GALEX
 Illustration of GALEX spacecraft | |
| Names | Explorer-83 SMEX-7 |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Ultraviolet astronomy |
| Operator | NASA / JPL (2003-2012) Caltech (2012-2013) |
| COSPAR ID | 2003-017A |
| SATCAT no. | 27783 |
| Website | https://www.galex.caltech.edu/ |
| Mission duration | 29 months (planned) [1] 10 years, 2 months (achieved) [2][3] |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | Orbital Sciences Corporation |
| Launch mass | 277 kg (611 lb) [4] |
| Dimensions | 1 × 2.5 m (3 ft 3 in × 8 ft 2 in) |
| Power | 290 watts |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 28 April 2003, 11:59:57 UTC[5] |
| Rocket | Pegasus XL |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral, Stargazer |
| Contractor | Orbital Sciences Corporation |
| Entered service | 28 May 2003 [2] |
| End of mission | |
| Disposal | Decommissioned |
| Deactivated | 28 June 2013, 19:09 UTC [3] |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit[6] |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Perigee altitude | 691 km (429 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 697 km (433 mi) |
| Inclination | 29.00° |
| Period | 98.60 minutes |
| Revolution no. | 85423 |
| Main telescope | |
| Type | Ritchey–Chrétien[1] |
| Diameter | 50 cm (20 in) |
| Focal length | f/6.0 |
| Wavelengths | 135–280 nm (Ultraviolet) |
Small Explorer program | |
The Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX) was an orbiting ultraviolet space telescope which was launched on 28 April 2003 and operated until early 2012 (decommissioned in June 2013).
History[]
An airlaunched Pegasus rocket placed the craft into a nearly circular orbit at an altitude of 697 km (433 mi) and an orbital inclination to the Earth's equator of 29.00°.
The first observation was dedicated to the crew of the Space Shuttle Columbia, and was images in the constellation of Hercules taken on 21 May 2003. This region was selected because it had been directly overhead the shuttle at the time of its last contact with the NASA Mission Control Center, Houston, Texas.
After its primary mission of 29 months, observation operations were extended to almost 9 years with NASA placing it into standby mode on 7 February 2012.[7] NASA cut off financial support for operations of GALEX in early February 2011 as it was ranked lower than other projects which were seeking a limited supply of funding. The mission's life-cycle cost to NASA was US$150.6 million. The California Institute of Technology negotiated to transfer control of GALEX and its associated ground control equipment to the California Institute of Technology in keeping with the Stevenson-Wydler Technology Innovation Act. Under this Act, excess research equipment owned by the U.S. government can be transferred to educational institutions and non-profit organizations.[8] On 17 May 2012, GALEX operations were transferred to Caltech.[9]
On 28 June 2013, NASA decommissioned GALEX. It is expected that the spacecraft will remain in orbit for at least 65 years before it will re-enter the atmosphere.[10]
Science mission[]
The telescope made observations in ultraviolet wavelengths to measure the history of star formation in the universe 80% of the way back to the Big Bang. Since scientists believe the Universe to be about 13.8 billion years old, the mission studied galaxies and stars across about 10 billion years of cosmic history.[11]
The spacecraft's mission was to observe hundreds of thousands of galaxies, with the goal of determining the distance of each galaxy from Earth and the rate of star formation in each galaxy. Near-UV and far-UV emissions as measured by GALEX can indicate the presence of young stars, but may also originate from old stellar populations (e.g. sdB stars).
Partnering with the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) on the mission were the California Institute of Technology, Orbital Sciences Corporation, University of California, Berkeley, Yonsei University, Johns Hopkins University, Columbia University, and .
The observatory participated in GOALS with Spitzer Space Telescope, Chandra X-ray Observatory, and Hubble Space Telescope.[12] GOALS stands for Great Observatories All-sky LIRG Survey, and Luminous Infrared Galaxies were studied at the multiple wavelengths allowed by the telescopes.[12]
Science objectives[]
The primary objective of the Galaxy Evolution Explorer is to learn what factors trigger star formation inside galaxies; how quickly stars form, evolve and die; and how heavy chemical elements form in stars. Additional goals include:[4]
- Determining how fast stars are forming inside each galaxy
- Determining when and how the stars we see today formed
- Creating the first map of the ultraviolet universe
- Helping scientists find and understand ultraviolet bright quasars. These objects can serve as background sources for the Hubble Space Telescope and FUSE as it probes the gases from which galaxies form stars
To accomplish its objectives, the Galaxy Evolution Explorer will conduct eight surveys, grouped into two broad categories - a local universe investigation and a star formation history investigation. The local universe investigation includes the following four surveys:
- All-sky imaging survey - will look at the entire sky and develop a comprehensive catalogue of ultraviolet galaxy images, useful to map the distribution of star formation within the local universe
- Nearby galaxy survey - will study about 150 nearby galaxies that are familiar to scientists to understand how stars formed in individual galaxies
- Wide-field spectroscopic survey - will analyze the light wavelengths of galaxies in a wide swath of the sky
- Medium spectroscopic survey - will examine the light properties of galaxies within a narrower portion of the sky
The star formation history investigation will take information gathered by the local universe investigation and apply it to more distant galaxies by looking further back in time. It includes the following four surveys:
- Deep imaging survey - will look at a portion of the sky to study the distribution of star formation in the deep universe
- Deep spectroscopic survey - will look for the most distant galaxies
- Ultra-deep imaging survey - will look as deep as possible at a very small portion of the sky
- Medium imaging survey - will study star formation in galaxies beyond our local cosmic neighborhood, but not as deep as the deep imaging survey
Telescope specifications[]
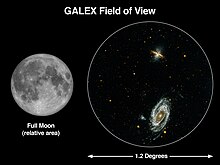
The telescope had a 50 cm diameter aperture primary, in a Ritchey–Chrétien telescope f/6.0 configuration. It can see light wavelengths from 135 nanometers to 280 nm, with a field of view of 1.2° wide (larger than a full moon). It had gallium arsenide solar cells which supply nearly 300 watts to the spacecraft.[13]
Pre-launch images[]

