Free People's State of Württemberg
| Free People's State of Württemberg Freier Volksstaat Württemberg | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State of the Weimar Republic | |||||||||||
| 1918–1945 | |||||||||||
 Flag
| |||||||||||
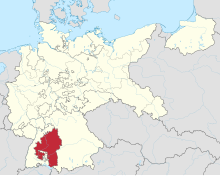 The Free People's State of Württemberg (red) within the Weimar Republic | |||||||||||
| Capital | Stuttgart | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
• 1925[1] | 19,508 km2 (7,532 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
• 1925[1] | 2580235 | ||||||||||
| Government | |||||||||||
| • Type | Republic | ||||||||||
| President | |||||||||||
• 1918–1920 (first) | Wilhelm Blos | ||||||||||
• 1933–1945 (last) | Christian Mergenthaler | ||||||||||
| Reichsstatthalter | |||||||||||
• 1933–1945 | Wilhelm Murr | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Interwar period | ||||||||||
• Established | 9 November 1918 | ||||||||||
• Constitution enacted | 29 September 1919 | ||||||||||
| 7 April 1933 | |||||||||||
• Abolition (de jure) | 1945 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||
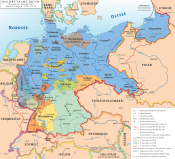
The Free People's State of Württemberg (German: Freier Volksstaat Württemberg) was a state in Württemberg, Germany, during the Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany.
1918 revolution[]
With the German revolution near the end of World War I, the Kingdom of Württemberg was transformed from a monarchy to a democratic republic without bloodshed; its borders and internal administration remained unchanged. King William II of Württemberg abdicated on 30 November 1918. Following the introduction of a new constitution (significantly amended later in the year) by an assembly elected in January,[2] and the Weimar Constitution in 1919, Württemberg was re-established as a member state of the German Reich.[3]
In comparison to the political turmoil that plagued Weimar Germany, political development in Württemberg was driven by continuity and stability. The attempt of some agitators to cause disturbances by a general strike was frustrated by the action of railway officials in paralysing communications with the capital, Stuttgart. The Bavarian Communist insurrection produced no effect in Württemberg; it was, on the contrary, suppressed with the aid of Württemberg troops before it could spread across the border.[2]
The three legislative periods of the Württemberg parliament from 1920 to 1932 each ran the full prescribed length of four years, unlike at the 1919-1933 Chancellors of Germany at the federal level. The social democrats lost their influence in Württemberg early in the state's history, with conservative coalitions forming government from 1924 to 1933. Despite the many financial crises that affected Germany during the 1920s and 1930s, the economic development of Württemberg proceeded better than in many other German states and Stuttgart became a regional centre of finance and culture.
1933–1952[]
With the Nazi seizure of federal power in 1933 and the following elimination of all non-Nazi organisations (Gleichschaltung), Württemberg and all other German states were abolished, in spirit if not in law. It was merged briefly into the "gau" of Württemberg-Hohenzollern. After World War II, Württemberg was split between the US and French Allied Occupation Zones in Germany and became parts of two new states: Württemberg-Baden (run by the Americans) and a smaller Württemberg-Hohenzollern run by the French. These two states were merged with Baden in 1952 to form the modern German state of Baden-Württemberg.
The former Free People's State coat of arms was used by the Porsche family as inspiration to create the logo of Porsche company.
See also[]
- List of Minister-Presidents of Württemberg
- List of Presidents of the Landtag of the Free People's State of Württemberg
- Württemberg Landtag elections in the Weimar Republic
References[]
- ^ Beckmanns Welt-Lexikon und Welt-Atlas. Leipzig / Vienna: Verlagsanstalt Otto Beckmann. 1931.
- ^ Jump up to: a b
 One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: von Blume, Wilhelm (1922). "Württemberg". In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. 32 (12th ed.). London & New York: The Encyclopædia Britannica Company. pp. 1089–1090. This source gives a detailed description of the constitutional balance, and of the political makeup after the 1920 elections.
One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: von Blume, Wilhelm (1922). "Württemberg". In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. 32 (12th ed.). London & New York: The Encyclopædia Britannica Company. pp. 1089–1090. This source gives a detailed description of the constitutional balance, and of the political makeup after the 1920 elections.
- ^ Article 1 of the Württemberg constitution (25 September 1919) states: "Württemberg is a democratic republic and member of the German Reich. Its state authority is exerted in accordance with both this constitution and German national law". Article 2 of the Weimar Constitution (11 August 1919) states: "The territory of the German Reich consists of the territory of its member states."
- States and territories established in 1918
- States and territories disestablished in 1945
- Former states and territories of Baden-Württemberg
- States of the Weimar Republic
- 20th century in Württemberg