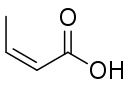
Isocrotonic acid
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2Z)-But-2-enoic acid | |
| Other names
(Z)-But-2-enoic acid
(Z)-2-Butenoic acid cis-2-Butenoic acid cis-β-Methylacrylic acid (Z)-β-Methylacrylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.249 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 86.090 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.03 g·cm−3 [1] |
| Melting point | 15 °C (59 °F; 288 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 168 to 169 °C (334 to 336 °F; 441 to 442 K)[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related carboxylic acids
|
Crotonic acid (trans isomer) Angelic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Isocrotonic acid (also known as quartenylic acid; formally named (Z)-2-butenoic acid) is the cis isomer of crotonic acid. It is an oil, possessing a smell similar to that of brown sugar. It boils at 171.9 °C, concomitant with conversion into crotonic acid. Isomerization is complete when the cis acid is heated to 170–180 °C in a sealed tube.
Rudolph Fittig and Hugo Erdmann showed that the γ-phenyl structural analog of isocrotonic acid forms α-naphthol when dehydrated, an observation that provided useful evidence in understanding the nature of naphthalene.[2]
- (Z)-(C6H5)CH=CHCH2COOH → α-naphthol + H2O
References[]
- ^ a b c The Merck Index. An Encyclopaedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. 14. Auflage, 2006, S. 894, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1.
- ^ Fittig, Rudolph; Erdmann, Hugo (1883). "Synthese des α-Naphtols" [Synthesis of α-Naphtol]. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. (in German). 16 (1): 43–44. doi:10.1002/cber.18830160115.
Categories:
- Enoic acids