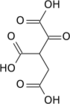
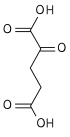
Isocitric acid

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-Hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.713 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Isocitrate |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H8O7 | |
| Molar mass | 192.124 |
| Melting point | 105 °C (221 °F; 378 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
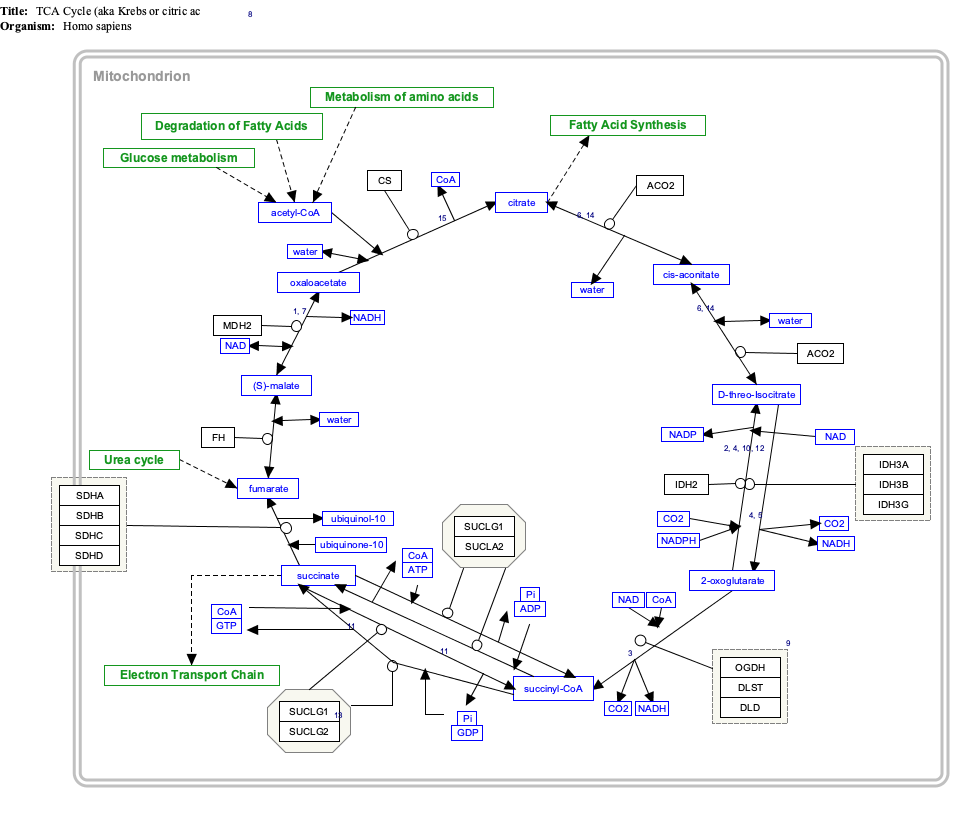
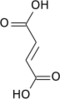
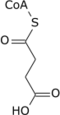
Isocitric acid is a structural isomer of citric acid. Salts and esters of isocitric acid are known as isocitrates. The isocitrate anion is a substrate of the citric acid cycle. Isocitrate is formed from citrate with the help of the enzyme aconitase, and is acted upon by isocitrate dehydrogenase.
Isocitric acid is commonly used as a marker to detect the authenticity and quality of fruit products, most often citrus juices. In authentic orange juice, for example, the ratio of citric acid to D-isocitric acid is usually less than 130. An isocitric acid value higher than this may be indicative of fruit juice adulteration.[1]
Interactive pathway map[]
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- ^ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "TCACycle_WP78".
See also[]
- Citric Acid
- Tartaric Acid
- Malic Acid
References[]
- ^ Saavedra, L.; Garcia, A.; Barbas, C. (9 June 2000). "Development and validation of a capillary electrophoresis method for direct measurement of isocitric, citric, tartaric and malic acids as adulteration markers in orange juice". Journal of Chromatography A. 881 (1–2): 395–401. doi:10.1016/s0021-9673(00)00258-2. PMID 10905722.
Categories:
- Alpha hydroxy acids
- Tricarboxylic acids
- Citric acid cycle compounds
- Aldols
- Biochemistry stubs