Industrial corridor
An industrial corridor is a package of infrastructure spending allocated to a specific geographical area, with the intent to stimulate industrial development.[1]
An industrial corridor aims to create an area with a cluster of manufacturing or another industry. Such corridors are often created in areas that have preexisting infrastructure, such as ports, highways and railroads.[1] These modalities are arranged such that an "" modality, such as a highway or railroad, receives "feeder" roads or railways. Concerns when creating corridors include correctly assessing demand and viability, transport options for goods and workers, land values, and economic incentives for companies.[2]
Industrial Corridors of India[]
Gati Shakti Master Plan envisions 11 Industrial Corridors(Economic Corridors) to be developed by 2024-25[3]
- Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor Project(DMIC)
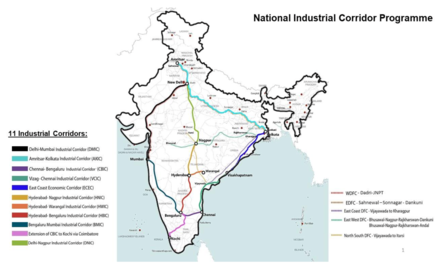 National Industrial Corridor Programme
National Industrial Corridor Programme - Chennai Bengaluru Industrial Corridor(CBIC)
- Amritsar Delhi Kolkata Industrial Corridor(AKIC)
- East Coast Industrial Corridor (ECIC) with Vizag Chennai Industrial Corridor (VCIC) as Phase 1
- Bengaluru Mumbai Industrial Corridor (BMIC)
- Extension of CBIC to Kochi via Coimbatore
- Hyderabad Nagpur Industrial Corridor(HNIC)[4][5]
- Hyderabad Warangal Industrial Corridor(HWIC)[6][7]
- Hyderabad Bangalore Industrial Corridor(HBIC)[8]
- Odisha Economic Corridor (OEC)
- Delhi Nagpur Industrial Corridor (DNIC)
See also[]
References[]
- ^ a b "Investment opportunities in Corridors, NIMZ and Clu ster under IIUS" (PDF). EMB India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 August 2016. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ Marrian, Brian. "TOWARDS A GENERAL THEORY OF CORRIDOR DEVELOPMENT IN SOUTH AFRICA" (PDF). Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ National Industrial Corridor programme
- ^ Singh, T. Lalith (2014-08-27). "Hyderabad-Nagpur industrial corridor planned". The Hindu. ISSN 0971-751X. Retrieved 2021-01-15.
- ^ "IIG | National Infrastructure Pipeline". indiainvestmentgrid.gov.in. Retrieved 2021-01-15.
- ^ "IIG | National Infrastructure Pipeline". indiainvestmentgrid.gov.in. Retrieved 2021-01-15.
- ^ "Press Information Bureau". pib.gov.in. Retrieved 2021-01-15.
- ^ "Hyderabad-Bengaluru Industrial Corridor gets Central nod". The New Indian Express. Retrieved 2021-01-15.
External links[]
- Make in India description: [1]
- Transport infrastructure
- Proposed infrastructure in India
