Hereditary progressive mucinous histiocytosis
| Hereditary progressive mucinous histiocytosis | |
|---|---|
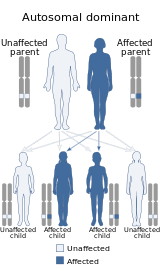 | |
| This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Hereditary progressive mucinous histiocytosis is a very rare, benign, non-Langerhans' cell histiocytosis. An autosomal dominant or X-linked hereditary disease described on the skin, it has been found almost exclusively in women.[1][2] One case of the disease in a male patient has been reported.[3]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. pp. 718. ISBN 978-0-7216-2921-6.
- ^ Antoni-Bach, N; Pfister, R; Grosshans, E; Kleinclaus, I; Boehm, N; Grange, F; Guillaume, J (2000). "Hereditary progressive mucinous histiocytosis". Annales de Dermatologie et de Vénéréologie. 127 (4): 400–4. PMID 10844262.
- ^ Schlegel, C; Metzler, G; Burgdorf, W; Schaller, M (2010). "Hereditary progressive mucinous histiocytosis: First report in a male patient". Acta Dermato Venereologica. 90 (1): 65–7. doi:10.2340/00015555-0763. PMID 20107728.
External links[]
Categories:
- Monocyte- and macrophage-related cutaneous conditions
- Cutaneous condition stubs