HD 126009
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Boötes |
| Right ascension | 14h 22m 14.00145s[2] |
| Declination | +29° 22′ 11.7169″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.6[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M3III[4] |
| U−B color index | +1.46[3] |
| B−V color index | +1.60[3] |
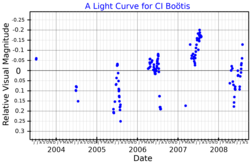
| Variable type | Irregular[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −19.66±0.54[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: -38.37[2] mas/yr Dec.: -25.87[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 4.23 ± 0.47[2] mas |
| Distance | approx. 770 ly (approx. 240 pc) |
| Details | |
| Luminosity | 1,875[7] L☉ |
| Temperature | 3,387[7] K |
| Other designations | |
CI Boötes, BD+30° 2513, HD126009, HIP 70236, SAO 83312. | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
HD 126009 or CI Boötis is a variable star[4] in the northern constellation of Boötes.
References[]
- ^ Tabur, V.; Bedding, T. R.; Kiss, L. L.; Moon, T. T.; Szeidl, B.; Kjeldsen, H. (December 2009). "Long-term photometry and periods for 261 nearby pulsating M giants". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 400 (4): 1945–1961. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15588.x. Retrieved 5 November 2021.
- ^ a b c d e van Leeuwen, F. (2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600.
- ^ a b c Mermilliod, J.-C. (1986), "Compilation of Eggen's UBV data, transformed to UBV (unpublished)", Catalogue of Eggen's UBV Data. SIMBAD, Bibcode:1986EgUBV........0M
- ^ a b Tabur, V.; Bedding, T. R. (2009), "Long-term photometry and periods for 261 nearby pulsating M giants", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 400 (4): 1945–61, arXiv:0908.3228, Bibcode:2009MNRAS.400.1945T, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15588.x, S2CID 15358380
- ^ Mennessier, M. O.; et al. (August 2001), "Long period variable stars: galactic populations and infrared luminosity calibrations", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 374 (3): 968–979, arXiv:astro-ph/0105552, Bibcode:2001A&A...374..968M, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20010764, S2CID 15721872.
- ^ Famaey, B.; et al. (2009). "Spectroscopic binaries among Hipparcos M giants,. I. Data, orbits, and intrinsic variations". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 498 (2): 627–640. arXiv:0901.0934. Bibcode:2009A&A...498..627F. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810698. S2CID 18739721.
- ^ a b McDonald, I.; et al. (2012), "Fundamental Parameters and Infrared Excesses of Hipparcos Stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 427 (1): 343–57, arXiv:1208.2037, Bibcode:2012MNRAS.427..343M, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x, S2CID 118665352
External links[]
Categories:
- Boötes
- Henry Draper Catalogue objects
- Hipparcos objects
- Objects with variable star designations
- M-type giants
- Slow irregular variables
- Durchmusterung objects
- Giant-star stubs
- Variable star stubs