JNR Class EF10
| Class EF10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 EF10 18 shortly after completion in 1938 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Class EF10 (EF10形) is an electric locomotive formerly operated on freight services in Japan from 1934 until 1983.
History[]
41 locomotives were built between 1934 and 1941 by the manufacturers Hitachi, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Kisha Seizo, Mitsubishi, and Toshiba.[1]
Locomotive construction was divided into four batches, with further differences within individual batches as follows.[1]
EF10 1 - 16[]
Locomotives EF10 1 to 16 had bodies with similar styling to the and locomotives.[1]

EF10 1-16

A Class ED16 locomotive for comparison
EF10 17[]
EF10 17 was built in 1937 with a welded body and more rounded styling.[1]

EF10 17
EF10 18 - 19[]
Locomotives EF10 18 and 19 continued with the same rounded body styling as EF10 17, but used a similar bar frame bogie design to the first batch of locomotives.[1]
EF10 20 - 24[]
Locomotives EF10 20 to 24 continued with the same body design, but with a different ventilator arrangement.[1]
EF10 25 - 29[]
Locomotives EF10 25 to 29 had welded bodies, but reverted to a more angular design.[1]
EF10 30 - 33[]
Locomotives EF10 30 to 33 continued with the same welded angular body design, but used cast bogie frames.[1]
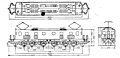
EF10 30-33
EF10 34 - 41[]
Locomotives EF10 34 to 41 used the original bar frame bogie design.[1]
Preservation[]

EF10 35 was preserved in a park in Moji-ku, Kitakyushu before being restored and moved to the newly opened Kyushu Railway History Museum in 2003, where it is preserved statically.[2]
Classification[]
The EF10 classification for this locomotive type is explained below.
- E: Electric locomotive
- F: Six driving axles
- 10: Locomotive with maximum speed 85 km/h or less
References[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to JNR EF10. |
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i Inoue, Koichi (1999). 国鉄機関車事典: 蒸気・電気・ディーゼル機関車66形式 国鉄機関車辞典 [JNR Locomotive Encyclopedia] (in Japanese). Japan: Sankaido. pp. 84–85. ISBN 978-4-381-10338-3.
- ^ Sasada, Masahiro (25 November 2014). 国鉄&jr 保存車大全 2015-2016 国鉄&JR保存車大全2015-2016 [JNR & JR Preserved Rolling Stock Complete Guide 2015-2016] (in Japanese). Tokyo, Japan: Ikaros Publications Ltd. p. 122. ISBN 978-4863209282.
Further reading[]
- 鉄道車輌ディテール・ファイル002 ひさし付車体のEF10(1〜16) [Rolling Stock Detail File 002: Sun visor type EF10 (1 to 16)] (in Japanese). Japan: Neko Publishing Co., Ltd. September 2009. ISBN 978-4777052622.
- 鉄道車輌ディテール・ファイル 004: 丸型車体のEf10(17~24) 鉄道車輌ディテール・ファイル004 丸型車体のEF10(17~24) [Rolling Stock Detail File 004: Round-bodied EF10 (17 to 24)] (in Japanese). Japan: Neko Publishing Co., Ltd. November 2009. ISBN 978-4777052707.
- 鉄道車輌ディテール・ファイル007 丸型車体のEF10(25~41) [Rolling Stock Detail File 007: Angular-bodied EF10 (25 to 41)] (in Japanese). Japan: Neko Publishing Co., Ltd. February 2010. ISBN 978-4777052783.
- Electric locomotives of Japan
- 1500 V DC locomotives
- 1067 mm gauge locomotives of Japan
- Railway locomotives introduced in 1934
- Hitachi locomotives
- Kawasaki locomotives
- Kisha Seizo locomotives
- Mitsubishi locomotives
- Toshiba locomotives
- (1′Co)+(Co1′) locomotives



