Jean Vacelet
Jean Vacelet is a French marine biologist who specialises in the underwater fauna of the Mediterranean.[1] After earning his licence at the Faculté des Sciences de Marseille and learning to dive in 1954, he specialised in the study of sponges at the Marine station of Endoume, and there he has stayed faithful to both sponges and place for more than half a century. His research has included all aspects of sponges: taxonomy, habitat, biology, anatomy, their bacterial associations, and their place in the evolution of multi-celled animals. He has studied them not only in the Mediterranean but in the Indian Ocean and the Pacific. Exploration of underwater grottoes,[2] together with and Jo Hamelin, revealed the existence of sponges dating from very ancient geological periods and the unexpected existence of carnivorous sponges,[3][4] and surprisingly, the grottoes in some ways mimicked life at much greater depths.[5]
He earned one doctorate in 1958 and his doctorat ès-sciences, under Professor Claude Lévi[6] in 1964.[7]
He, together with other colleagues, has written definitive works on Porifera (sponges),[8][3][9][10][11] in addition to his many specific works on carnivorous sponges.[12][13][14][15] And again with many colleagues, is responsible for the World Porifera Database (accessed via the World Register of Marine Species. (See e.g. Acanthella dendyi)[16]
He continues his researches on sponges[17] at Endoume as emeritus professor.[3]
Gallery[]
- from 'Global Diversity of Sponges (Porifera)'
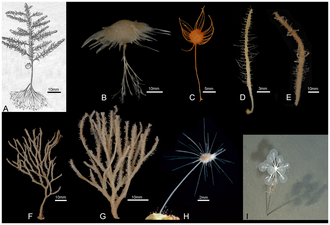
Carnivorous sponge diversity

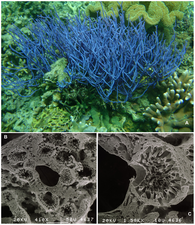
Calcarea diversity
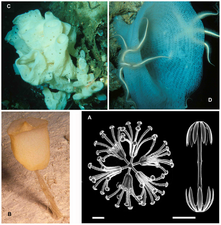
Porifera morphology
Hexactinellida diversity
(Source)[8]
Awards[]
- Médaille Prince Albert 1er de Monaco( Prix Mansley-Bendall), 1991.
- Prix Savigny (Académie des Sciences de Paris), 1994.
- Prix des Sciences de la Mer, Académie des Sciences. 2001
Source[6]
See also[]
| Scholia has a profile for Jean Vacelet (Q21388097). |
- Taxa named by Jean Vacelet
References[]
- ^ "Vacelet, Jean - Persée". www.persee.fr. Retrieved 2020-09-25.
- ^ Laborel, J. & Vacelet, J. (1958). "Etude des peuplements d'une grotte sous-marine du Golfe de Marseille". Bulletin de l'Institut océanographique de Monaco. 55 (1120): 1–20.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Jean VACELET". doris.ffessm.fr. Retrieved 2020-09-25.
- ^ Crew, B. "New carnivorous harp sponge discovered in deep sea". Scientific American Blog Network. Retrieved 2020-09-26.
- ^ "A La Ciotat, une grotte reproduit les conditions des grands fonds et dévoile des espèces rares". LaProvence.com (in French). 2017-09-05. Retrieved 2020-09-26.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Futura. "Jean Vacelet". Futura (in French). Retrieved 2020-09-26.
- ^ "renseignements personnel Jean VACELET : DIMAR". 2009-02-06. Archived from the original on 2009-02-06. Retrieved 2020-09-26.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Van Soest, R.W.M.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Vacelet, J.; Dohrmann, M.; Erpenbeck, D.; De Voogd, N.J.; Santodomingo, N.; Vanhoorne, B.; Kelly, M.; Hooper, J.N.A. (2012-04-27). Roberts, J.M. (ed.). "Global Diversity of Sponges (Porifera)". PLOS ONE. 7 (4): e35105. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...735105V. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035105. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 3338747. PMID 22558119.
- ^ Gazave, E.; Lapébie, P.; Ereskovsky, A.V.; Vacelet, J.; Renard, E.; Cárdenas, P.; Borchiellini, C. (2011), Maldonado, M.; Turon, X.; Becerro, M.l; Jesús Uriz, M. (eds.), "No longer Demospongiae: Homoscleromorpha formal nomination as a fourth class of Porifera", Ancient Animals, New Challenges, Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, pp. 3–10, doi:10.1007/978-94-007-4688-6_2, ISBN 978-94-007-4687-9, retrieved 2020-09-26
- ^ Boury-Esnault, N.; Efremova, S.; Bézac, C.; Vacelet, J. (1999). "Reproduction of a hexactinellid sponge: first description of gastrulation by cellular delamination in the Porifera". Invertebrate Reproduction & Development. 35 (3): 187–201. doi:10.1080/07924259.1999.9652385. ISSN 0792-4259.
- ^ Chombard, C.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Tillier, A.; Vacelet, J. (1997). "Polyphyly of "Sclerosponges" (Porifera, Demospongiae) Supported by 28S Ribosomal Sequences". The Biological Bulletin. 193 (3): 359–367. doi:10.2307/1542938. ISSN 0006-3185. JSTOR 1542938. PMID 9457769.
- ^ Vacelet, J.; Duport, E. (2004). "Prey capture and digestion in the carnivorous sponge Asbestopluma hypogea (Porifera: Demospongiae)". Zoomorphology. 123 (4): 179–190. doi:10.1007/s00435-004-0100-0. ISSN 0720-213X. S2CID 24484610.
- ^ Vacelet, J. & Boury-Esnault, N. (1996). "A new species of carnivorous sponge (Demospongiae: Cladorhizidae) from a Mediterranean cave". Bulletin de l'Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de Belgique. 66 suppl.: 109–115.
- ^ Dupont, S.; Corre, E.; Li, Y.; Vacelet, J.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L. (2013). "First insights into the microbiome of a carnivorous sponge". FEMS Microbiology Ecology. 86 (3): 520–531. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12178. PMID 23845054.
- ^ Vacelet, J; Fiala-Médioni, A; Fisher, Cr; Boury-Esnault, N (1996). "Symbiosis between methane-oxidizing bacteria and a deep-sea carnivorous cladorhizid sponge". Marine Ecology Progress Series. 145: 77–85. Bibcode:1996MEPS..145...77V. doi:10.3354/meps145077. ISSN 0171-8630.
- ^ Van Soest, R.W.M.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Rützler, K.; de Voogd, N.J.; Alvarez, B.; Hajdu, E.; Pisera, A.B.; Manconi, R.; Schönberg, C.; Klautau, M.; Kelly, M.; Vacelet, J.; Dohrmann, M.; Díaz, M.-C.; Cárdenas, P.; Carballo, J.L.; Ríos, P.; Downey, R.; Morrow, C.C. (2020). "World Porifera Database. Acanthella dendyi (Bergquist, 1970). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species".
- ^ Vacelet, J. (2020-04-24). "Carnivorous sponges (Porifera, Cladorhizidae) from the deep South Pacific (New Caledonia) with the description of three new species of the genus Abyssocladia and remarks on genus Cercicladia". Zootaxa. 4767 (2): 257–276. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4767.2.3. ISSN 1175-5334.
- Aix-Marseille University faculty
- Spongiologists
- French marine biologists




