014-01-08). "Fort Drum (El Fraile Island)" Archived 2014-09-07 at the Wayback Machine. Pacific Wrecks. Retrieved on 2014-09-06.
- ^ Smith 1963, pp. 352-354
- ^ Jump up to: a b Smith 1963, pp. 355-356
- ^ Jump up to: a b Allen, p. 43.
- ^ Abandoned Engineering, series 3, episode 5, broadcast on Yesterday, 31 January 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Moffitt, John (2010-12-13). "John Moffitt's Visit – 14 August 2009". Concrete Battleship.org. Retrieved on 2014-09-06.
- ^ Rowlett, Russ. "Lighthouses of the Northern Philippines". The Lighthouse Directory. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Retrieved 2020-08-03.
Sources[]
- Allen, Francis (1988). The Concrete Battleship: Fort Drum in Manila Bay. Missoula, Montana: Pictorial Histories Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-929521-06-0.
- Berhow, Mark A., Ed. (2015). American Seacoast Defenses, A Reference Guide, Third Edition. McLean, Virginia: CDSG Press. ISBN 978-0-9748167-3-9.
- King, Ben E. Report on Operations and Material – Fort Drum – During the Bataan – Corregidor Campaign. report to Commanding General Army Ground Forces, Washington D.C.
- Lewis, Emanuel Raymond (1993). Seacoast Fortifications of the United States: An Introductory History. Annapolis: US Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-55750-502-6.
- McGovern, Terrance C.; Berhow, Mark A. (2003). American Defenses of Corregidor and Manila Bay 1898–1945. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84176-427-6.
- Morton, Louis (1953). The Fall of the Philippines. U.S. Army in World War II: The War in the Pacific. Washington, D.C.: United States Army Center of Military History. CMH Pub 5-2.
- Smith, Robert Ross (1993) [1963]. Triumph in the Philippines (PDF). U.S. Army in World War II: The War in the Pacific. Washington, D.C.: United States Army Center of Military History. CMH Pub 5-10-1.
Further reading[]
- Belote, James H. (1967). Corregidor, Saga of a Fortress. Harper&Row.
- Kaufmann, J.E.; Kaufmann, H.W. (2004). Fortress America: The Forts That Defended America, 1600 to the Present. Da Capo Press. ISBN 978-0-306-81550-8.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Fort Drum (El Fraile Island). |
- Harbor Defenses of Manila and Subic Bays at the Coast Defense Study Group
- Forts in the Philippines at American Forts Network
- Wainwright Report – Capt. Ben King's Report Post War
- Fort Drum: Concrete Battleship of the Philippines
- Fort Drum: Unsinkable Battleship in the Manila Bay, 1. part – Czech only
- Fort Drum and the Battle of Philippines, 2. part – Czech only
- Forts in the Philippines
- Military facilities in Cavite
- United States military in the Philippines
- Closed installations of the United States Army
- World War II operations and battles of the Pacific theatre
- Military history of the Philippines during World War II
- Cavite City
- Islands of Cavite
- Islands of Manila Bay
- Sea forts
