G-Cloud
| Interstellar cloud | |
|---|---|
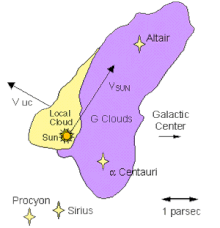 The G-Cloud complex and neighboring Local Interstellar Cloud | |
| Observation data | |
| Designations | G Cloud[1] |
The G-Cloud (or G-Cloud complex) is an interstellar cloud located next to the Local Interstellar Cloud, within the Local Bubble. It is unknown whether the Solar System is embedded in the Local Interstellar Cloud or in the region where the two clouds are interacting, although the Solar System is currently moving towards the G-Cloud. The G-Cloud contains the stars Alpha Centauri (a triple star system that includes Proxima Centauri) and Altair (and possibly others).[2][3][4][5][6][7]
References[]
- ^ "NAME G Cloud". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 15 March 2014.
- ^ "Our Local Galactic Neighborhood". Interstellar.jpl.nasa.gov. Archived from the original on 21 November 2013. Retrieved 7 October 2015.
- ^ Paul Gilster (1 September 2010). "Into the Interstellar Void". Centauri-dreams.org.
- ^ "The Interstellar Medium". Archived from the original on 19 April 2012. Retrieved 22 October 2012.
- ^ Seth Redfield (2009). "Physical Properties of the Local Interstellar Medium" (PDF). Igpp.ucla.edu.
- ^ Frisch., Priscilla (3 February 2003). "Local Interstellar Matter: The Apex Cloud". The Astrophysical Journal. 593 (2): 868. arXiv:astro-ph/0302037. Bibcode:2003ApJ...593..868F. doi:10.1086/376684.
- ^ "Short Sharp Science: Spacecraft probes gas cloud swaddling the solar system". Newscientist.com. 2 February 2012.
Categories:
- G-Cloud