Holy Innocents' Cemetery
 The Holy Innocents' Cemetery, c. 1550. The Church of the Holy Innocents, bordering the Rue Saint-Denis, is in the background. | |
 Location of Holy Innocents' Cemetery | |
| Details | |
|---|---|
| Established | 12th century Closed: 1780 |
| Location | |
| Country | France |
| Coordinates | 48°51′36″N 2°20′56″E / 48.860°N 2.349°E |
| Type | Public (not extant) |
| Style | churchyard |
| Find a Grave | Holy Innocents' Cemetery |
The Holy Innocents' Cemetery (French: Cimetière des Saints-Innocents or Cimetière des Innocents) is a defunct cemetery in Paris that was used from the Middle Ages until the late 18th century. It was the oldest and largest cemetery in Paris and had often been used for mass graves.[1] It was closed because of overuse in 1780, and in 1786 the remaining corpses were exhumed and transported to the unused subterranean quarries near Montparnasse known as the Catacombs. The place Joachim-du-Bellay in the Les Halles district now covers the site of the cemetery.
The cemetery took its name (referring to the Biblical Massacre of the Innocents) from the attached church of the Holy Innocents that was demolished at the same time as the cemetery was cleared.[2]
History[]
Sources describe the burial ground, then called Champeaux, and the associated church in the 12th century.[1] It was located next to the central market (the original location of Les Halles).
Under the reign of Philip II (1180-1223) the cemetery was enlarged and surrounded by a three-meter-high wall. Les Innocents had begun as a cemetery with individual sepulchres, but by then had become a site for mass graves. People were buried together in the same pit (a pit could hold about 1,500 dead at a time); only when it was full would another be opened.
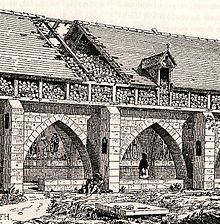
In the 14th and 15th centuries, citizens constructed arched structures called charniers or charnel houses along the cemetery walls to relieve the overcrowding of the mass graves; bones from the graves were excavated and then deposited here.
Between August 1424 and Lent 1425, during the Anglo-Burgundian alliance when John Duke of Bedford ruled Paris as Regent after the deaths of Henry V of England and Charles VI of France, a mural of the Danse Macabre was painted on the back wall of the arcade below the charnel house on the south side of the cemetery.[3] It was one of the earliest and best-known depictions of this theme. It was destroyed in 1669 when this wall was demolished to allow the narrow road behind it to be widened.[1][3]


In the 16th century, the prominent Renaissance anatomist Andreas Vesalius studied the bones of corpses in the Holy Innocents cemetery.
During the reign of Louis XV, inspectors recorded accounts of the difficulties in conducting business in the area due to the unsanitary conditions of the cemetery, caused by overuse and incomplete decomposition of bodies.
Two edicts by Louis XVI to move the parish cemeteries out of the city were resisted by the church, which was operating from burial fees. To reduce the number of burials, the price of burials was increased. After a prolonged period of rain in spring 1780, conditions became untenable. On 4 September 1780, an edict forbade burying corpses in Les Innocents and in all other Paris cemeteries.
Bodies were exhumed and the bones were moved to the Catacombs in 1786.[4] Many bodies had incompletely decomposed and had reduced into large deposits of fat ("corpse wax", or adipocere), chiefly in the form of palmitic acid.[5] During the exhumation, this fat was collected and subsequently turned into candles and soap.[6]


The church was destroyed in 1787 and the cemetery was replaced by a herb and vegetable market. The Fountain of the Nymphs, which had been erected in 1549 next to the church, was dismantled and rebuilt in the center of the new market. Now known as the "Fountain of Innocents", it still stands on Joachim-du-Bellay Square.[1]
At its closure, it was estimated that from the Middle Ages until the eighteenth century the Holy Innocents' Cemetery had been the repository of corpses from 22 parishes in Paris, including the remains of those who died at the Hôtel-Dieu, plague victims, and various unknowns who drowned in the Seine, died on the roads, or were crippled at the nearby crossroads of the "Court of miracles", for a total of about two million Parisians.[citation needed]
There are no signs of the charnel house today as the present location contains buildings, arcades, and shops.[7]
In modern fiction[]
The destruction of the church and removal of the cemetery at Les Innocents is the subject of Andrew Miller's Costa prize winning 2011 novel Pure.[8]
In Anne Rice's The Vampire Lestat, Armand's coven of vampires resides in the Cimetière des Innocents when Lestat first encounters them, and they remain there until shortly before the cemetery is finally destroyed.
The cemetery and the Catacombs to which the remains were relocated play an important part in Barbary Hambly's novel Those Who Hunt The Night.
In Patrick Süskind's novel Perfume, the main character Jean-Baptiste Grenouille was born here on 17 July 1738.
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Philippe Landru (7 February 2008). "Cimetière des INNOCENTS (disparu)" (in French).
- ^ https://vads.ac.uk/large.php?uid=90224
- ^ Jump up to: a b Sophie Oosterwijk (2008). "Of dead kings, dukes and constables. The historical context of the Danse Macabre in late-medieval Paris". Journal of the British Archaeological Association. 161: 131–162. doi:10.1179/174767008x330563. S2CID 154086960.
- ^ "Paris' Les Innocents cemetery". Retrieved February 6, 2011.
- ^ R.F. Ruttan, J.F. Marshall (1917). "The Composition of Adipocere" (PDF). Journal of Biological Chemistry. 29 (2): 319–327. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)86795-3.
- ^ "You (posthumously) light up my life". Scientific American blog. 15 April 2011.
- ^ Trouilleux, Rodolphe (1997). Unexplored Paris. Parigramme. p. 11.
- ^ Kyte, Holly (2011-06-16). "Pure by Andrew Miller: review". Telegraph. Retrieved 2012-01-05.
External links[]
 Media related to Cimetière des Innocents at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Cimetière des Innocents at Wikimedia Commons
- Cemeteries in Paris
- Roman Catholic cemeteries in France
- History of Paris
- 12th-century establishments in France
- 1780s disestablishments in France