GALEX at the pre-launch tests

GALEX being mated to a Pegasus XL rocket

GALEX's Pegasus XL being attached to the Lockheed L-1011 Stargazer

The L-1011 Stargazer take-off with GALEX attached under-belly
See also[]
- Ultraviolet astronomy
- GALEX Arecibo SDSS Survey
- Arecibo Observatory
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b "GALEX". NASA. 27 April 2021. Retrieved 8 June 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Mission to Universe: Galaxy Evolution Explorer". NASA. Retrieved 14 September 2015.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "NASA Decommissions Its Galaxy Hunter Spacecraft" (Press release). California Institute of Technology. 28 June 2013. Retrieved 14 September 2015.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Press Kit: Galaxy Evolution Explorer Launch" (PDF). NASA. April 2003. Retrieved 8 June 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Display: GALEX 2003-017A". NASA. 27 April 2021. Retrieved 8 June 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Trajectory: GALEX 2003-017A". NASA. 27 April 2021. Retrieved 8 June 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ GALEX ends
- ^ Stephen Clark (10 February 2012). "NASA, Caltech mull over unique satellite donation". Spaceflight Now. Retrieved 8 June 2021.
- ^ Marcus Woo - NASA lends ultraviolet space telescope to Caltech (17 May 2012) - Phys.org
- ^ NASA Decommissions Its Galaxy Hunter Spacecraft
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Cosmic Detectives". The European Space Agency (ESA). 2 April 2013. Retrieved 26 April 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b GOALS: The Great Observatories All-Sky LIRG Survey
- ^ Encyclopedia Astronautica - GALEX Archived 2008-07-06 at the Wayback Machine
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to GALEX. |
- GALEX website by the California Institute of Technology
- GALEX website by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory
- GALEX data archive by the STScI / MAST
- GALEXView Search Tool by the STScI / MAST
- GALEX Ultraviolet Sky Survey at Wikisky.org
- Satellites orbiting Earth
- Explorers Program
- Space telescopes
- Ultraviolet telescopes
- Spacecraft launched in 2003
- Spacecraft launched by Pegasus rockets




